
Derive Lens maker formula \[\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {n - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)\]. The lower half of the concave mirror reflecting surface is covered with an opaque material. What will be the effect on the image formed by the mirror?
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: Consider a thin lens for the experiment. Consider the curvature radii and the corresponding refractive indices. Use the formula,
\[\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}\]and \[\mu = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}\].
Complete step by step solution:
Lens manufacturers utilize formula from the lens supplier to create lenses with the desired focal length. The equation of the lens maker is another formula used for lenses which gives us a relation between the focal length, refractive index, and curvature radii of the two spheres used in lenses.
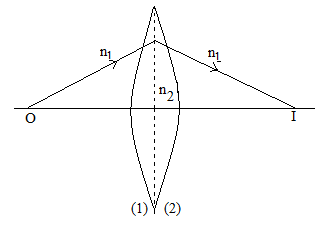
The following steps were followed in order to obtain formula for lens creator:
Let us consider the thin lens seen in the above picture with two refracting surfaces having the \[{R_1}\] and \[{R_2}\] curvature radii, respectively.
Let \[{n_1}\] and \[{n_2}\] be the refractive indices of the surrounding medium and the lens material respectively.
In case of the first surface,
\[\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{v_1}}} - \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{n_2} - {n_1}}}{{{R_1}}}\] …… (i)
In case of the second surface,
\[\dfrac{{{n_1}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{v_1}}} = \dfrac{{{n_1} - {n_2}}}{{{R_2}}}\] …… (ii)
Now, add equations (i) and (ii)
\[
\dfrac{{{n_1}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{u} = \left( {{n_2} - {n_1}} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right] \\
\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \left( {\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} - 1} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right] \\
\] …… (iv)
Let us consider, \[u = \propto \] and \[v = f\]
Now place the values of \[u\] and \[v\] in equation (iv),
\[\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} - 1} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right]\]
Rewrite the above equation as
\[\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right]\]
Where \[\mu \] is the refractive index of the material and is equal to \[\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}\]
This above equation is known as the Lens Maker formula.
Let us presume that all events on the concave mirror are parallel streams of light rays. Actually, as the lower half of the mirror is shielded, not all light rays will bounce back from its surface and meet at the focal point (which, by the way, often changes slightly), as they usually would. This would decrease the strength of the image created, and the image formed.
Note: For the experiment a thin lens is considered. Refractive index of the right side medium is \[{n_1}\] and the left side medium is \[{n_2}\]. The formula for refractive index is \[\mu = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}\]. Use the formula \[\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}\].
\[\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}\]and \[\mu = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}\].
Complete step by step solution:
Lens manufacturers utilize formula from the lens supplier to create lenses with the desired focal length. The equation of the lens maker is another formula used for lenses which gives us a relation between the focal length, refractive index, and curvature radii of the two spheres used in lenses.

The following steps were followed in order to obtain formula for lens creator:
Let us consider the thin lens seen in the above picture with two refracting surfaces having the \[{R_1}\] and \[{R_2}\] curvature radii, respectively.
Let \[{n_1}\] and \[{n_2}\] be the refractive indices of the surrounding medium and the lens material respectively.
In case of the first surface,
\[\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{v_1}}} - \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{n_2} - {n_1}}}{{{R_1}}}\] …… (i)
In case of the second surface,
\[\dfrac{{{n_1}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{v_1}}} = \dfrac{{{n_1} - {n_2}}}{{{R_2}}}\] …… (ii)
Now, add equations (i) and (ii)
\[
\dfrac{{{n_1}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{u} = \left( {{n_2} - {n_1}} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right] \\
\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \left( {\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} - 1} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right] \\
\] …… (iv)
Let us consider, \[u = \propto \] and \[v = f\]
Now place the values of \[u\] and \[v\] in equation (iv),
\[\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} - 1} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right]\]
Rewrite the above equation as
\[\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right]\]
Where \[\mu \] is the refractive index of the material and is equal to \[\dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}\]
This above equation is known as the Lens Maker formula.
Let us presume that all events on the concave mirror are parallel streams of light rays. Actually, as the lower half of the mirror is shielded, not all light rays will bounce back from its surface and meet at the focal point (which, by the way, often changes slightly), as they usually would. This would decrease the strength of the image created, and the image formed.
Note: For the experiment a thin lens is considered. Refractive index of the right side medium is \[{n_1}\] and the left side medium is \[{n_2}\]. The formula for refractive index is \[\mu = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}\]. Use the formula \[\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




