
What is reflection? Write the laws of reflection.
Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: Imagine a surface reflecting a beam of light. The light will be bounced back to the medium from which light was incident on it. Draw a ray diagram to see how it works and define the laws on the basis of this.
Complete step by step answer:
Reflection can be defined as a phenomenon where direction of the wave front of light changes in the interface of the two media and the light ray returns to the first media after striking at the interface.
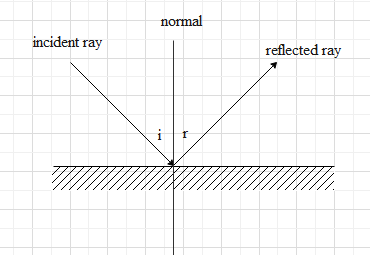
As shown in the picture, the incident ray comes and strikes at the interface of the two mediums and reflects back to the first medium again, which is shown as the reflected ray.
The laws of reflection are –
1.)The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are equal to each other.
2.)The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the surface at the point of contact of the incident ray, all lie in the same plane
The angle of incidence is the angle which is made by the incident ray with the normal to the surface. The angle of reflection is the angle which is made by the reflected ray with the normal to the surface. These two angles will always be equal.
Changing the direction of the incident ray will result in the change in direction of the reflected ray, but they will always lie in the same plane. However, the angle incidence and the angle of reflection will remain the same even if the direction of the rays are changed.
Note: The image formation process in plane mirrors and in spherical mirrors can be understood with the help of the laws of reflection of light. In case of the plane mirrors the image formed or seen by the observer is seen in the direction in which the light is reflected in the same distance as the distance of the object from the mirror.
Complete step by step answer:
Reflection can be defined as a phenomenon where direction of the wave front of light changes in the interface of the two media and the light ray returns to the first media after striking at the interface.

As shown in the picture, the incident ray comes and strikes at the interface of the two mediums and reflects back to the first medium again, which is shown as the reflected ray.
The laws of reflection are –
1.)The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are equal to each other.
2.)The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the surface at the point of contact of the incident ray, all lie in the same plane
The angle of incidence is the angle which is made by the incident ray with the normal to the surface. The angle of reflection is the angle which is made by the reflected ray with the normal to the surface. These two angles will always be equal.
Changing the direction of the incident ray will result in the change in direction of the reflected ray, but they will always lie in the same plane. However, the angle incidence and the angle of reflection will remain the same even if the direction of the rays are changed.
Note: The image formation process in plane mirrors and in spherical mirrors can be understood with the help of the laws of reflection of light. In case of the plane mirrors the image formed or seen by the observer is seen in the direction in which the light is reflected in the same distance as the distance of the object from the mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




