
Draw molecular orbital diagram for ${{F}_{2}}$ molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property.
Answer
528.6k+ views
Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT).
The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic configuration. Thus, the magnetic property can be explained when we know electronic configuration of molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
-Before solving the illustration given let us see about the VBT, MOT, bond order and magnetic property relations.
-MOT and VBT are the foundational theories of quantum chemistry. The VBT gives a more understandable pictorial representation of molecules but, MOT explains the molecular formation in a better way. MOT describes the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics.
-According to MOT, the atomic orbitals of comparable energy undergo overlap and give the formation of the same number of molecular orbitals.
-Addition of atomic orbitals- The atomic orbitals with the same sign combine to give bonding molecular orbitals. In the molecular orbital, the region between the two nuclei is the place where there is overlap of individual orbitals. Hence, there is greater probability of electron density in this region.
-MOT uses a linear combination of atomic orbitals strategy to represent molecular orbitals resulting from bonds between atoms. These are bonding, anti-bonding and non-bonding.
-Magnetic character- If all the electrons in the molecule of a substance are paired, then the substance is diamagnetic i.e. can be repelled by the magnetic field. Whereas, presence of unpaired electrons shows that the substance is paramagnetic i.e. can be attracted by magnetic field. Now, let us see the MO diagram of ${{F}_{2}}$ molecule-
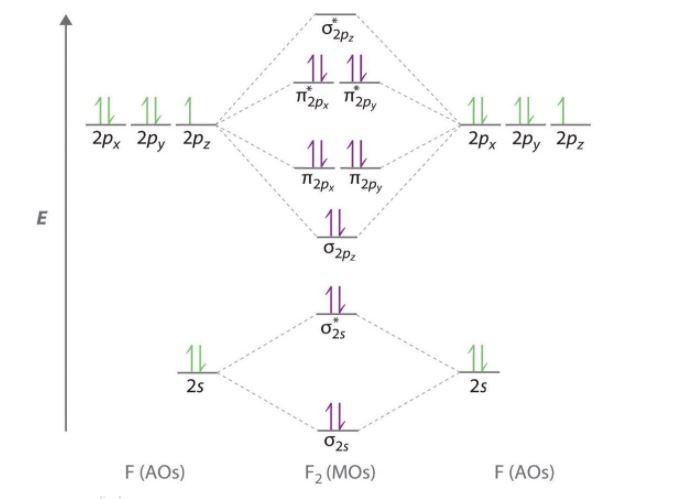
-Molecular orbital electronic configuration is given by,
MOEC = $KK{{\left( \sigma 2s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( {{\sigma }^{*}}2s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( \sigma 2{{p}_{z}} \right)}^{2}}\left[ {{\left( \pi 2{{p}_{x}} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \pi 2{{p}_{y}} \right)}^{2}} \right]\left[ {{\left( {{\pi }^{*}}2{{p}_{x}} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( {{\pi }^{*}}2{{p}_{y}} \right)}^{2}} \right]$
-where, KK denotes ${{\left( \sigma 1s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( {{\sigma }^{*}}1s \right)}^{2}}$
-Bonding orbitals are $\sigma 2s,\sigma 2{{p}_{z}},\pi 2{{p}_{x}},\pi 2{{p}_{y}}$
-Anti-bonding orbitals are ${{\sigma }^{*}}2s,{{\sigma }^{*}}2{{p}_{z}},{{\pi }^{*}}2{{p}_{x}},{{\pi }^{*}}2{{p}_{y}}$
-Therefore, Bond order = $\dfrac{{{N}_{b}}-{{N}_{a}}}{2}$
-Here, ${{N}_{b}}$ denotes number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals
${{N}_{a}}$ denotes number of electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals
-So, Bond order of ${{F}_{2}}$ = $\dfrac{8-6}{2}=1$
-Since, all the electrons in the molecular orbitals are paired, it is diamagnetic.
Note: The bonding MO has lower energy and hence greater stability whereas, anti-bonding MO has more energy and hence lesser stability. That is why, electrons will be added or removed from antibonding orbitals first forming an ion.
The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic configuration. Thus, the magnetic property can be explained when we know electronic configuration of molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
-Before solving the illustration given let us see about the VBT, MOT, bond order and magnetic property relations.
-MOT and VBT are the foundational theories of quantum chemistry. The VBT gives a more understandable pictorial representation of molecules but, MOT explains the molecular formation in a better way. MOT describes the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics.
-According to MOT, the atomic orbitals of comparable energy undergo overlap and give the formation of the same number of molecular orbitals.
-Addition of atomic orbitals- The atomic orbitals with the same sign combine to give bonding molecular orbitals. In the molecular orbital, the region between the two nuclei is the place where there is overlap of individual orbitals. Hence, there is greater probability of electron density in this region.
-MOT uses a linear combination of atomic orbitals strategy to represent molecular orbitals resulting from bonds between atoms. These are bonding, anti-bonding and non-bonding.
-Magnetic character- If all the electrons in the molecule of a substance are paired, then the substance is diamagnetic i.e. can be repelled by the magnetic field. Whereas, presence of unpaired electrons shows that the substance is paramagnetic i.e. can be attracted by magnetic field. Now, let us see the MO diagram of ${{F}_{2}}$ molecule-

-Molecular orbital electronic configuration is given by,
MOEC = $KK{{\left( \sigma 2s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( {{\sigma }^{*}}2s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( \sigma 2{{p}_{z}} \right)}^{2}}\left[ {{\left( \pi 2{{p}_{x}} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \pi 2{{p}_{y}} \right)}^{2}} \right]\left[ {{\left( {{\pi }^{*}}2{{p}_{x}} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( {{\pi }^{*}}2{{p}_{y}} \right)}^{2}} \right]$
-where, KK denotes ${{\left( \sigma 1s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( {{\sigma }^{*}}1s \right)}^{2}}$
-Bonding orbitals are $\sigma 2s,\sigma 2{{p}_{z}},\pi 2{{p}_{x}},\pi 2{{p}_{y}}$
-Anti-bonding orbitals are ${{\sigma }^{*}}2s,{{\sigma }^{*}}2{{p}_{z}},{{\pi }^{*}}2{{p}_{x}},{{\pi }^{*}}2{{p}_{y}}$
-Therefore, Bond order = $\dfrac{{{N}_{b}}-{{N}_{a}}}{2}$
-Here, ${{N}_{b}}$ denotes number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals
${{N}_{a}}$ denotes number of electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals
-So, Bond order of ${{F}_{2}}$ = $\dfrac{8-6}{2}=1$
-Since, all the electrons in the molecular orbitals are paired, it is diamagnetic.
Note: The bonding MO has lower energy and hence greater stability whereas, anti-bonding MO has more energy and hence lesser stability. That is why, electrons will be added or removed from antibonding orbitals first forming an ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




