
$\square XYZW$ is the rectangle. If $XY+YZ=17$ and $XZ+YW=26$ then find $XY$ and $YZ$ (where $XY>YZ$ ).
Answer
613.5k+ views
Hint: For solving this question we should know about the rectangle and how to apply Pythagoras Theorem in right-angled triangles. And by using a simple whole square formula we will solve this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
The polygon $\square XYZW$ is a rectangle as shown in the figure below.
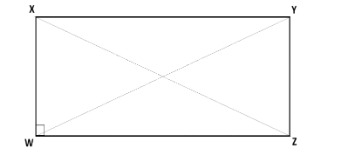
A rectangle is a polygon in which adjacent sides are perpendicular to each other and the length of opposite sides are equal. In other words, for the above rectangle,
\[\angle WXY=\angle XYZ=\angle YZW=\angle ZWX={{90}^{0}}\]
\[XY=WZ\] and \[WX=YZ\]
Now, let $XY=WZ=a$ and $WX=YZ=b$ .
It is given that $XY+YZ=17$ .
Then, we can write, $a+b=17.................\left( equationA \right)$ .
As we have two unknown variables $a$ and $b$ , so we need two different equations to find the values of $a$ and $b$ .
We need one more equation in terms of $a$ and $b$ . Before proceeding further just take a look at the result of the Pythagoras Theorem. The Pythagoras Theorem states that in a right-angled triangle as shown below $\Delta ABC$ , the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In the $\Delta ABC$ , $\angle ACB={{90}^{0}}$ and AB is the hypotenuse, BC is the base and AC is the perpendicular. From Pythagoras Theorem, we have:
${{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}$
Then, we can write, ${{\left( base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( perpendicular \right)}^{2}}={{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}$ .
If we look at the figure of the $\square XYZW$ , $\Delta XZW$ and $\Delta YZW$ are right-angled triangles and we can apply the result of Pythagoras theorem in both these triangles.
In the $\Delta XZW$ ,
$\angle XWZ={{90}^{0}}$ and the side $XZ$ is the hypotenuse. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( XW \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( WZ \right)}^{2}}={{\left( XZ \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}={{\left( XZ \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Then, $XZ=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}..............(equationB)$ .
Similarly, in the \[\Delta YZW\] ,
$\angle YZW={{90}^{0}}$ and the side $YW$ is the hypotenuse. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( YZ \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( ZW \right)}^{2}}={{\left( YW \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}={{\left( YW \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Then, $YW=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}................(equationC)$ .
Adding $equationB$ and $equationC$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& XZ+YW=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}+\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow XZ+YW=2\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
It is given that, $XZ+YW=26$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& 2\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=26 \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=13 \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{13}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}=169..............(equationD) \\
\end{align}$
We will use $equationA$ and $equationD$ to find the values of $a$ and $b$ .
As $a$ and $b$ are two positive numbers where $a$ is greater than $b$ . Now, we will use the whole square identities formulae written below:
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab \\
& {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab \\
\end{align}$
Adding the above two equations, we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab \right]+\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab \right] \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=2\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right] \\
\end{align}$
Now substituting the value of $\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right]$ from $equationD$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=2\times 169 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338-{{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now substituting the value of $\left( a+b \right)$ from $equationA$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338-{{\left( 17 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338-289 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=49 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{7}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow a-b=7.................(equationE) \\
\end{align}$
Here one point is very important in the above equation that we cannot write $b-a=7$ as we have taken $a>b$ so, the value of $b-a$ will be negative.
From $equationA$ and $equationE$ , we have:
$\begin{align}
& a+b=17 \\
& a-b=7 \\
\end{align}$
Adding the above two equations, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \left( a+b \right)+\left( a-b \right)=17+7 \\
& \Rightarrow 2a=24 \\
& \Rightarrow a=12 \\
\end{align}$
Now put the value of $a$ from the above equation in $equationA$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& 12+b=17 \\
& \Rightarrow b=17-12 \\
& \Rightarrow b=5 \\
\end{align}$
Now,
$\because XY=WZ=a$ and $WX=YZ=b$
Thus, $XY=12$ and $YZ=5$ .
Note: For solving this question we have to use the geometrical properties of the rectangle and we should know how to apply Pythagoras Theorem in case of any right-angled triangle and then apply every formula very carefully and find the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
The polygon $\square XYZW$ is a rectangle as shown in the figure below.

A rectangle is a polygon in which adjacent sides are perpendicular to each other and the length of opposite sides are equal. In other words, for the above rectangle,
\[\angle WXY=\angle XYZ=\angle YZW=\angle ZWX={{90}^{0}}\]
\[XY=WZ\] and \[WX=YZ\]
Now, let $XY=WZ=a$ and $WX=YZ=b$ .
It is given that $XY+YZ=17$ .
Then, we can write, $a+b=17.................\left( equationA \right)$ .
As we have two unknown variables $a$ and $b$ , so we need two different equations to find the values of $a$ and $b$ .
We need one more equation in terms of $a$ and $b$ . Before proceeding further just take a look at the result of the Pythagoras Theorem. The Pythagoras Theorem states that in a right-angled triangle as shown below $\Delta ABC$ , the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In the $\Delta ABC$ , $\angle ACB={{90}^{0}}$ and AB is the hypotenuse, BC is the base and AC is the perpendicular. From Pythagoras Theorem, we have:
${{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}$
Then, we can write, ${{\left( base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( perpendicular \right)}^{2}}={{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}$ .
If we look at the figure of the $\square XYZW$ , $\Delta XZW$ and $\Delta YZW$ are right-angled triangles and we can apply the result of Pythagoras theorem in both these triangles.
In the $\Delta XZW$ ,
$\angle XWZ={{90}^{0}}$ and the side $XZ$ is the hypotenuse. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( XW \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( WZ \right)}^{2}}={{\left( XZ \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}={{\left( XZ \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Then, $XZ=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}..............(equationB)$ .
Similarly, in the \[\Delta YZW\] ,
$\angle YZW={{90}^{0}}$ and the side $YW$ is the hypotenuse. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( YZ \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( ZW \right)}^{2}}={{\left( YW \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}={{\left( YW \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Then, $YW=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}................(equationC)$ .
Adding $equationB$ and $equationC$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& XZ+YW=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}+\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow XZ+YW=2\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
It is given that, $XZ+YW=26$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& 2\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=26 \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=13 \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{13}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}=169..............(equationD) \\
\end{align}$
We will use $equationA$ and $equationD$ to find the values of $a$ and $b$ .
As $a$ and $b$ are two positive numbers where $a$ is greater than $b$ . Now, we will use the whole square identities formulae written below:
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab \\
& {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab \\
\end{align}$
Adding the above two equations, we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab \right]+\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab \right] \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=2\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right] \\
\end{align}$
Now substituting the value of $\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right]$ from $equationD$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=2\times 169 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338-{{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now substituting the value of $\left( a+b \right)$ from $equationA$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338-{{\left( 17 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338-289 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=49 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{7}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow a-b=7.................(equationE) \\
\end{align}$
Here one point is very important in the above equation that we cannot write $b-a=7$ as we have taken $a>b$ so, the value of $b-a$ will be negative.
From $equationA$ and $equationE$ , we have:
$\begin{align}
& a+b=17 \\
& a-b=7 \\
\end{align}$
Adding the above two equations, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \left( a+b \right)+\left( a-b \right)=17+7 \\
& \Rightarrow 2a=24 \\
& \Rightarrow a=12 \\
\end{align}$
Now put the value of $a$ from the above equation in $equationA$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& 12+b=17 \\
& \Rightarrow b=17-12 \\
& \Rightarrow b=5 \\
\end{align}$
Now,
$\because XY=WZ=a$ and $WX=YZ=b$
Thus, $XY=12$ and $YZ=5$ .
Note: For solving this question we have to use the geometrical properties of the rectangle and we should know how to apply Pythagoras Theorem in case of any right-angled triangle and then apply every formula very carefully and find the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




