
What are the primary rainbow and secondary rainbow?
Answer
492.6k+ views
Hint:The sunlight that falls on the water droplet gets reflected and disintegrates into the constituent colors. These refracted rays are reflected inside the droplet and go through another refraction before it reaches our eyes. These refracted rays form the primary and secondary rainbow.
Complete answer:
Rainbow:Rainbows will form from the refraction of sunlight in falling water droplets plus reflection of the light from the back of the droplet.
Primary rainbow: Primary rainbow forms between about $40^\circ $ and $42^\circ $ from the antisolar point. This light path involves refraction and single reflection inside the water droplets. And if the drops through which the light passes are large thet is $1$ millimeter or more in diameter then the red red, green and violet are bright but there is little blue. Hence such large water droplets are suggested by the rainbow at right. But as the droplets get smaller than its usual size then the red becomes weak and in fine mist, all colors except violet may disappear.
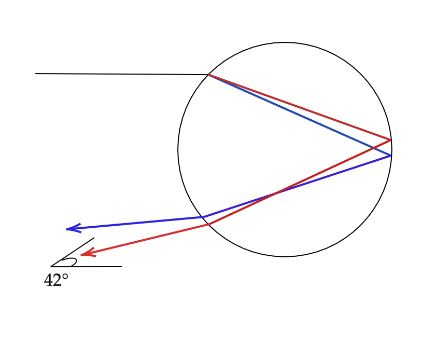
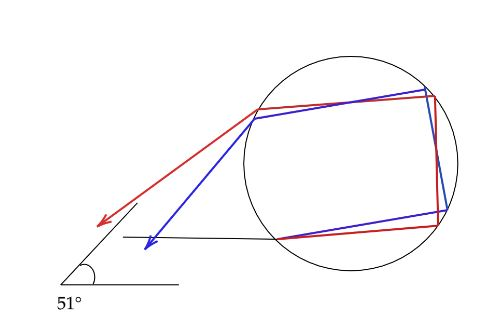
Secondary rainbow:Secondary rainbow is about $10^\circ $ further out from the antisolar point than the primary bow, is about twice as wide, and has its colors reversed. This rainbow involves two reflections inside the falling droplets. It appears outside of the primary rainbow and it develops when light entering the water droplets undergoes two internal reflections and there the color scheme is just opposite of the primary rainbow. The secondary rainbow is different from that of the primary rainbow.
Note:Remember that it is not possible to see the complete rainbow from the ground, you can see a complete rainbow from an aeroplane. It is impossible to see the rainbow in the afternoon if you are facing aways from the sun. Also not that the angle $42^\circ $ is below the horizon most of the time.
Complete answer:
Rainbow:Rainbows will form from the refraction of sunlight in falling water droplets plus reflection of the light from the back of the droplet.
Primary rainbow: Primary rainbow forms between about $40^\circ $ and $42^\circ $ from the antisolar point. This light path involves refraction and single reflection inside the water droplets. And if the drops through which the light passes are large thet is $1$ millimeter or more in diameter then the red red, green and violet are bright but there is little blue. Hence such large water droplets are suggested by the rainbow at right. But as the droplets get smaller than its usual size then the red becomes weak and in fine mist, all colors except violet may disappear.

Secondary rainbow:Secondary rainbow is about $10^\circ $ further out from the antisolar point than the primary bow, is about twice as wide, and has its colors reversed. This rainbow involves two reflections inside the falling droplets. It appears outside of the primary rainbow and it develops when light entering the water droplets undergoes two internal reflections and there the color scheme is just opposite of the primary rainbow. The secondary rainbow is different from that of the primary rainbow.

Note:Remember that it is not possible to see the complete rainbow from the ground, you can see a complete rainbow from an aeroplane. It is impossible to see the rainbow in the afternoon if you are facing aways from the sun. Also not that the angle $42^\circ $ is below the horizon most of the time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




