
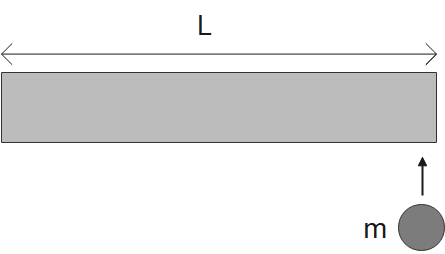
A Stick of length L and mass M lies on a frictionless horizontal surface on which it is free to move in any way. A ball of mass m moving with speed v collides elastically with the stick as shown in figure, If after the collision ball comes to rest, then what should be the mass of the ball?
a.) m = 2M
b.) m = M
c.) $m=\dfrac{M}{2}$
d.) $m=\dfrac{M}{4}$

Answer
542.7k+ views
Hint: In this question,given that the stick is at rest and the ball hits the stick and after the Collision ball comes to rest this means that he whole momentum of ball is transferred to the stick and it is also given that the Collision is elastic this means there is no energy loss in the Collison
Complete answer:
Since it is given in the question that the stick is free to move in any direction, so this means that stick will have to follow both conservation of angular momentum as well as conservation of linear momentum
Let’s first start by applying conservation of Linear momentum
So according to conservation of linear momentum
MV = mv
Or $V=\dfrac{mv}{V}$ ……….. (1)
Where “M” is the mass of the stick and “V” is the velocity if the stick
“m” is the mass of the ball and “v” is the velocity of the ball
Now apply law of conservation of angular momentum
$mv(\dfrac{L}{2})=(\dfrac{M{{L}^{2}}}{12})\omega $
On solving we get,
$\omega =\dfrac{6mv}{ML}$ ………. (2)
Now since it is given that the Collision is elastic and we know that initially the kinetic energy of stick was zero as it is given that initially the stick was at rest so this means we will have only kinetic energy of ball at initial stage, so we can write as
$0+\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}M{{V}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}}$
Now putting the values of from equation (1) and (2) we get
$m=\dfrac{M}{4}$
This means that the mass of stick is four times at that of mass of ball
So, we can say that option (d) is the correct answer .
Note:
In the above question we have to find the mass of the ball and since the stick was at rest then this means that the conservation of momentum will be followed. We need to make sure that we remember the equation for conservation of momentum as this is used very widely in physics.
Complete answer:
Since it is given in the question that the stick is free to move in any direction, so this means that stick will have to follow both conservation of angular momentum as well as conservation of linear momentum
Let’s first start by applying conservation of Linear momentum
So according to conservation of linear momentum
MV = mv
Or $V=\dfrac{mv}{V}$ ……….. (1)
Where “M” is the mass of the stick and “V” is the velocity if the stick
“m” is the mass of the ball and “v” is the velocity of the ball
Now apply law of conservation of angular momentum
$mv(\dfrac{L}{2})=(\dfrac{M{{L}^{2}}}{12})\omega $
On solving we get,
$\omega =\dfrac{6mv}{ML}$ ………. (2)
Now since it is given that the Collision is elastic and we know that initially the kinetic energy of stick was zero as it is given that initially the stick was at rest so this means we will have only kinetic energy of ball at initial stage, so we can write as
$0+\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}M{{V}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}}$
Now putting the values of from equation (1) and (2) we get
$m=\dfrac{M}{4}$
This means that the mass of stick is four times at that of mass of ball
So, we can say that option (d) is the correct answer .
Note:
In the above question we have to find the mass of the ball and since the stick was at rest then this means that the conservation of momentum will be followed. We need to make sure that we remember the equation for conservation of momentum as this is used very widely in physics.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




