
The major mono halo product in the reaction is X. Identify the product X.
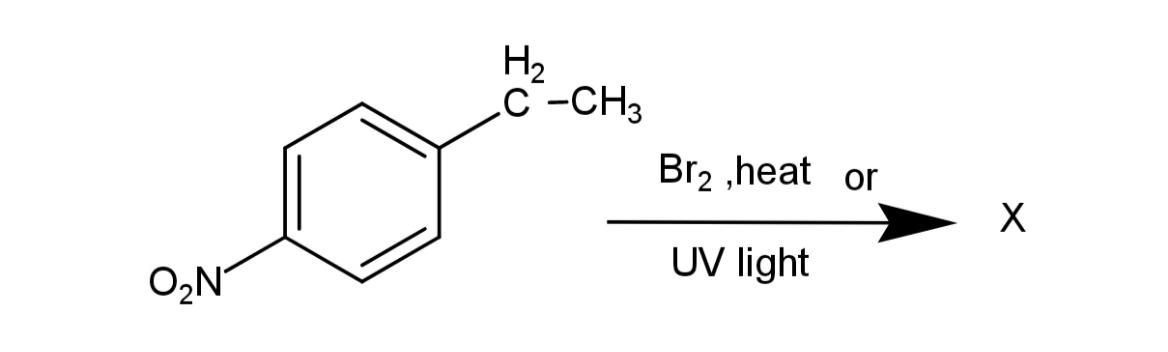

Answer
531.6k+ views
Hint: Halogenation is the process of substitution of a halogen atom in any organic molecule in the presence of catalysts. The catalyst may be sunlight along with a halogen or anhydrous ferrous bromide or ferrous chloride. It is an example of electrophilic substitution reaction.
Complete answer:
Halogenation is the process through which a halogen atom is substituted on the alkyl group by the removal of one hydrogen atom. This process happens in the presence of di halogen molecules along with ultraviolet rays or heat which is sunlight. This reaction happens through a free radical halogenations mechanism. The free radical of halogen is formed when the halogen is exposed to the sunlight. These free radicals formed, contain one free radical on hemolytic cleavage of the bond between the di halogen molecule. This free radical gets attached to the carbon of the most stable carbocation intermediate.
Here the reactant consists of a side chain of carbon, which favors the halogenation, and the substitution occurs at this side chain. The major mono halogenated product will form on the carbon of the side chain that has more substitution. So, the major product will form on the secondary carbocation, hence, the carbon 2 of the side chain will have a bromine atom attached and a hydrogen atom removed. The reaction is as follows:
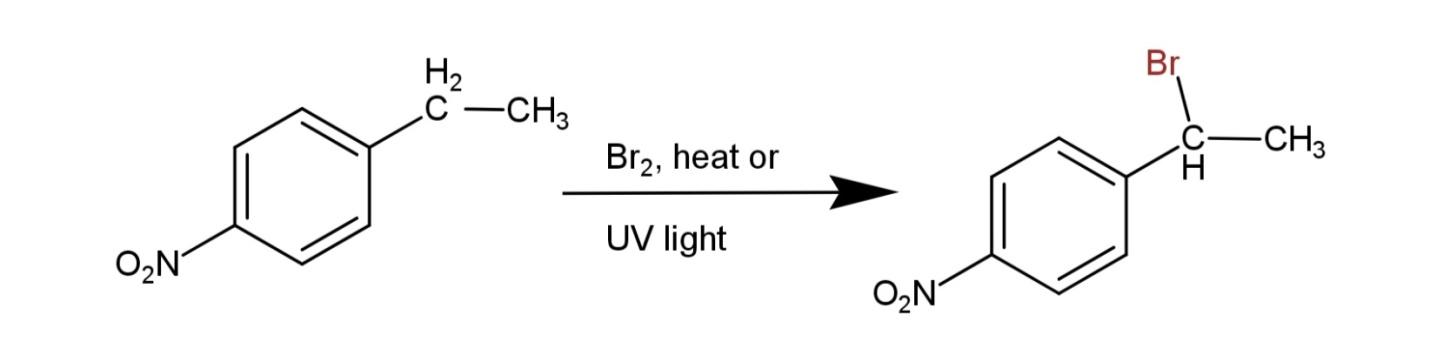
Hence, the major product formed from the compound 4-ethylnitrobenzene on halogenations is 4- (1-bromoethyl) nitrobenzene.
Note:
The halogenations where addition of halogen occurs in the presence of anhydrous ferrous bromide or chloride results in the addition of halogen into the benzene ring, the reaction may be
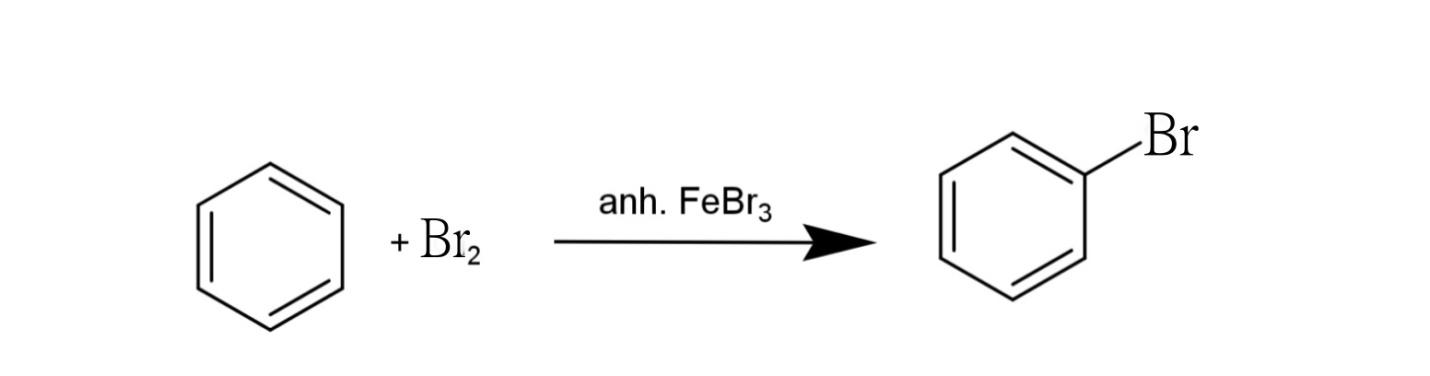
Anhydrous ferrous bromide acts as a halogen carrier and carries out the reaction by generating an electrophile.
Complete answer:
Halogenation is the process through which a halogen atom is substituted on the alkyl group by the removal of one hydrogen atom. This process happens in the presence of di halogen molecules along with ultraviolet rays or heat which is sunlight. This reaction happens through a free radical halogenations mechanism. The free radical of halogen is formed when the halogen is exposed to the sunlight. These free radicals formed, contain one free radical on hemolytic cleavage of the bond between the di halogen molecule. This free radical gets attached to the carbon of the most stable carbocation intermediate.
Here the reactant consists of a side chain of carbon, which favors the halogenation, and the substitution occurs at this side chain. The major mono halogenated product will form on the carbon of the side chain that has more substitution. So, the major product will form on the secondary carbocation, hence, the carbon 2 of the side chain will have a bromine atom attached and a hydrogen atom removed. The reaction is as follows:

Hence, the major product formed from the compound 4-ethylnitrobenzene on halogenations is 4- (1-bromoethyl) nitrobenzene.
Note:
The halogenations where addition of halogen occurs in the presence of anhydrous ferrous bromide or chloride results in the addition of halogen into the benzene ring, the reaction may be

Anhydrous ferrous bromide acts as a halogen carrier and carries out the reaction by generating an electrophile.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




