
Give one basic difference between conservative and dispersive replication of DNA.
Answer
567.9k+ views
Hint: According to Watson and Crick’s model, DNA is a double-helical structure. During the cellular division, both these strands must be perfectly duplicated to maintain cellular structure and functions in the subsequent cells.
Complete answer:
Based on the double-helical structure of the DNA three modes of replication are probable.
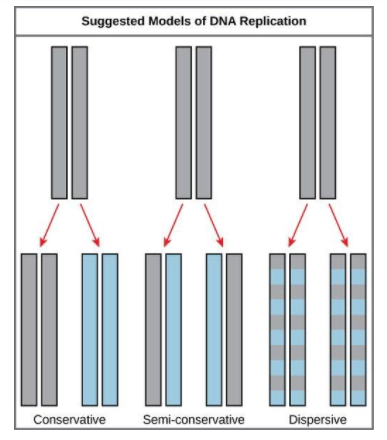
(a) Conservative:
-In this model the parental strands temporarily separate from each other, two new daughter strands are synthesized against each of these template parents strands.
-Following the replication, the parental strands recombine with each other while the daughter strands combine with each other.
-Thus, at the end of each replication cycle, we have an original parent strand and a new daughter copy.
(b) Semi-conservative:
-In this model the parental strands serve as a template for the production of new strands. However,
-At the end of each repetition cycle each of the DNA contains one of the “parent” strands and one of the daughter strands respectively.
(c) Dispersive
-In this model the separation of parental strands is necessarily more chaotic.
-Instead of continuous strands the parental component is distributed much more randomly among the daughter strands.
-This pattern continues to get more randomized following each cycle of DNA replication.
Additional information: Messelson and Stahl’s experiment: The scientists grew E. coli in a medium rich with a heavier isotope of Nitrogen (15N) long enough to assume that this nitrogen was assimilated in the nitrogenous bases that constitute the genetic material of the bacteria. Some of these bacteria were then shifted into a medium rich with normal nitrogen (14N) and allowed to grow for a generation. After one generation, some of these cells were harvested and centrifuged to break down their cellular structure and release their DNA. This DNA when loaded in a gradient made of Cesium chloride settled to a particular depth within the centrifuge tube. Cells from each subsequent generation on centrifugation produced two distinct bands of DNA (one of 15N and another of 14N). In case the conservative model was true, the relative concentration of these bands should remain constant however, the scientist observed that in each subsequent generation the concentration of heavier bands reduced. Therefore disapproving the conservative model of replication.
Note: The structure of DNA suggests that the two strands might separate during the duplication process such that each strand acts as a base template against which the complimentary copy of duplicate stands is produced.
Complete answer:
Based on the double-helical structure of the DNA three modes of replication are probable.
(a) Conservative:
-In this model the parental strands temporarily separate from each other, two new daughter strands are synthesized against each of these template parents strands.
-Following the replication, the parental strands recombine with each other while the daughter strands combine with each other.
-Thus, at the end of each replication cycle, we have an original parent strand and a new daughter copy.
(b) Semi-conservative:
-In this model the parental strands serve as a template for the production of new strands. However,
-At the end of each repetition cycle each of the DNA contains one of the “parent” strands and one of the daughter strands respectively.
(c) Dispersive
-In this model the separation of parental strands is necessarily more chaotic.
-Instead of continuous strands the parental component is distributed much more randomly among the daughter strands.
-This pattern continues to get more randomized following each cycle of DNA replication.
Additional information: Messelson and Stahl’s experiment: The scientists grew E. coli in a medium rich with a heavier isotope of Nitrogen (15N) long enough to assume that this nitrogen was assimilated in the nitrogenous bases that constitute the genetic material of the bacteria. Some of these bacteria were then shifted into a medium rich with normal nitrogen (14N) and allowed to grow for a generation. After one generation, some of these cells were harvested and centrifuged to break down their cellular structure and release their DNA. This DNA when loaded in a gradient made of Cesium chloride settled to a particular depth within the centrifuge tube. Cells from each subsequent generation on centrifugation produced two distinct bands of DNA (one of 15N and another of 14N). In case the conservative model was true, the relative concentration of these bands should remain constant however, the scientist observed that in each subsequent generation the concentration of heavier bands reduced. Therefore disapproving the conservative model of replication.

Note: The structure of DNA suggests that the two strands might separate during the duplication process such that each strand acts as a base template against which the complimentary copy of duplicate stands is produced.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




