
What are the main types of electromagnetic radiation in order of increasing energy?
Answer
517.8k+ views
Hint : We know that by arranging them in order of the increasing order of frequency of radiation and decreasing order of wavelength. Results observed that the interactions of radiations with the matter have provided more information regarding the structure of atoms and molecules. From these results, Neils Bohr improved a model which was proposed by Rutherford. Two major developments by Bohr’s model of an atom.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Before knowing what are the main types of electromagnetic radiations and what is its increasing order of energy, let us know what is electromagnetic radiation so electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that is all around us and takes many forms such as radio waves, microwaves, X-rays and gamma rays, sunlight is also a form of electromagnetic energy but visible light is only a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum which contains a broad range of electromagnetic wave lengths. Electromagnetic radiations have two components which are electric field and magnetic field and both are perpendicular to each other and these two fields are perpendicular to the path of propagation so let us take a look at the electromagnetic spectrum.
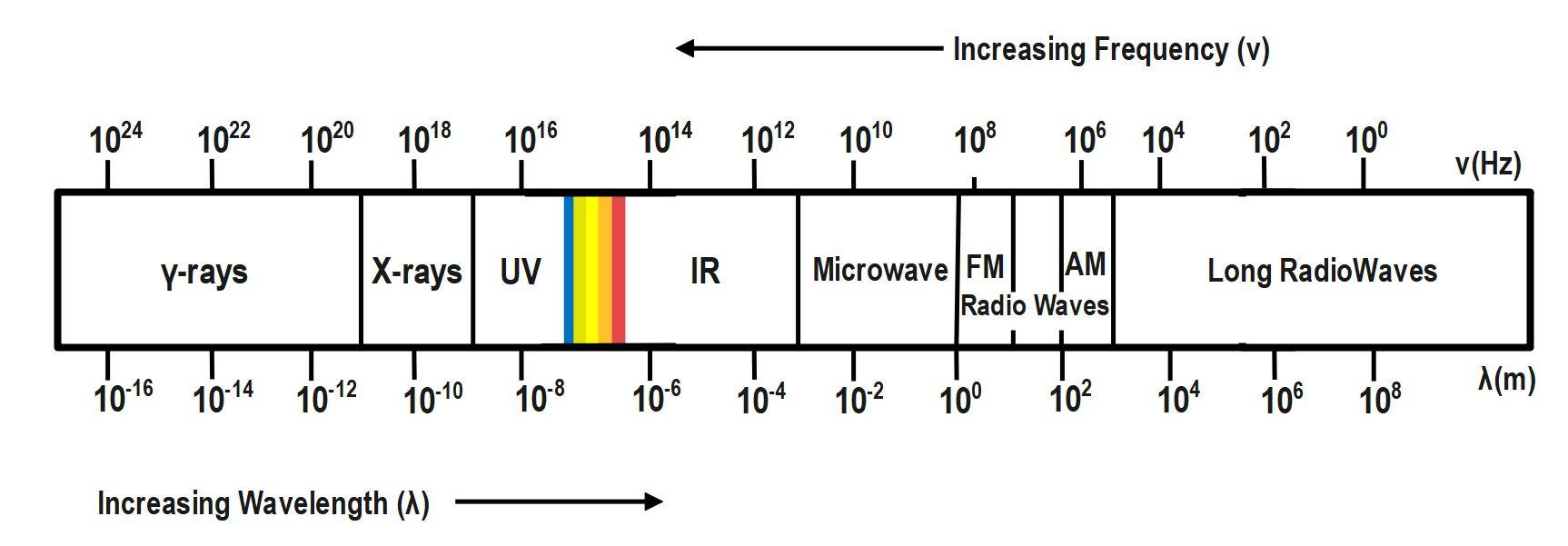
Now here it is the whole electromagnetic spectrum and we can see that in right most side it is radio waves which has the minimum energy in the electromagnetic spectrum as its frequency is very less and its wavelength is very high after that it comes microwaves and after that infrared then visible and after ultraviolet then X rays and gamma rays in electromagnetic spectrum Gamma rays has the maximum energy and the radio waves has the minimum energy as the energy of radiation is directly proportional to its frequency and inversely proportional to its wavelength so the order of increasing energy will be like this:
$ Radio\text{ waves Microwaves Infrared visible Ultraviolet X-rays Gamma rays} $ .
Note :
Remember that especially in spectroscopy, a commonly used quantity is the wave number. This is defined as the number of wavelengths per unit length. Its unit is the reciprocal of the wavelength unit. Small waves of different kinds in electromagnetic radiation have smaller wavelengths and smaller units.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Before knowing what are the main types of electromagnetic radiations and what is its increasing order of energy, let us know what is electromagnetic radiation so electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that is all around us and takes many forms such as radio waves, microwaves, X-rays and gamma rays, sunlight is also a form of electromagnetic energy but visible light is only a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum which contains a broad range of electromagnetic wave lengths. Electromagnetic radiations have two components which are electric field and magnetic field and both are perpendicular to each other and these two fields are perpendicular to the path of propagation so let us take a look at the electromagnetic spectrum.

Now here it is the whole electromagnetic spectrum and we can see that in right most side it is radio waves which has the minimum energy in the electromagnetic spectrum as its frequency is very less and its wavelength is very high after that it comes microwaves and after that infrared then visible and after ultraviolet then X rays and gamma rays in electromagnetic spectrum Gamma rays has the maximum energy and the radio waves has the minimum energy as the energy of radiation is directly proportional to its frequency and inversely proportional to its wavelength so the order of increasing energy will be like this:
$ Radio\text{ waves Microwaves Infrared visible Ultraviolet X-rays Gamma rays} $ .
Note :
Remember that especially in spectroscopy, a commonly used quantity is the wave number. This is defined as the number of wavelengths per unit length. Its unit is the reciprocal of the wavelength unit. Small waves of different kinds in electromagnetic radiation have smaller wavelengths and smaller units.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




