
The efficiency of the heat engine
(A) Is independent of temperature of the source and the sink.
(B) Is independent of working substance.
(C) Can be $ 100\% $
(D) Is not affected by thermal capacity of the source and sink.
Answer
539.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem we should know about the heat engine working and their characteristics.
Heat engine: It is a system that converts heat or thermal energy into a mechanical energy. Which will be used to do mechanical work.
Efficiency: The fraction of work done by engine to heat given to the engine is called its efficiency.
Complete step by step solution:
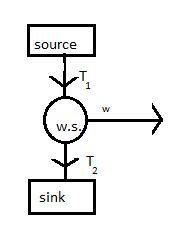
As from the figure we can see that the working substance takes heat from the source and rejects heat to sink. So, in ideal conditions we assume that source and sink have infinite thermal capacity. Heat rejected by the source is equal to its temperature and heat going to the sink will be equal to temperature of sink.
So, efficiency will be, $ \eta = \dfrac{{work\,output}}{{heat\,input}} $
$ \Rightarrow \eta = \dfrac{{{T_1} - {T_2}}}{{{T_1}}} = 1 - \dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}} $
So, we can conclude that
Efficiency is dependent on source and sink temperature.
From formula we can say efficiency is independent of working substance.
From the formula, we can say its efficiency will never be $ 100\% $ because $ \dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}} $ is always a positive number.
The amount of heat taken from source and heat going to decapitate on the sink depend on its thermal capacity.
Hence, from the above observation, we can say option (b) is the correct option.
Note:
Heat engines distinguish themselves from other types of engine by the fact that their efficiency is limited by Carnot’s theorem. This efficiency limitation can be a drawback. Advantage of a heat engine is that most forms of energy can be easily converted to heat by processes like exothermic reaction, nuclear fission and absorption of light. Since heat sources that supply heat to the engine can be supplied energy by virtue of any kind of energy.
Heat engine: It is a system that converts heat or thermal energy into a mechanical energy. Which will be used to do mechanical work.
Efficiency: The fraction of work done by engine to heat given to the engine is called its efficiency.
Complete step by step solution:

As from the figure we can see that the working substance takes heat from the source and rejects heat to sink. So, in ideal conditions we assume that source and sink have infinite thermal capacity. Heat rejected by the source is equal to its temperature and heat going to the sink will be equal to temperature of sink.
So, efficiency will be, $ \eta = \dfrac{{work\,output}}{{heat\,input}} $
$ \Rightarrow \eta = \dfrac{{{T_1} - {T_2}}}{{{T_1}}} = 1 - \dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}} $
So, we can conclude that
Efficiency is dependent on source and sink temperature.
From formula we can say efficiency is independent of working substance.
From the formula, we can say its efficiency will never be $ 100\% $ because $ \dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}} $ is always a positive number.
The amount of heat taken from source and heat going to decapitate on the sink depend on its thermal capacity.
Hence, from the above observation, we can say option (b) is the correct option.
Note:
Heat engines distinguish themselves from other types of engine by the fact that their efficiency is limited by Carnot’s theorem. This efficiency limitation can be a drawback. Advantage of a heat engine is that most forms of energy can be easily converted to heat by processes like exothermic reaction, nuclear fission and absorption of light. Since heat sources that supply heat to the engine can be supplied energy by virtue of any kind of energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




