
What is a declination? Draw a diagram to show the angle between the declination and true direction of geographic north.
Answer
513.6k+ views
Hint: The angle between magnetic north and true north is described using both declination and variation. From time to time, the term deviation is also employed. This is the term that individuals who study the magnetic field prefer; it is also the one that land navigators use the most. The term "magnetic declination" is sometimes used.
Complete answer:
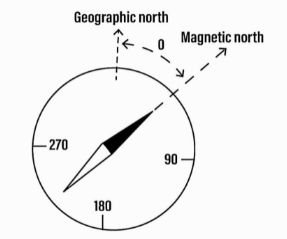
The angle of the horizontal plane between magnetic north and geographic north is known as magnetic declination. This angle is represented in the figure by a symbol. The angle of declination varies from place to location on the earth's surface, and it also changes with time. The declination is positive if the magnetic north is east of true north, as shown in the diagram, and negative if the magnetic north is west of true north, as shown in the diagram.
Additional Information:
-The declination is greater in higher latitudes than in equators because, the lines of the field close to the magnetic poles come out abruptly by the side of the Earth's axis, by protocol at the South magnetic pole, at a comparatively vertical angle to the polar edges, and curve round to enter again at the north magnetic pole.
-Halfway lines develop between the Earth's surface and the edge of the Earth at a lesser vertical angle after the Earth's surface has previously shifted the direction away from the axis.
Note:The declination angle can be calculated using the following equation\[\delta = 23.45^\circ cos\left( {\dfrac{{360}}{{365}}\left( {d + 10} \right)} \right)\], where \[d\] is the number of days since the year began. At the equinoxes (March 22 and September 22), the declination angle is zero, positive during the summer in the northern hemisphere, and negative during the winter in the northern hemisphere. The declination reaches a maximum angle of \[23.45^\circ \] on June 22 (the northern hemisphere summer solstice) and a minimum angle of \[ - 23.45^\circ \] on December 21-22 (the northern hemisphere winter solstice) (the northern hemisphere winter solstice).
Complete answer:
The angle of the horizontal plane between magnetic north and geographic north is known as magnetic declination. This angle is represented in the figure by a symbol. The angle of declination varies from place to location on the earth's surface, and it also changes with time. The declination is positive if the magnetic north is east of true north, as shown in the diagram, and negative if the magnetic north is west of true north, as shown in the diagram.

Additional Information:
-The declination is greater in higher latitudes than in equators because, the lines of the field close to the magnetic poles come out abruptly by the side of the Earth's axis, by protocol at the South magnetic pole, at a comparatively vertical angle to the polar edges, and curve round to enter again at the north magnetic pole.
-Halfway lines develop between the Earth's surface and the edge of the Earth at a lesser vertical angle after the Earth's surface has previously shifted the direction away from the axis.
Note:The declination angle can be calculated using the following equation\[\delta = 23.45^\circ cos\left( {\dfrac{{360}}{{365}}\left( {d + 10} \right)} \right)\], where \[d\] is the number of days since the year began. At the equinoxes (March 22 and September 22), the declination angle is zero, positive during the summer in the northern hemisphere, and negative during the winter in the northern hemisphere. The declination reaches a maximum angle of \[23.45^\circ \] on June 22 (the northern hemisphere summer solstice) and a minimum angle of \[ - 23.45^\circ \] on December 21-22 (the northern hemisphere winter solstice) (the northern hemisphere winter solstice).
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




