
In a transistor, the base is
(A) a conductor of low resistance
(B) a conductor of high resistance
(C ) an insulator
(D) an extrinsic semiconductor
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: A transistor is an extrinsic semiconductor. That is, the emitter, collector and base is made of extrinsic semiconductor. The emitter and collector region of a transistor is heavily doped and the base of a transistor is lightly doped. Thus compared to emitter and collector base is made of thin layered semiconductor.
Complete answer:
A transistor is a semiconductor device. It usually has three terminals. That is, emitter, base and collector. It is a three terminal device which has two p-n junctions. These two p-n junctions are placed back to back in a single piece of semiconductor material. Mainly there are two types of transistors. They are bipolar junction transistor and field effect transistor. An npn transistor is formed by sandwiching p-type material between two n-type materials. Similarly, a pnp transistor is formed by sandwiching n-type material between two p-type materials. BJT is a three terminal device. They are emitter, base and collector.
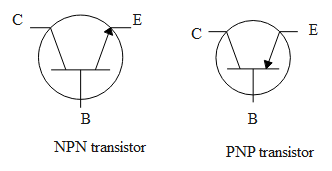
Emitter region usually supplies charge carriers to other two regions. Usually, the emitter is heavily doped. In npn transistors, the emitter supplies free electrons to the junction. Collector is usually used to collect charge carriers. Collector is the largest part of a transistor rather than the emitter and base. The doping of the collector is intermediated between the emitter and base.
Hence, option (D) is correct.
Note:
For normal operations of a transistor the emitter-base junction is forward biased, so that the junction offers low resistance to the flow of current. The collector-base junction is reverse biased, so that the junction offers high resistance to the flow of current. The emitter and collector region of a transistor is heavily doped and the base of a transistor is lightly doped. Thus compared to emitter and collector base is made of thin layered semiconductor.
Complete answer:
A transistor is a semiconductor device. It usually has three terminals. That is, emitter, base and collector. It is a three terminal device which has two p-n junctions. These two p-n junctions are placed back to back in a single piece of semiconductor material. Mainly there are two types of transistors. They are bipolar junction transistor and field effect transistor. An npn transistor is formed by sandwiching p-type material between two n-type materials. Similarly, a pnp transistor is formed by sandwiching n-type material between two p-type materials. BJT is a three terminal device. They are emitter, base and collector.

Emitter region usually supplies charge carriers to other two regions. Usually, the emitter is heavily doped. In npn transistors, the emitter supplies free electrons to the junction. Collector is usually used to collect charge carriers. Collector is the largest part of a transistor rather than the emitter and base. The doping of the collector is intermediated between the emitter and base.
Hence, option (D) is correct.
Note:
For normal operations of a transistor the emitter-base junction is forward biased, so that the junction offers low resistance to the flow of current. The collector-base junction is reverse biased, so that the junction offers high resistance to the flow of current. The emitter and collector region of a transistor is heavily doped and the base of a transistor is lightly doped. Thus compared to emitter and collector base is made of thin layered semiconductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




