
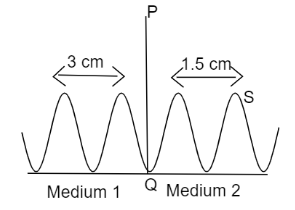
What is the ratio of speed of wave in medium \[1\] and \[2\].
A. \[{\text{ 2:1}}\]
B. \[{\text{ 1:2}}\]
C. \[{\text{ 1:1}}\]
D. \[{\text{ 3:1}}\]

Answer
495.3k+ views
Hint:Whenever the wave travels in the medium then it travels with some velocity which is known as wave velocity or velocity of wave. The velocity of a wave is equal to the product of the frequency of the wave and the wavelength of the wave in that medium respectively. We will find the ratio of speed of wave in both mediums respectively by using the relation of wavelength and wave velocity.
Complete step by step answer:
The distance between consecutive crests or consecutive troughs of a wave is known as the wavelength of the wave. Let us assume that a wave travels with wavelength \[\lambda \] and frequency \[f\] in the medium then the velocity of the wave can be calculated by the relation as: \[v = f\lambda \],
Where \[v\] is the velocity of a wave, \[\lambda \] is the wavelength of a wave and \[f\] is the frequency of a wave in the medium.
According to question the wavelength of wave in medium \[1\] is \[3{\text{ cm}}\], then the velocity of wave in medium \[{\text{1 }}\left( {{v_1}} \right)\] can be calculated as:
\[{v_1}{\text{ = 3 cm}}\] ___________\[(1)\]........(Since there is no change in frequency in question \[f\] can be ignored)
Similarly in medium \[2\] the wavelength of wave given is \[1.5{\text{ cm}}\] then velocity of wave \[{v_2}\] will be equals to:
\[{v_2}{\text{ = 1}}{\text{.5 cm}}\] __________\[(2)\]
On taking ratio of equation \[(1)\] and equation \[(2)\] we get the result as:
\[\dfrac{{{v_1}}}{{{v_2}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{\text{3}}}{{1.5}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{v_1}}}{{{v_2}}}{\text{ = 2}}\]
\[\therefore {v_1}{\text{ = 2}}{v_2}\]
Therefore the speed of the wave in medium first is double that that of medium second. The ration comes to be \[2:1\].
Hence the correct option is A.
Note: The wave velocity also depends on the frequency of the wave in the respective medium, but here the frequency does not change therefore we can ignore the frequency. Thus more the wavelength of the wave will be its speed in an equal interval of time.
Complete step by step answer:
The distance between consecutive crests or consecutive troughs of a wave is known as the wavelength of the wave. Let us assume that a wave travels with wavelength \[\lambda \] and frequency \[f\] in the medium then the velocity of the wave can be calculated by the relation as: \[v = f\lambda \],
Where \[v\] is the velocity of a wave, \[\lambda \] is the wavelength of a wave and \[f\] is the frequency of a wave in the medium.
According to question the wavelength of wave in medium \[1\] is \[3{\text{ cm}}\], then the velocity of wave in medium \[{\text{1 }}\left( {{v_1}} \right)\] can be calculated as:
\[{v_1}{\text{ = 3 cm}}\] ___________\[(1)\]........(Since there is no change in frequency in question \[f\] can be ignored)
Similarly in medium \[2\] the wavelength of wave given is \[1.5{\text{ cm}}\] then velocity of wave \[{v_2}\] will be equals to:
\[{v_2}{\text{ = 1}}{\text{.5 cm}}\] __________\[(2)\]
On taking ratio of equation \[(1)\] and equation \[(2)\] we get the result as:
\[\dfrac{{{v_1}}}{{{v_2}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{\text{3}}}{{1.5}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{v_1}}}{{{v_2}}}{\text{ = 2}}\]
\[\therefore {v_1}{\text{ = 2}}{v_2}\]
Therefore the speed of the wave in medium first is double that that of medium second. The ration comes to be \[2:1\].
Hence the correct option is A.
Note: The wave velocity also depends on the frequency of the wave in the respective medium, but here the frequency does not change therefore we can ignore the frequency. Thus more the wavelength of the wave will be its speed in an equal interval of time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




