
How will you compare the emfs of two cells using a potentiometer?
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: The emf of two cells can be compared using a potentiometer either by connecting one cell at a time or both cells at a time. You can use the two-way key to connect one cell at a time in a circuit. Obtain the balancing length for each cell separately by placing the jockey on potentiometer wire such that the ammeter shows zero or null deflection. By taking the ratio of both balancing lengths you can compare emfs of two cells.
Formula used:
\[\dfrac{{{E}_{1}}}{{{E}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{l}_{1}}}{{{l}_{2}}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \text{where, }{{\text{l}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ is balancing length for cell having e}\text{.m}\text{.f}\text{. }{{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ and} \\
& \text{ }{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ is balancing length of cell having e}\text{.m}\text{.f}\text{. }{{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}. \\
\end{align}\]
Complete answer:
Comparison of e.m.f. of the two cells by using a potentiometer can be done by two methods:
1. Individual cell method.
2. Sum and difference method.
The individual cell method is described below.
Make connections as per the following circuit diagram.
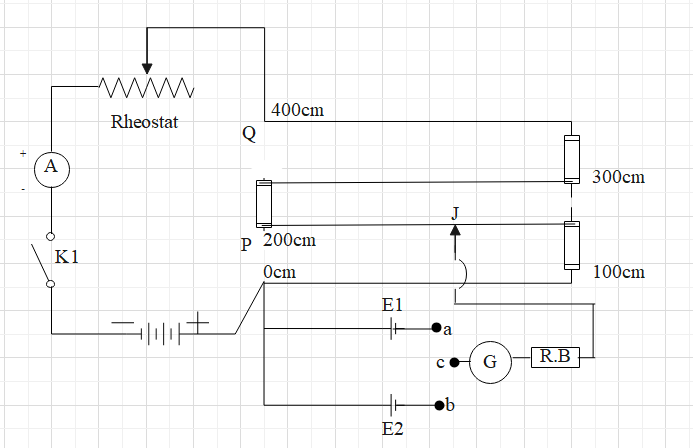
A potentiometer circuit is set up by connecting a battery B, with a key K1 and a rheostat such that point P is at a higher potential than point Q. The cells whose emfs ${{E}_{1}}$ and ${{E}_{2}}$are to be compared are connected with their positive terminals at point P and negative terminals to the extreme terminals of a two way key at a and b. The central terminal c of the two way key is connected to a galvanometer. The other end of the galvanometer is connected to a jockey (J). Key K1 is closed and then, terminal c is tapped towards terminal a and terminal b is kept open. Therefore, the cell of emfs ${{E}_{1}}$ comes into the circuit. The null point is obtained by touching the jockey at various points on the potentiometer wire PQ. Let \[{{l}_{1}}\] be the length of the wire between the null point and the point P. \[{{l}_{1}}\] corresponds to emfs ${{E}_{1}}$of the cell. Therefore,
${{E}_{1}}=x{{l}_{1}}$
where $x$ is the potential gradient along the potentiometer wire.
Now, terminal c is tapped towards terminal b and terminal a is kept open. The cell of emfs ${{E}_{2}}$now comes in the circuit. Again, the null point is obtained with the help of the Jockey. Let \[{{l}_{2}}\] be the length of the wire between the null point and point P. This length corresponds to the emfs ${{E}_{2}}$of the cell. Therefore,
${{E}_{2}}=x{{l}_{2}}$
From the above two equations, we get
\[\dfrac{{{E}_{1}}}{{{E}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{l}_{1}}}{{{l}_{2}}}\]
Thus, we can compare the emfs of the two cells. If anyone of the emfs is known, the other can be determined.
Note:
The Potentiometer is one such device that does not draw any current from the circuit and it acts as an ideal voltmeter. It is generally used to determine e.m.f.s of the unknown cell, compare the e.m.f of two cells and to determine the internal resistance of a cell. Do not slide the jockey over the potentiometer wire.
Formula used:
\[\dfrac{{{E}_{1}}}{{{E}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{l}_{1}}}{{{l}_{2}}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \text{where, }{{\text{l}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ is balancing length for cell having e}\text{.m}\text{.f}\text{. }{{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ and} \\
& \text{ }{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ is balancing length of cell having e}\text{.m}\text{.f}\text{. }{{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}. \\
\end{align}\]
Complete answer:
Comparison of e.m.f. of the two cells by using a potentiometer can be done by two methods:
1. Individual cell method.
2. Sum and difference method.
The individual cell method is described below.
Make connections as per the following circuit diagram.

A potentiometer circuit is set up by connecting a battery B, with a key K1 and a rheostat such that point P is at a higher potential than point Q. The cells whose emfs ${{E}_{1}}$ and ${{E}_{2}}$are to be compared are connected with their positive terminals at point P and negative terminals to the extreme terminals of a two way key at a and b. The central terminal c of the two way key is connected to a galvanometer. The other end of the galvanometer is connected to a jockey (J). Key K1 is closed and then, terminal c is tapped towards terminal a and terminal b is kept open. Therefore, the cell of emfs ${{E}_{1}}$ comes into the circuit. The null point is obtained by touching the jockey at various points on the potentiometer wire PQ. Let \[{{l}_{1}}\] be the length of the wire between the null point and the point P. \[{{l}_{1}}\] corresponds to emfs ${{E}_{1}}$of the cell. Therefore,
${{E}_{1}}=x{{l}_{1}}$
where $x$ is the potential gradient along the potentiometer wire.
Now, terminal c is tapped towards terminal b and terminal a is kept open. The cell of emfs ${{E}_{2}}$now comes in the circuit. Again, the null point is obtained with the help of the Jockey. Let \[{{l}_{2}}\] be the length of the wire between the null point and point P. This length corresponds to the emfs ${{E}_{2}}$of the cell. Therefore,
${{E}_{2}}=x{{l}_{2}}$
From the above two equations, we get
\[\dfrac{{{E}_{1}}}{{{E}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{l}_{1}}}{{{l}_{2}}}\]
Thus, we can compare the emfs of the two cells. If anyone of the emfs is known, the other can be determined.
Note:
The Potentiometer is one such device that does not draw any current from the circuit and it acts as an ideal voltmeter. It is generally used to determine e.m.f.s of the unknown cell, compare the e.m.f of two cells and to determine the internal resistance of a cell. Do not slide the jockey over the potentiometer wire.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




