
Construct the following quadrilateral:
Quadrilateral \[MORE\] : \[MO = 6\] cm, \[OR = 4.5\] cm, \[\angle M = 60^\circ \], \[\angle O = 105^\circ \], and \[\angle R = 105^\circ \]
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: Here, we need to construct a quadrilateral with the given dimensions. First, we will draw a side whose length is given. Then, from an end of the line segment, we will draw the angle given using ruler and compasses. Then, we will draw the side through the angle, touching the end vertex of the first side, and cut off the length given using compasses. Finally, we would draw the remaining two given angles from the ends of the two line segments. The lines drawn through the angles (connecting the end vertices of the side drawn from) will intersect in the final vertex and hence, give us the required quadrilateral.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We will write down the step by step process of constructing the quadrilateral.
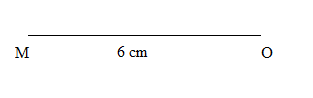
1) First, we will draw a line segment \[MO = 6\] cm.
2) From the end vertex \[O\], we will draw the angle \[\angle O = 105^\circ \] using ruler and compasses. We will draw a line \[l\] starting from \[O\] and making an angle \[\angle O = 105^\circ \] with \[MO\].
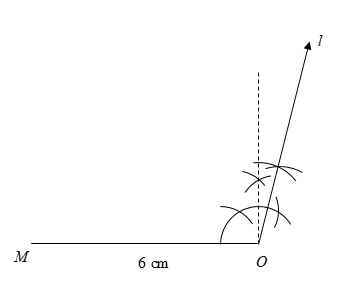
3) It is given that \[OR = 4.5\] cm. Therefore, using a ruler, we will open the compasses to measure \[4.5\] cm. Then, by placing the needle of the compasses on \[O\], we will mark the point on the line \[l\] which is \[4.5\]cm away from the vertex.
This point is the vertex \[R\] where \[OR = 4.5\] cm.
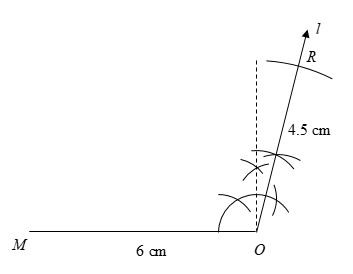
4) From the vertex \[M\], we will draw the angle \[\angle M = 60^\circ \] using ruler and compasses. We will draw a line \[m\] starting from \[M\] and making an angle \[\angle M = 60^\circ \] with \[MO\].

5) From the end vertex \[R\], we will draw the angle \[\angle R = 105^\circ \] using ruler and compasses. We will draw a line \[n\] starting from \[R\] and making an angle \[\angle R = 105^\circ \] with \[MO\].
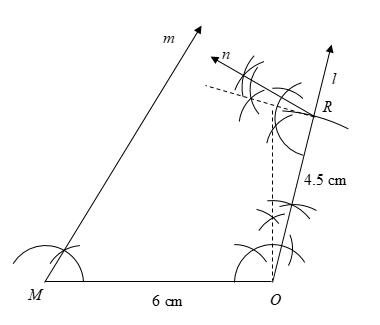
6) Finally, we will extend the lines \[m\] and \[n\] till they intersect at a point.
This point is the vertex \[E\] of the quadrilateral.
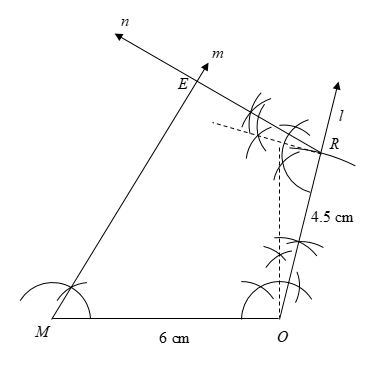
Hence, we have constructed the quadrilateral \[MORE\].
Note: We constructed angles of \[60^\circ \] and \[105^\circ \] using ruler and compasses.
Here are the steps to construct the angle of \[60^\circ \]
1) Taking vertex M of the line segment MO as the centre and any radius, we will draw a circle. This circle intersects the line segment at one point.
2) From the point, keeping the same radius, we will cut an arc in the circumference of the drawn circle.
3) We will now mark the above point as point P.
4) We will join M and P, and/or extend MP.
5) The angle \[\angle PMO\] will measure \[60^\circ \].
Here are the steps to construct the angle of \[105^\circ \]
1) Taking vertex O of the line segment MO as the centre and any radius, we will draw a circle. This circle intersects the line segment at one point.
2) From the point, keeping the same radius, we will cut an arc in the circumference of the drawn circle.
3) Now, we will mark the above point as point P.
4) From P, keeping the same radius, we will cut another arc in the circumference of the drawn circle.
5) We will mark this point as Q.
6) Now, taking point P as vertex, and any radius, we will again draw an arc above and between points P and Q. Similarly, taking point Q as vertex, and keeping the same radius, we will draw an arc intersecting the above arc.
7) We will now join the intersection point and point O and will mark the point where this line intersects the drawn circle as point X.
The angle \[\angle XOM\] measures \[90^\circ \]. We bisected the angles of \[60^\circ \] and \[120^\circ \] to construct it.
8) Now, taking point Q as vertex, and any radius, we will draw an arc above and between points X and Q. Similarly, taking point X as vertex, and keeping the same radius, we will again draw an arc intersecting the above arc.
9) We will join the intersection point and point O and mark the point where this line intersects the drawn circle as point R.
10) The angle \[\angle ROM\] will measure \[105^\circ \]. We bisected the angles of \[90^\circ \] and \[120^\circ \] to construct it.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We will write down the step by step process of constructing the quadrilateral.
1) First, we will draw a line segment \[MO = 6\] cm.

2) From the end vertex \[O\], we will draw the angle \[\angle O = 105^\circ \] using ruler and compasses. We will draw a line \[l\] starting from \[O\] and making an angle \[\angle O = 105^\circ \] with \[MO\].

3) It is given that \[OR = 4.5\] cm. Therefore, using a ruler, we will open the compasses to measure \[4.5\] cm. Then, by placing the needle of the compasses on \[O\], we will mark the point on the line \[l\] which is \[4.5\]cm away from the vertex.
This point is the vertex \[R\] where \[OR = 4.5\] cm.

4) From the vertex \[M\], we will draw the angle \[\angle M = 60^\circ \] using ruler and compasses. We will draw a line \[m\] starting from \[M\] and making an angle \[\angle M = 60^\circ \] with \[MO\].

5) From the end vertex \[R\], we will draw the angle \[\angle R = 105^\circ \] using ruler and compasses. We will draw a line \[n\] starting from \[R\] and making an angle \[\angle R = 105^\circ \] with \[MO\].

6) Finally, we will extend the lines \[m\] and \[n\] till they intersect at a point.
This point is the vertex \[E\] of the quadrilateral.

Hence, we have constructed the quadrilateral \[MORE\].
Note: We constructed angles of \[60^\circ \] and \[105^\circ \] using ruler and compasses.
Here are the steps to construct the angle of \[60^\circ \]
1) Taking vertex M of the line segment MO as the centre and any radius, we will draw a circle. This circle intersects the line segment at one point.
2) From the point, keeping the same radius, we will cut an arc in the circumference of the drawn circle.
3) We will now mark the above point as point P.
4) We will join M and P, and/or extend MP.
5) The angle \[\angle PMO\] will measure \[60^\circ \].
Here are the steps to construct the angle of \[105^\circ \]
1) Taking vertex O of the line segment MO as the centre and any radius, we will draw a circle. This circle intersects the line segment at one point.
2) From the point, keeping the same radius, we will cut an arc in the circumference of the drawn circle.
3) Now, we will mark the above point as point P.
4) From P, keeping the same radius, we will cut another arc in the circumference of the drawn circle.
5) We will mark this point as Q.
6) Now, taking point P as vertex, and any radius, we will again draw an arc above and between points P and Q. Similarly, taking point Q as vertex, and keeping the same radius, we will draw an arc intersecting the above arc.
7) We will now join the intersection point and point O and will mark the point where this line intersects the drawn circle as point X.
The angle \[\angle XOM\] measures \[90^\circ \]. We bisected the angles of \[60^\circ \] and \[120^\circ \] to construct it.
8) Now, taking point Q as vertex, and any radius, we will draw an arc above and between points X and Q. Similarly, taking point X as vertex, and keeping the same radius, we will again draw an arc intersecting the above arc.
9) We will join the intersection point and point O and mark the point where this line intersects the drawn circle as point R.
10) The angle \[\angle ROM\] will measure \[105^\circ \]. We bisected the angles of \[90^\circ \] and \[120^\circ \] to construct it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





