
What is reflection of light? Explain reflection of light with the help of an activity.
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: Knowing the process of reflection during which the light rays emerging from an object hits a reflecting surface and causes the light rays to bounce back causing an image to be produced. Understanding how the multiple reflections of normal mirrors which are used in a periscope equipped by submarines work will help us in understanding reflection better.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When a light ray hits a surface and upon hitting a surface gets bounced back, such a phenomenon is known as reflection. The ray incident on the surface is known as incident ray. The ray which gets bounced back is known as reflected ray. The surface causing this phenomenon is known as a reflecting medium.
One of the important properties of reflection is: angle of incidence = angle of reflection.
Any ray which is perpendicular to the reflecting medium is known as the normal ray.
The regular mirror that we use is an excellent example of reflecting surface.
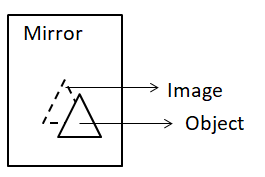
Let’s consider the first case as, Whenever we use the mirror to set up a look at our face for example, we stand parallel to the mirror’s surface. This causes the image of our face to form at the same height as much height as we are standing at. This is an example of normal reflection, where the incident rays are perpendicular and hence the reflected rays are perpendicular too.That means, normally incident rays were hitting the mirror. The above image is an example of the same.
Now,for the second case: Let’s consider the same example as above, however this time the mirror has a coating of water on it. Like let’s say, you spilled water on it.
What will happen here is that, even though you are standing parallel to the mirror, due to the uneven surface created due to water on the mirror’s surface the reflection will not be an exact image of you. Instead it will be a hazy image of you. This is known as diffused reflection, which happens when the reflecting surface isn’t plane or polished.
The first case is known as regular or specular reflection and the second case is known as diffused reflection.
Note: Angle of incidence = angle of reflection will always be satisfied for reflection, until any diffused reflection doesn’t take place.
Even though we consider the mirror to be a reflecting surface, it’s actually the reflective coating at the base of the mirror which causes the reflection. The glass slab on top of it causes refraction. To minimize any distortion due to the refraction, we generally use the mirror normal/parallel to our condition. Since, in this case, the normal rays are produced, which doesn’t get affected due to refraction.
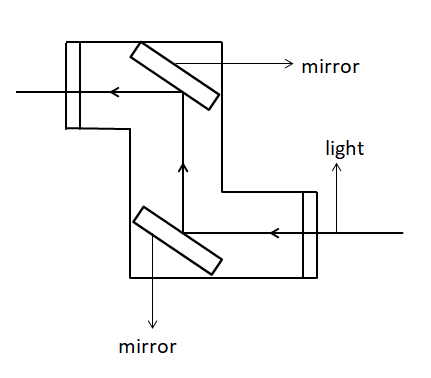
Periscope is an optical instrument used by submarines to look above the water level using the multiple reflections concept of mirrors. The mirrors used in periscope are regular mirrors. Two regular mirrors are used, which are placed one above the other and the mirrors are placed at an angle of 45 degrees. Below is a picture of how the reflection would be.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When a light ray hits a surface and upon hitting a surface gets bounced back, such a phenomenon is known as reflection. The ray incident on the surface is known as incident ray. The ray which gets bounced back is known as reflected ray. The surface causing this phenomenon is known as a reflecting medium.
One of the important properties of reflection is: angle of incidence = angle of reflection.
Any ray which is perpendicular to the reflecting medium is known as the normal ray.
The regular mirror that we use is an excellent example of reflecting surface.

Let’s consider the first case as, Whenever we use the mirror to set up a look at our face for example, we stand parallel to the mirror’s surface. This causes the image of our face to form at the same height as much height as we are standing at. This is an example of normal reflection, where the incident rays are perpendicular and hence the reflected rays are perpendicular too.That means, normally incident rays were hitting the mirror. The above image is an example of the same.
Now,for the second case: Let’s consider the same example as above, however this time the mirror has a coating of water on it. Like let’s say, you spilled water on it.
What will happen here is that, even though you are standing parallel to the mirror, due to the uneven surface created due to water on the mirror’s surface the reflection will not be an exact image of you. Instead it will be a hazy image of you. This is known as diffused reflection, which happens when the reflecting surface isn’t plane or polished.
The first case is known as regular or specular reflection and the second case is known as diffused reflection.
Note: Angle of incidence = angle of reflection will always be satisfied for reflection, until any diffused reflection doesn’t take place.
Even though we consider the mirror to be a reflecting surface, it’s actually the reflective coating at the base of the mirror which causes the reflection. The glass slab on top of it causes refraction. To minimize any distortion due to the refraction, we generally use the mirror normal/parallel to our condition. Since, in this case, the normal rays are produced, which doesn’t get affected due to refraction.
Periscope is an optical instrument used by submarines to look above the water level using the multiple reflections concept of mirrors. The mirrors used in periscope are regular mirrors. Two regular mirrors are used, which are placed one above the other and the mirrors are placed at an angle of 45 degrees. Below is a picture of how the reflection would be.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




