
How can I find the length of a side of this regular star-sharped pentagon inscribed in a circle with a radius of 25 cm?

Answer
539.7k+ views
Hint: The above problem can be solved in 3 steps. In step1, we find the length of side BE from the figure. In step2, we find the length of the side BA from the above figure. Let F be a point of intersection of B and A in the given figure. In step3, we find the length of side BF in the given figure.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first represent a diagram to understand better.
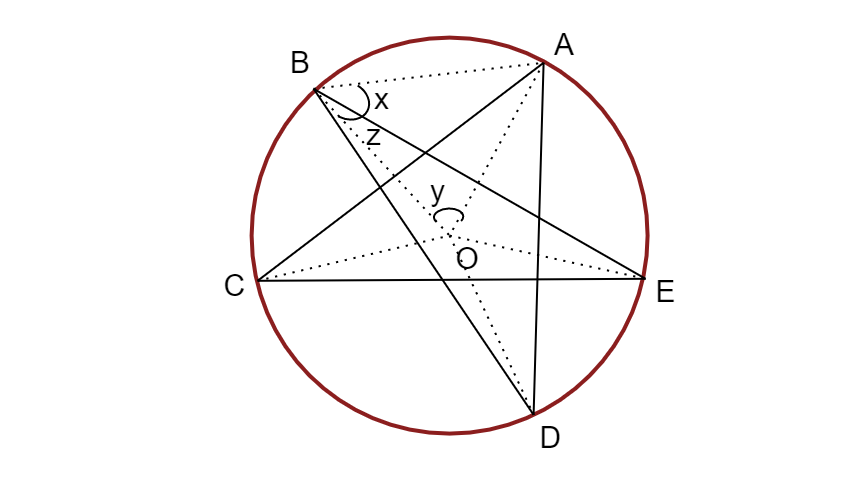
Step1:
Let O be the centre of the circle.
From the figure,
Let the $\angle AOB$=$y$
The value of angle y is given by,
$\Rightarrow \angle y=\dfrac{360}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \angle y=72$
In the triangle $OBE\;$,
The sides OB and OE are equal to the radius of the circle.
OB $=\;$ OE $=\;$ r $=\;$ 25cm
As the two sides of the triangle are of equal length, Triangle $OBE\;$ is an isosceles triangle.
Angles opposite to the two equal sides in an isosceles triangle are equal.
Following the same,
$\angle OBE=\angle OEB$
Let F be the midpoint of the side BE in the figure.
Now,
The two triangles $OFB\;$ and $OFE\;$ are both right-angled and congruent triangles.
From the figure,
$\Rightarrow BF=r\sin x$
F is the midpoint of side BE so, the length of BE is twice that of BF.
$\Rightarrow BE=2\times BF$
$\Rightarrow BE=2\times r\sin y$
$\Rightarrow BE=2\times 25\times \sin 72$
$\Rightarrow BE=2\times 25\times \left( \dfrac{\left( \sqrt{10+2\sqrt{5}} \right)}{4} \right)$
$\Rightarrow BE=\left( \dfrac{25\sqrt{10+2\sqrt{5}}}{2} \right)$
Upon evaluation,
We get,
$\Rightarrow BE\approx 47.55cm$
Step2:
From the above figure,
$\Rightarrow z=\dfrac{\left( 180-2y \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow z=\dfrac{\left( 180-\left( 2\times 72 \right) \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow z=\dfrac{\left( 180-144 \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow z=\dfrac{36}{2}$
$\Rightarrow z=18$
Triangle $BOE\;$ is an isosceles triangle.
From the given figure,
Triangle $BOA\;$ is also an isosceles triangle.
$\Rightarrow \angle OBA=\dfrac{\left( 180-y \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \angle OBA=\dfrac{\left( 180-72 \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \angle OBA=\dfrac{\left( 108 \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \angle OBA=54$
Let F be a point of intersection of B and A in the given figure.
$\Rightarrow \angle FBA=y=\angle OBA-z$
$\Rightarrow \angle FBA=y=54-18$
$\Rightarrow \angle FBA=y=36$
The length of the side BA from the figure is given by
$\Rightarrow BA=2r\sin \left( \dfrac{y}{2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow BA=2\times 25\times \sin \left( \dfrac{72}{2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow BA=2\times 25\times \sin \left( 36 \right)$
$\Rightarrow BA=2\times 25\times \dfrac{\left( \sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}} \right)}{4}$
$\Rightarrow BA=25\times \dfrac{\left( \sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}} \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow BA=\dfrac{25\left( \sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}} \right)}{2}$
Upon evaluation,
We get,
$\Rightarrow BA\approx 29.39cm$
Step3:
From the above figure,
We find that the triangle $BFA\;$ is an isosceles triangle.
From the above figure,
$\Rightarrow BA=2\times BF\times \cos y$
$\Rightarrow BF=\dfrac{BA}{2\times \cos y}$
$\Rightarrow BF=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{25\left( \sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}} \right)}{2} \right)}{2\times \left( \dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1}{4} \right)}$
$\Rightarrow BF=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{25\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{2}\times \dfrac{4}{\sqrt{5}+1}$
$\Rightarrow BF=\dfrac{25\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{\sqrt{5}+1}$
Upon evaluation,
We get,
$\Rightarrow BF=18.16cm$
Note: In an isosceles triangle, the length of the two sides is equal. The angle opposite to the two equal sides is the same. Two triangles are said to be congruent if
1. Corresponding sides are equal
2. Two pairs of corresponding sides and angles between them are equal
3. Two pairs of corresponding angles and the sides between them are equal
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first represent a diagram to understand better.

Step1:
Let O be the centre of the circle.
From the figure,
Let the $\angle AOB$=$y$
The value of angle y is given by,
$\Rightarrow \angle y=\dfrac{360}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \angle y=72$
In the triangle $OBE\;$,
The sides OB and OE are equal to the radius of the circle.
OB $=\;$ OE $=\;$ r $=\;$ 25cm
As the two sides of the triangle are of equal length, Triangle $OBE\;$ is an isosceles triangle.
Angles opposite to the two equal sides in an isosceles triangle are equal.
Following the same,
$\angle OBE=\angle OEB$
Let F be the midpoint of the side BE in the figure.
Now,
The two triangles $OFB\;$ and $OFE\;$ are both right-angled and congruent triangles.
From the figure,
$\Rightarrow BF=r\sin x$
F is the midpoint of side BE so, the length of BE is twice that of BF.
$\Rightarrow BE=2\times BF$
$\Rightarrow BE=2\times r\sin y$
$\Rightarrow BE=2\times 25\times \sin 72$
$\Rightarrow BE=2\times 25\times \left( \dfrac{\left( \sqrt{10+2\sqrt{5}} \right)}{4} \right)$
$\Rightarrow BE=\left( \dfrac{25\sqrt{10+2\sqrt{5}}}{2} \right)$
Upon evaluation,
We get,
$\Rightarrow BE\approx 47.55cm$
Step2:
From the above figure,
$\Rightarrow z=\dfrac{\left( 180-2y \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow z=\dfrac{\left( 180-\left( 2\times 72 \right) \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow z=\dfrac{\left( 180-144 \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow z=\dfrac{36}{2}$
$\Rightarrow z=18$
Triangle $BOE\;$ is an isosceles triangle.
From the given figure,
Triangle $BOA\;$ is also an isosceles triangle.
$\Rightarrow \angle OBA=\dfrac{\left( 180-y \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \angle OBA=\dfrac{\left( 180-72 \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \angle OBA=\dfrac{\left( 108 \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \angle OBA=54$
Let F be a point of intersection of B and A in the given figure.
$\Rightarrow \angle FBA=y=\angle OBA-z$
$\Rightarrow \angle FBA=y=54-18$
$\Rightarrow \angle FBA=y=36$
The length of the side BA from the figure is given by
$\Rightarrow BA=2r\sin \left( \dfrac{y}{2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow BA=2\times 25\times \sin \left( \dfrac{72}{2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow BA=2\times 25\times \sin \left( 36 \right)$
$\Rightarrow BA=2\times 25\times \dfrac{\left( \sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}} \right)}{4}$
$\Rightarrow BA=25\times \dfrac{\left( \sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}} \right)}{2}$
$\Rightarrow BA=\dfrac{25\left( \sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}} \right)}{2}$
Upon evaluation,
We get,
$\Rightarrow BA\approx 29.39cm$
Step3:
From the above figure,
We find that the triangle $BFA\;$ is an isosceles triangle.
From the above figure,
$\Rightarrow BA=2\times BF\times \cos y$
$\Rightarrow BF=\dfrac{BA}{2\times \cos y}$
$\Rightarrow BF=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{25\left( \sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}} \right)}{2} \right)}{2\times \left( \dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1}{4} \right)}$
$\Rightarrow BF=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{25\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{2}\times \dfrac{4}{\sqrt{5}+1}$
$\Rightarrow BF=\dfrac{25\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{\sqrt{5}+1}$
Upon evaluation,
We get,
$\Rightarrow BF=18.16cm$
Note: In an isosceles triangle, the length of the two sides is equal. The angle opposite to the two equal sides is the same. Two triangles are said to be congruent if
1. Corresponding sides are equal
2. Two pairs of corresponding sides and angles between them are equal
3. Two pairs of corresponding angles and the sides between them are equal
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?




