
List the properties of electromagnetic waves.
Answer
604.5k+ views
Hint: In this question, we start with the definition of Electromagnetic waves that is the waves formed by an oscillating or varying magnetic and electric field. We see the property one by one like the electric and magnetic field are transverse in nature, EM wave can travel in vacuum also unlike mechanical wave with velocity of light given by $c = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{\mu _o}{\varepsilon _o}} }}$, Pointing vector P describes the energy transferred by electromagnetic waves given by $\vec P = \vec E \times \vec B$.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
When an electric field is varying it induces the magnetic field and when a magnetic field is varying it induces an electric field therefore, these two fields are interconnected.
Using this concept James Clerk Maxwell and Heinrich Hertz gave us the concept of Electromagnetic wave or EM wave.
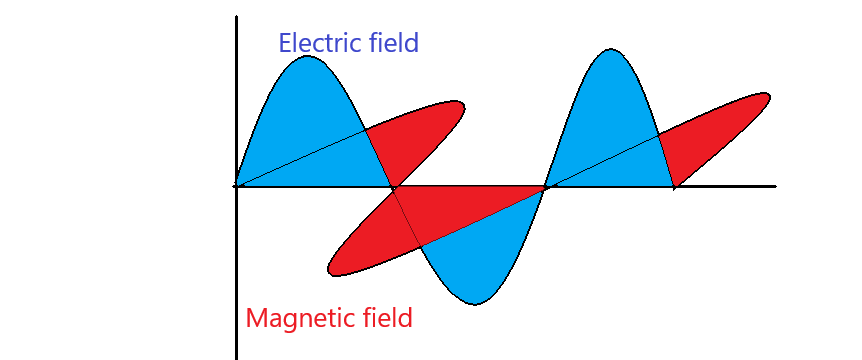
Therefore Electromagnetic waves are defined as the waves formed by an oscillating or varying magnetic and electric field so that they are perpendicular to each other and also perpendicular to the direction of propagation.
The equation of EM waves are obtained from the solutions of Maxwell’s equations
1. Electromagnetic waves are formed by varying the electric and magnetic fields in such a way that these two fields are perpendicular to one another and also perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Therefore Electromagnetic waves are called transverse waves.
2. The electromagnetic wave can propagate in a vacuum; it does not need any material medium to propagate.
3. The phase and the magnitude of the oscillating magnetic and electric field are the same for EM waves. The ratio of the amplitudes of the electric field to the magnetic field will give us the velocity of light that is $c = \dfrac{{{E_O}}}{{{B_O}}}$
4. The velocity of the electromagnetic wave in the vacuum is same as the velocity of light \[c = 3 \times {10^8}\] m/s and $c = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{\mu _o}{\varepsilon _o}} }}$ .
5. The electromagnetic wave always follows the principle of superposition.
6. The wavelength of electromagnetic wave changes as it propagates from one medium to another, however, its frequency remains unaffected
7. The refractive index of a medium is given as
$\eta = \sqrt {{\mu _r}{\varepsilon _r}} $
8. The energy of electric and magnetic fields of electromagnetic waves is equal.
9. The Pointing vector P describes the energy transferred by electromagnetic waves per second per unit area and also the direction of propagation of The electromagnetic wave that is $\vec P = \vec E \times \vec B$
Note: For these types of questions we need to know the concepts of electromagnetic waves, mechanical waves, electric field, magnetic field, Maxwell’s equation, and properties of the electromagnetic wave in a vacuum. We also need to know the concepts of wavelength, frequency, velocity and vectors.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
When an electric field is varying it induces the magnetic field and when a magnetic field is varying it induces an electric field therefore, these two fields are interconnected.
Using this concept James Clerk Maxwell and Heinrich Hertz gave us the concept of Electromagnetic wave or EM wave.
Therefore Electromagnetic waves are defined as the waves formed by an oscillating or varying magnetic and electric field so that they are perpendicular to each other and also perpendicular to the direction of propagation.

The equation of EM waves are obtained from the solutions of Maxwell’s equations
1. Electromagnetic waves are formed by varying the electric and magnetic fields in such a way that these two fields are perpendicular to one another and also perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Therefore Electromagnetic waves are called transverse waves.
2. The electromagnetic wave can propagate in a vacuum; it does not need any material medium to propagate.
3. The phase and the magnitude of the oscillating magnetic and electric field are the same for EM waves. The ratio of the amplitudes of the electric field to the magnetic field will give us the velocity of light that is $c = \dfrac{{{E_O}}}{{{B_O}}}$
4. The velocity of the electromagnetic wave in the vacuum is same as the velocity of light \[c = 3 \times {10^8}\] m/s and $c = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{\mu _o}{\varepsilon _o}} }}$ .
5. The electromagnetic wave always follows the principle of superposition.
6. The wavelength of electromagnetic wave changes as it propagates from one medium to another, however, its frequency remains unaffected
7. The refractive index of a medium is given as
$\eta = \sqrt {{\mu _r}{\varepsilon _r}} $
8. The energy of electric and magnetic fields of electromagnetic waves is equal.
9. The Pointing vector P describes the energy transferred by electromagnetic waves per second per unit area and also the direction of propagation of The electromagnetic wave that is $\vec P = \vec E \times \vec B$
Note: For these types of questions we need to know the concepts of electromagnetic waves, mechanical waves, electric field, magnetic field, Maxwell’s equation, and properties of the electromagnetic wave in a vacuum. We also need to know the concepts of wavelength, frequency, velocity and vectors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




