
What are Schottky defects and frenkel defects?
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:We call a defect as a shortcoming or imperfections in a solid. Solid crystals have some types of defects. Schottky defect and frenkel defect are the two types of defects. Let us discuss them in detail.
Complete step by step answer:
Now we discuss about the details of schottky defect as,
Schottky Defect:
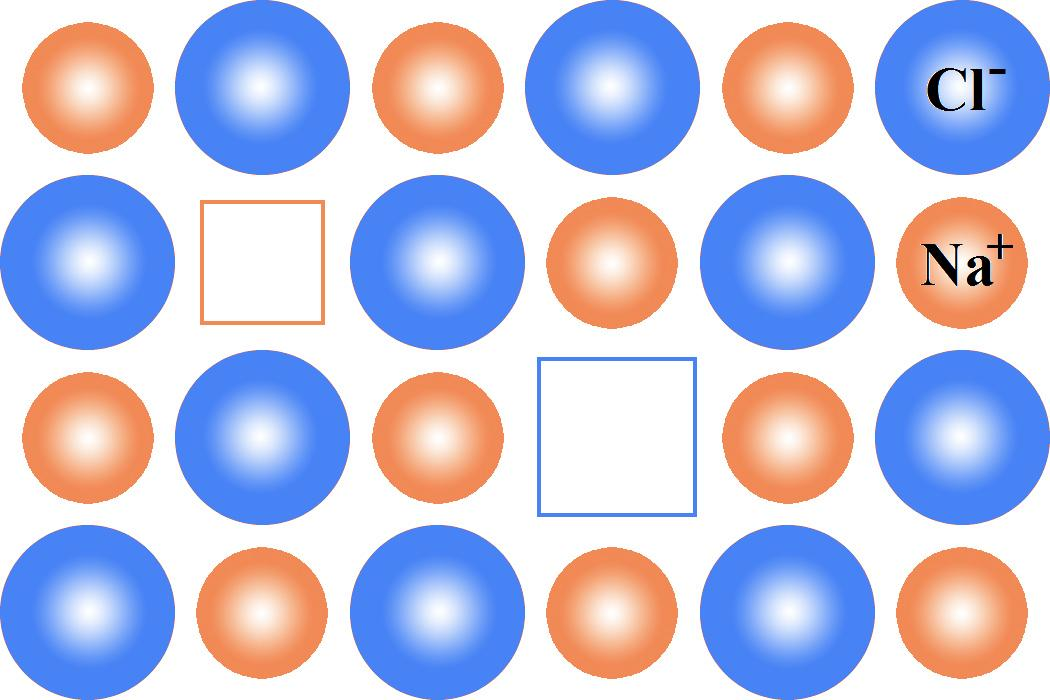
We must remember that the schottky defect occurs when some of the lattice points are unoccupied. The points that are unoccupied are known as lattice vacancies. The number of misplaced positive and negative ions is equal in this case and thus the crystal remains neutral. The existence of two vacancies, one due to a missing sodium ion and the other due to a missing chloride ion in a crystal of sodium, chloride. It appears in ionic crystals in which positive and negative ions do not vary much in size. The below diagram clearly explains how schottky defect takes place,
Now we discuss about the details of frenkel defects as,
Frenkel Defects:
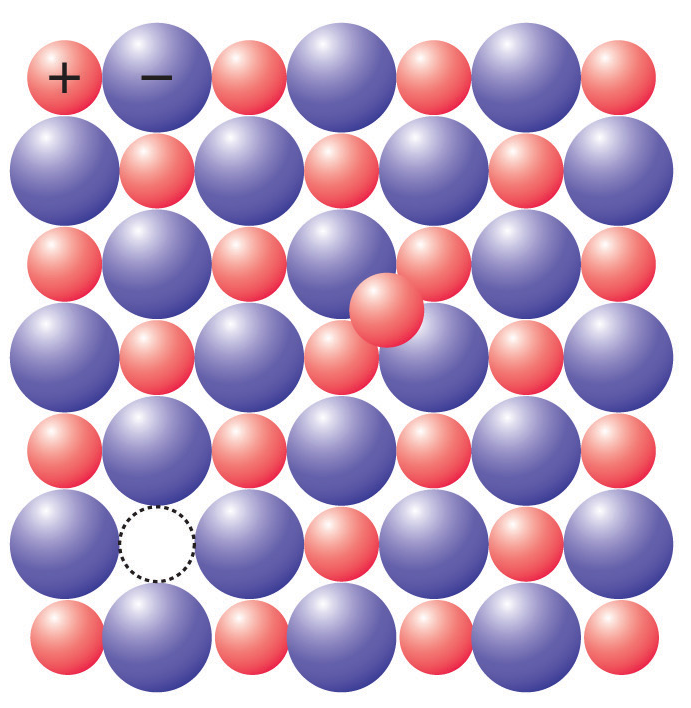
We must know that the frenkel defect arises if an ion occupies an interstitial place among the lattice points. This defect is usually noticed in ionic crystals in which the anions are larger in size than the cation. Silver bromide is an example for this type of defect. One of the silver ions occupies a position in the interstitial gap rather than its own suitable place in the lattice. The crystal remains neutral as the number of positive ions is the same as the number of negative ions. The given diagram clearly explains how frenkel defects takes place,
Note:
Schottky defect may be a sort of point defect in solids which is caused by a vacant position that's generated during a space lattice because the atoms or ions are displaced from the surface of the crystal. A Frenkel defect is another sort of some extent defect which is made when an atom or cation leaves its original place within the lattice structure to make a vacancy as occupying another interstitial place within the solid crystal.
Complete step by step answer:
Now we discuss about the details of schottky defect as,
Schottky Defect:
We must remember that the schottky defect occurs when some of the lattice points are unoccupied. The points that are unoccupied are known as lattice vacancies. The number of misplaced positive and negative ions is equal in this case and thus the crystal remains neutral. The existence of two vacancies, one due to a missing sodium ion and the other due to a missing chloride ion in a crystal of sodium, chloride. It appears in ionic crystals in which positive and negative ions do not vary much in size. The below diagram clearly explains how schottky defect takes place,

Now we discuss about the details of frenkel defects as,
Frenkel Defects:
We must know that the frenkel defect arises if an ion occupies an interstitial place among the lattice points. This defect is usually noticed in ionic crystals in which the anions are larger in size than the cation. Silver bromide is an example for this type of defect. One of the silver ions occupies a position in the interstitial gap rather than its own suitable place in the lattice. The crystal remains neutral as the number of positive ions is the same as the number of negative ions. The given diagram clearly explains how frenkel defects takes place,

Note:
Schottky defect may be a sort of point defect in solids which is caused by a vacant position that's generated during a space lattice because the atoms or ions are displaced from the surface of the crystal. A Frenkel defect is another sort of some extent defect which is made when an atom or cation leaves its original place within the lattice structure to make a vacancy as occupying another interstitial place within the solid crystal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




