
Periscope is used for:
(A) Observation beyond the obstruction
(B) Watching TV more clearly
(C) Viewing nearby objects by persons suffering from visual deformities
(D) All of these
Answer
529.5k+ views
Hint :Periscope is an optical instrument used in land and sea warfare, submarine navigation, and other applications to allow an observer to see his surroundings while remaining concealed, covered, or submerged. It is made up of an outer case with $ 45^\circ $ mirrors on each end. Parallel to the surface, these mirrors are positioned.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A periscope has two mirrors or reflecting prisms that adjust the path of light coming from the scene being observed: the first deflects it down into a vertical tunnel, while the second diverts it horizontally, enabling the scene to be seen more easily.
The most basic periscope consists of a tube with two mirrors at either end that are parallel to each other but at $ 45^\circ $ to the tube's axis. This system does not provide magnification or a cross line image. The basic geometry of the tube limits the arc of vision: the longer or narrower the tube, the wider the field of view.
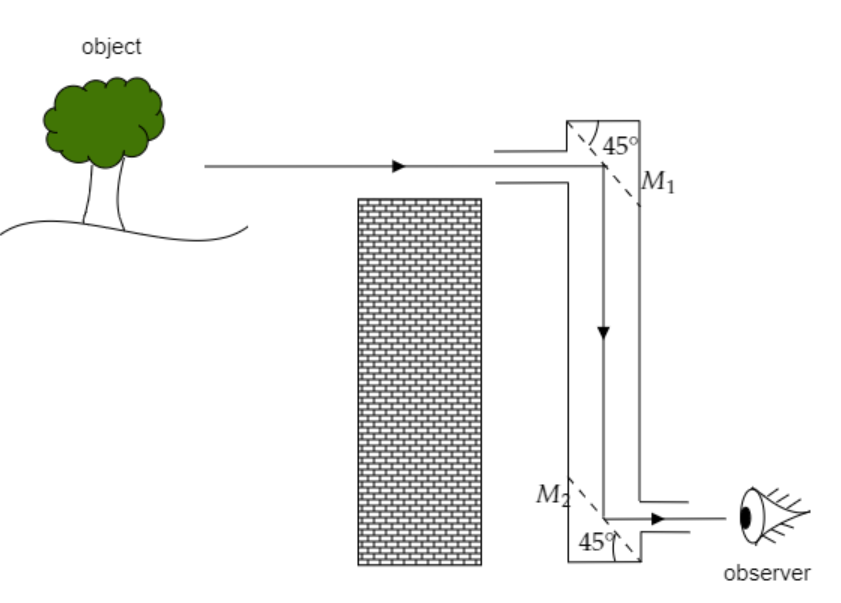
As we can see from the figure, periscopes are used to see objects which can’t be seen due to some obstacle between the observer and the object. They usually facilitate light from an object to bend, so the observer can view it.
So, the correct option is A. observation beyond the obstruction. Situations in options B and C do not necessarily require a periscope. Moreover, a person with visual deformities will have the same difficulty in viewing the images formed by the periscope.
Hence, option A is the only correct option.
Note :
Periscopes may be used for a variety of purposes in addition to observing objects that are not in direct line of sight. For example, it's used in submarines to figure out how far a torpedo can travel and when the best time to strike is. It can also be used in nuclear reactors to track the chemical reactions that are occurring.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A periscope has two mirrors or reflecting prisms that adjust the path of light coming from the scene being observed: the first deflects it down into a vertical tunnel, while the second diverts it horizontally, enabling the scene to be seen more easily.
The most basic periscope consists of a tube with two mirrors at either end that are parallel to each other but at $ 45^\circ $ to the tube's axis. This system does not provide magnification or a cross line image. The basic geometry of the tube limits the arc of vision: the longer or narrower the tube, the wider the field of view.

As we can see from the figure, periscopes are used to see objects which can’t be seen due to some obstacle between the observer and the object. They usually facilitate light from an object to bend, so the observer can view it.
So, the correct option is A. observation beyond the obstruction. Situations in options B and C do not necessarily require a periscope. Moreover, a person with visual deformities will have the same difficulty in viewing the images formed by the periscope.
Hence, option A is the only correct option.
Note :
Periscopes may be used for a variety of purposes in addition to observing objects that are not in direct line of sight. For example, it's used in submarines to figure out how far a torpedo can travel and when the best time to strike is. It can also be used in nuclear reactors to track the chemical reactions that are occurring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




