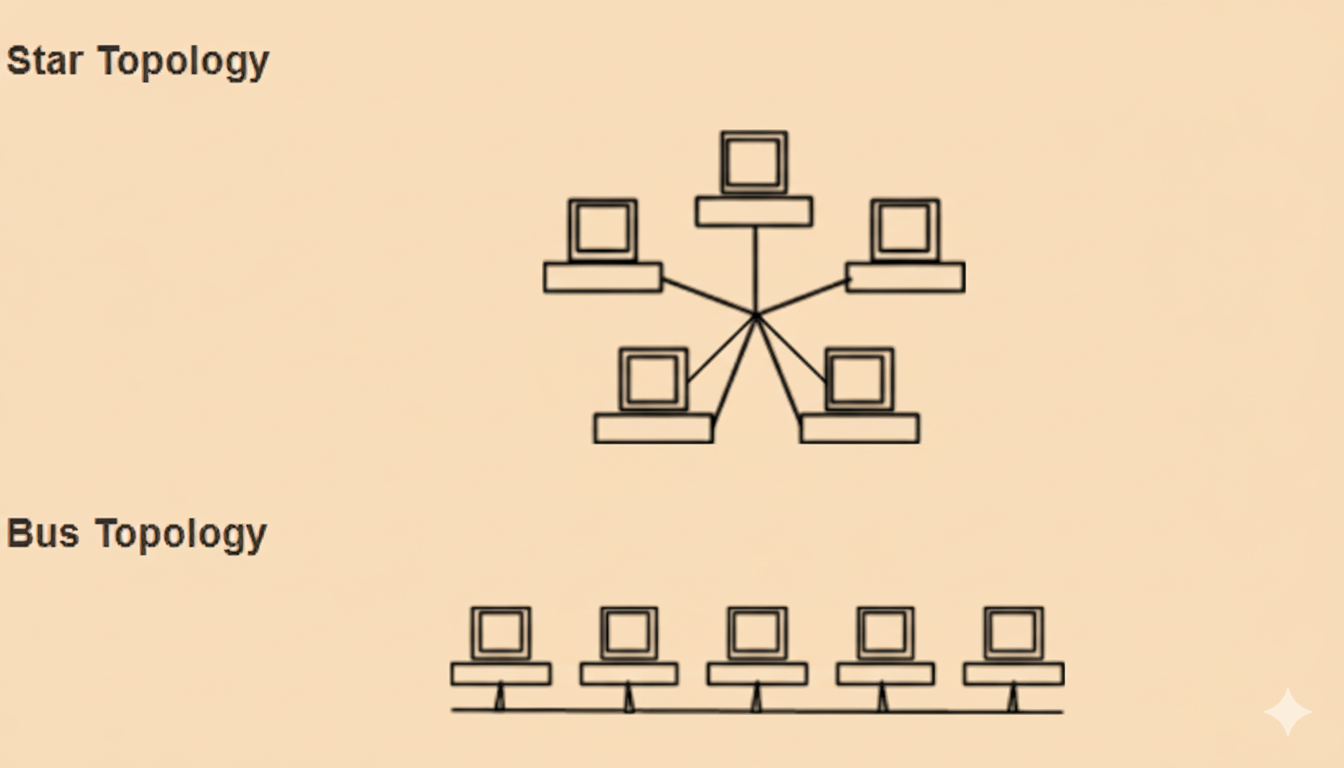
Stepwise Solutions and Exam Tips for Class 12 Computer Networks
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 10 Computer Networks - 2025-26
1. What are NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 10 Computer Networks?
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 10 Computer Networks provide detailed, stepwise answers to all textbook exercises following the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
- Covers all intext and back exercise questions with explanations
- Includes key definitions, diagrams, and examples
- Strictly designed as per CBSE marking scheme for full-score answers
- Available in downloadable PDF format for exam revision
2. How can I prepare Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 10 for board exams effectively?
To prepare Computer Networks for Class 12 CBSE board exams, follow a systematic approach:
- Study NCERT Solutions chapter-wise and highlight important definitions
- Practice drawing and labelling network diagrams
- Revise key differences and types of networks (LAN, MAN, WAN)
- Solve chapter-end exercise and exemplar questions
- Use revision planners and quick notes for last-minute prep
3. Are definitions, diagrams, and examples necessary in NCERT answers for Computer Networks?
Yes, including definitions, diagrams, and relevant examples is essential for scoring full marks in Computer Networks NCERT answers.
- Definitions clarify concepts and are often directly asked
- Diagrams demonstrate understanding of network structures and earn easy marks
- Examples help explain practical uses and differences between concepts
4. Where can I download the Computer Networks Class 12 NCERT Solutions PDF?
You can download the Class 12 Computer Networks NCERT Solutions PDF from trusted educational websites that follow the CBSE curriculum.
- Look for a single-click download option for offline study
- Ensure the solutions are updated as per the 2025–26 CBSE syllabus
- Most platforms provide PDFs for both intext and back exercises
5. What topics are most important in Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 10 Computer Networks?
The most important topics in Chapter 10 Computer Networks include:
- Types of networks (LAN, MAN, WAN, PAN)
- Network devices (switch, hub, router, modem)
- Transmission media (wired and wireless)
- Protocols and network topologies
- Data transfer techniques and security measures
6. How should I write long answers for better marks in Class 12 Computer Networks?
For long answers in Class 12 Computer Networks, structure your response clearly:
- Start with a short introduction or definition
- Use headings, subheadings, or bullet points for key points
- Include neat, labelled diagrams if relevant
- Explain using examples or case studies
- Conclude with a brief summary or significance
7. Are NCERT Solutions enough for scoring high marks in Class 12 Computer Science?
NCERT Solutions are usually sufficient for scoring well in Class 12 Computer Science, especially for Computer Networks, since CBSE exams primarily follow the NCERT syllabus.
- Thoroughly revise all exercises, definitions, and diagrams from NCERT
- For higher scores, practice additional exemplar and sample questions
- Master stepwise answer writing as shown in NCERT Solutions
8. What are the common mistakes students make when answering Computer Networks questions?
Common mistakes to avoid in Computer Networks answers:
- Missing key definitions or writing incomplete answers
- Incorrect or missing diagrams and labels
- Confusing network types or devices
- Ignoring CBSE answer structure; not using points/bullets
- Skipping stepwise explanations in multi-part answers
9. How does using stepwise NCERT Solutions help improve exam scores in Computer Networks?
Stepwise NCERT Solutions ensure your answers match the CBSE board exam standards, helping to maximize step marks.
- Each answer is broken into clear points matching examiner marking criteria
- Ensures all components (definition, explanation, diagram) are covered
- Improves recall and presentation skills during revision and exams
10. Do examiners award partial marks for correct steps even if the final answer is wrong?
Yes, CBSE examiners often award step marks for correct procedures or partial answers, even if the final answer is incomplete or incorrect.
- Always show your working and steps in Computer Networks answers
- This approach can earn you marks for the process, not just the result
- Following a stepwise format, as in NCERT Solutions, is essential for this