
A small electric dipole is of dipole moment p. The electric potential at a distance ‘r’ from the center and making an angle $ \theta $ with the axis of dipole will be:
Answer
515.7k+ views
Hint: Electric dipole is a couple of opposite charges given by q and -q. they are separated by the distance d. In this given space the direction of the dipole is always from -q to positive charge q. In the question we need to find potential at distance r from center. It is making an angle $ \theta $ with the axis.
Formula Used:
$
V = \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} \\
\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{y^2} + {z^2} - {x^2}}}{{2yz}} \\
(1 + {x^n}) = 1 + nx\,for\,x < < 1 \\
$
Complete step-by-step solution:
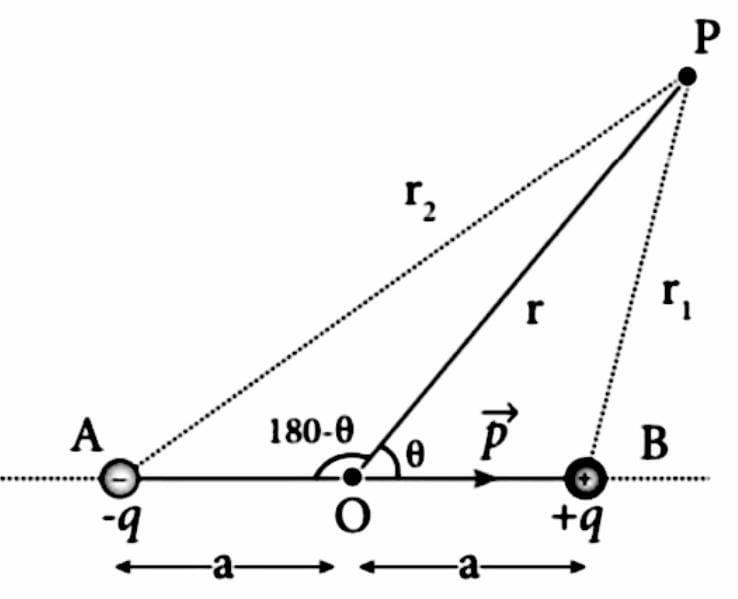
First of all we have the dipole with charges q and -q at the ends.
The potential at the distance ‘r’ can be found out as follows:
First from the figure we will get,
\[
USING, \\
\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{y^2} + {z^2} - {x^2}}}{{2yz}} \\
\]
Cosine formula for any triangle.
Here, z is hypotenuse.
According to our dimensions
$
\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{r^2} + {a^2} - {r_1}^2}}{{2ra}} \\
\Rightarrow {r_1}^2 = {r^2} + {a^2} - 2ra\cos \theta \\
$
By taking square root on both sides we get,
$
{r_1} = {({r^2} + {a^2} - 2ra\cos \theta )^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \\
taking\,'r'\,common \\
\Rightarrow {r_1} = r{\left[ {1 - \dfrac{a}{r}\cos \theta } \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \\
$
Now using the identity,
$ (1 + {x^n}) = 1 + nx\,for\,x < < 1$
We get,
$
{r_1} = r\left[ {1 - \dfrac{a}{r}\cos \theta } \right] \\
this\,gives \\
\Rightarrow {r_1} = r - a\cos \theta \\
\Rightarrow {r_2} = r + a\cos \theta \\
$
We know for the potential we need to find individual potentials from each charge and add them. So,
$
V = \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} \\
adding\,all \\
\Rightarrow V = \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}{r_1}}} + \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}{r_2}}} \\
\\
$
Putting the values taken found out above and solving,
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{r - a\cos \theta }} - \dfrac{1}{{r + a\cos \theta }}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\left[ {\dfrac{{r + a\cos \theta - r + a\cos \theta }}{{{r^2} - {a^2}{{\cos }^2}\theta }}} \right] \\
$
Further solving the equations and neglecting a as it is very small we get
$
As\,p = q(2a) \\
\Rightarrow V = \dfrac{{p\cos \theta }}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}({r^2} - {a^2}{{\cos }^2}\theta )}} \\
\Rightarrow V = \dfrac{{p\cos \theta }}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}({r^2})}}.....(if\,a\,is\,small) \\
$
Note: Potential at the point is always an addition of potential due to all charges/dipoles. Potential negative means whatever the system is under study it is stable. If potential is positive it is an unstable system. Force varies inversely with square of the distance and potential inversely with first power of distance.
Formula Used:
$
V = \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} \\
\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{y^2} + {z^2} - {x^2}}}{{2yz}} \\
(1 + {x^n}) = 1 + nx\,for\,x < < 1 \\
$
Complete step-by-step solution:

First of all we have the dipole with charges q and -q at the ends.
The potential at the distance ‘r’ can be found out as follows:
First from the figure we will get,
\[
USING, \\
\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{y^2} + {z^2} - {x^2}}}{{2yz}} \\
\]
Cosine formula for any triangle.
Here, z is hypotenuse.
According to our dimensions
$
\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{r^2} + {a^2} - {r_1}^2}}{{2ra}} \\
\Rightarrow {r_1}^2 = {r^2} + {a^2} - 2ra\cos \theta \\
$
By taking square root on both sides we get,
$
{r_1} = {({r^2} + {a^2} - 2ra\cos \theta )^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \\
taking\,'r'\,common \\
\Rightarrow {r_1} = r{\left[ {1 - \dfrac{a}{r}\cos \theta } \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \\
$
Now using the identity,
$ (1 + {x^n}) = 1 + nx\,for\,x < < 1$
We get,
$
{r_1} = r\left[ {1 - \dfrac{a}{r}\cos \theta } \right] \\
this\,gives \\
\Rightarrow {r_1} = r - a\cos \theta \\
\Rightarrow {r_2} = r + a\cos \theta \\
$
We know for the potential we need to find individual potentials from each charge and add them. So,
$
V = \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} \\
adding\,all \\
\Rightarrow V = \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}{r_1}}} + \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}{r_2}}} \\
\\
$
Putting the values taken found out above and solving,
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{r - a\cos \theta }} - \dfrac{1}{{r + a\cos \theta }}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\left[ {\dfrac{{r + a\cos \theta - r + a\cos \theta }}{{{r^2} - {a^2}{{\cos }^2}\theta }}} \right] \\
$
Further solving the equations and neglecting a as it is very small we get
$
As\,p = q(2a) \\
\Rightarrow V = \dfrac{{p\cos \theta }}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}({r^2} - {a^2}{{\cos }^2}\theta )}} \\
\Rightarrow V = \dfrac{{p\cos \theta }}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}({r^2})}}.....(if\,a\,is\,small) \\
$
Note: Potential at the point is always an addition of potential due to all charges/dipoles. Potential negative means whatever the system is under study it is stable. If potential is positive it is an unstable system. Force varies inversely with square of the distance and potential inversely with first power of distance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




