
How does a pitch ball electroscope work ?
Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint:In early scientific research, an electroscope was widely used to detect the presence of an electric charge on a body. It’s an instrument which tells us about whether a body has a charge on it or not. An electroscope works on the principle of electrostatic Force which was formulated by coulomb’s such that” two bodies having charges ${q_1}$ and ${q_2}$ separated by a distance of $r$ will experience a force which mathematically written as $F = \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{4\pi { \in _0}}}{r^2}$, where ${ \in _0}$ is called the permittivity of free space.
Complete answer:
A pith ball electroscope consists of two very small sized non-conductor lightweight balls, initially in place of nonconductive balls a spongy plant material was used which was called pith; these lightweight balls are suspended by either a silk or linen thread.
When we have to examine a substance whether it has a charge on it or not, we bring the tested substance near the uncharged pith ball and according to coulomb’s law if this tested substance have a charge then it will tends to move towards the pith ball due to electrostatic force of attraction between two bodies of having charges opposite in sign.
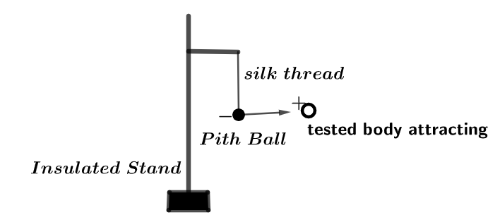
This attraction between pith ball and tested substance is mainly due to polarisation. Let us suppose the tested substance had a positive charge on it and when it bring closer to the uncharged pith ball then electrons of the pith ball atoms in outermost orbits tends to oppose the electrons of the positive charged tested substance with a magnitude of coulomb’s force but there’s also an attraction force between pith ball atom’s electrons and the extra positive charge atom of tested substance with a force, and this attraction force is greater than the repelling force between the atom electrons of two bodies and hence this cause attractive force between pith ball and tested substance.
Note:In the year $1754$ , physicist John canton invented the pith ball electroscope. It should be remember that if a tested substance had a negative charge on it then due to larger repulsion force between electrons of pith ball atoms and tested substance atoms, the pith ball will tends to move away from the tested substance, but in both case that main purpose of pith ball telescope was to detect the presence of charge on a body.
Complete answer:
A pith ball electroscope consists of two very small sized non-conductor lightweight balls, initially in place of nonconductive balls a spongy plant material was used which was called pith; these lightweight balls are suspended by either a silk or linen thread.
When we have to examine a substance whether it has a charge on it or not, we bring the tested substance near the uncharged pith ball and according to coulomb’s law if this tested substance have a charge then it will tends to move towards the pith ball due to electrostatic force of attraction between two bodies of having charges opposite in sign.

This attraction between pith ball and tested substance is mainly due to polarisation. Let us suppose the tested substance had a positive charge on it and when it bring closer to the uncharged pith ball then electrons of the pith ball atoms in outermost orbits tends to oppose the electrons of the positive charged tested substance with a magnitude of coulomb’s force but there’s also an attraction force between pith ball atom’s electrons and the extra positive charge atom of tested substance with a force, and this attraction force is greater than the repelling force between the atom electrons of two bodies and hence this cause attractive force between pith ball and tested substance.
Note:In the year $1754$ , physicist John canton invented the pith ball electroscope. It should be remember that if a tested substance had a negative charge on it then due to larger repulsion force between electrons of pith ball atoms and tested substance atoms, the pith ball will tends to move away from the tested substance, but in both case that main purpose of pith ball telescope was to detect the presence of charge on a body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




