




Essential Tools and Real-World Examples for Measuring Length
The term "length" refers to the size of an object or the distance between two points. The length of an object or the distance between two places is measured in length. It is used to determine the size of an object or the distance between two points.
In order to figure out what the basic length units are, we discover that there isn't one. This is because many measurement methods or systems are currently in use all over the world. However, the most commonly used length units today are US customary units and metric units, which include both SI and non-SI units. In addition, some countries continue to utilise British Imperial units. In this blog post, we'll be running through just a few of the most common units of measurement!
Units of Measurement List
There are two types of units of measurement:
Non-standard unit
Standard unit
Non-Standard Unit
Non Standard unit is one unit from units of measurement list. Children in Foundation Stage learn about measuring without needing to read any scales by using non-standard units.
The objective of non-standard measures is to focus the child on the concept of heavier, lighter, longer, shorter, etc. before they proceed onto the next step of measuring using standard units. Reading scales of any kind is a difficult ability in and of itself.
For example, in order to measure height, handspan or foot is used but all people don’t have equal length of hand or foot this implies getting a standard unit of measurement.

Non-standard Unit
Standard Unit
A common unit of measurement is a quantifiable language that makes the relationship between the item and the measurement clear to all parties.
In the US, it is measured in inches, feet, and pounds; in the metric system, it is measured in centimetres, metres, and kilograms.
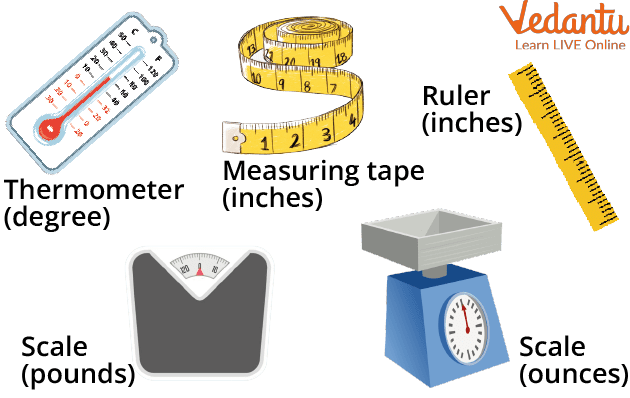
Standard Unit
For example, a ruler (used to measure height), measuring tape (used to measure length), scale (used for weight measurement), thermometer (temperature measurement), etc all are used to measure different types of things.
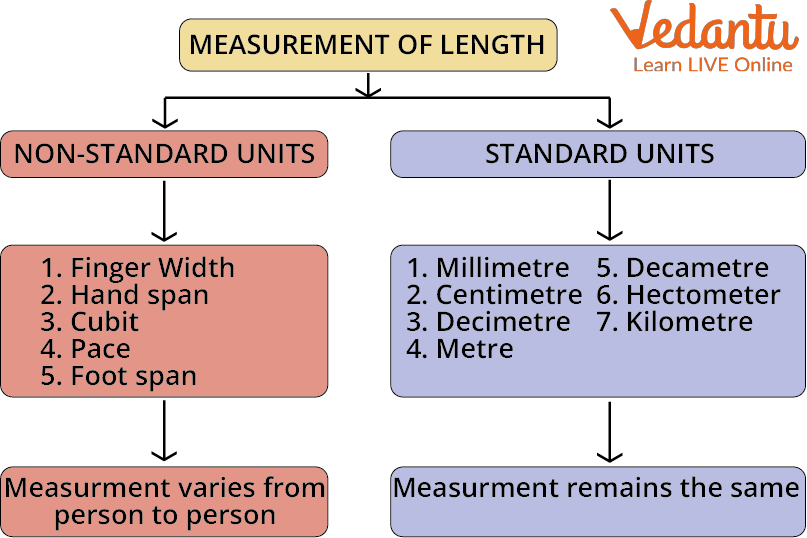
Non-standard Unit and Standard Unit
SI Unit of Length
The SI unit of length in the metric system is the metre.
The following are some of the other length units:
Kilometre
Hectometer
Decameter
Nanometer
Millimetre
Centimetre
Decimeter
Tools for Measuring Length
Tools help to get accurate measurements and this is the same for everyone at any place. A few tools that use for measuring length are:
Ruler
Scales
Measuring tape
Thermometer
Protractors
Order of Measurement
Small lengths (i.e. distances) are measured in cm and mm, while long lengths (i.e. distances) are measured in m and km. The 'Metre,' abbreviated as 'm,' is the standard unit of length.
One metre of length is divided into 100 equal parts. Each division is called a centimetre and is denoted by the letter 'cm.' As a result, 1 metre equals 100 centimetres.
The kilometre is the unit of measurement for the longest distance. One kilometre is divided into 1000 equal parts. A metre is the unit of measurement for each division. As a result; 1 kilometre equals 1000 metres.

Order of Measurement
Units of length and their counterparts, according to the length conversion charts, are:
1000 m = 1 kilometre (km) = 10 Hectometres (hm)
10 Decametres (dcm) = 100 Metres = 1 Hectometre (hm)
1 Metre (m) = 10 Decimetres (dm) = 100 Centimetres (cm) = 1000 Millimetres (mm)
10 Centimetres = 1 Decimetre (dm) (cm)
1 decimetre = 0.1 Metre
1 Centimetre (cm) = 10 Millimetres (mm) = 0.01 Metre
1 Millimetre = 0.001 Metre
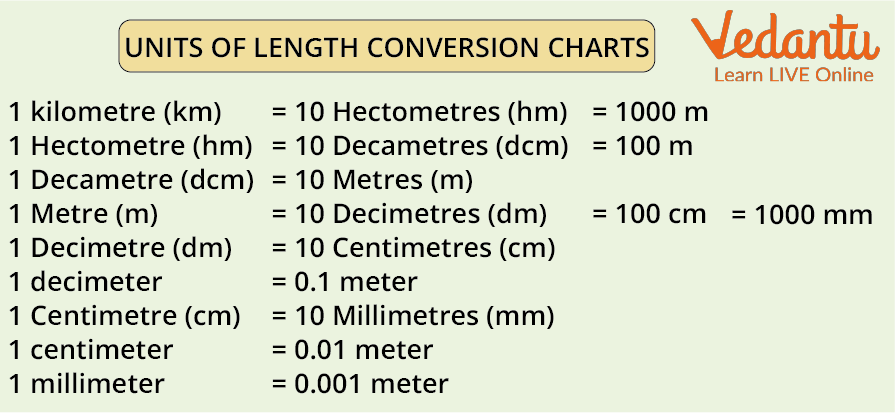
Units of Length
Metric System
A metric system is a unit of measurement for distance, length, volume, weight, and temperature. There are many different types of metric systems. It is built on three fundamental units that can be used to measure practically anything in the world.
Kg- kilogram, used to measure the mass
S- second, used to measure time
M- metre, used to measure the length
L-litre used to measure the length

Basic SI unit
Types of Metric Systems
There are many different types of metric systems mentioned below;
1. SI System
The SI Units (Standard International System of Units) define the metre, kilogram, and second correctly.
2. CGS System
The CGS system of units is another system of expressing units in terms of length, weight, distance, and time.
3. Metric Units Smallest to Largest
Order of metric units smallest to largest: Nanometer, Millimetre, Decimeter, Metre, Decameter, Hectometer, Kilometre
Summary
Length measurement is used to determine an object's length or the separation between two locations. It is employed to calculate an object's size or the separation between two spots. US customary units and metric units, which comprise both SI and non-SI units, are currently the most widely used length units. Additionally, some nations still make use of British Imperial units. The yard is the basic unit of length in both the Imperial and United States customary systems. In 1799, the metric system was created. The metric system of units is consistent and logical. This is a big benefit for usage in the home, in education, in business, and in science.
FAQs on Units of Measurement in Maths: Length Explained
1. What are the 7 basic units of measurement?
The seven basic units of measurement in the International System of Units (SI) are fundamental quantities used in science and everyday life. They include:
- Meter (m) for length
- Kilogram (kg) for mass
- Second (s) for time
- Ampere (A) for electric current
- Kelvin (K) for temperature
- Mole (mol) for amount of substance
- Candela (cd) for luminous intensity
2. What are the 22 derived units?
The 22 SI derived units are combinations of the 7 base units, often used to measure physical quantities. Some key examples are:
- Newton (N) for force: $1\,\text{N} = 1\,\text{kg} \cdot \text{m} / \text{s}^2$
- Joule (J) for energy: $1\,\text{J} = 1\,\text{kg} \cdot \text{m}^2 / \text{s}^2$
- Watt (W) for power: $1\,\text{W} = 1\,\text{kg} \cdot \text{m}^2 / \text{s}^3$
- Coulomb (C) for electric charge: $1\,\text{C} = 1\,\text{A} \cdot \text{s}$
- Volt (V) for electric potential: $1\,\text{V} = 1\,\text{W} / \text{A}$
3. What are different types of units?
There are several types of units in measurement, which include:
- Fundamental (base) units – like meter, kilogram, and second, which are independent and not derived from other units.
- Derived units – formed by combining base units (for example, Newton, Joule, and Pascal).
- Supplementary units (no longer part of SI, but sometimes referenced in older materials).
- Non-SI units – such as degree (for angles), liter (for volume), and tonne (for mass).
4. What is in a unit of measurement?
A unit of measurement is a standard quantity used to express and compare physical quantities. It consists of:
- A magnitude (amount or number)
- A defined standard (like meter for length or second for time)
5. How are SI units different from CGS and FPS units?
SI units (International System of Units) use the meter, kilogram, and second as base units, while the CGS system uses centimeter, gram, and second, and the FPS system uses foot, pound, and second. Key differences include:
- SI units are the most widely adopted and standardized worldwide.
- CGS units are common in older scientific literature and certain physics contexts.
- FPS units are used primarily in the United States and were more common historically.
6. Why is standardization of units important in measurement?
The standardization of units is crucial for ensuring consistency and accuracy in scientific and mathematical measurements. Standardization allows:
- Clear communication of results globally.
- Replication of experiments and calculations in science and engineering.
- Simplified comparison of values across different nations and education systems.
7. What are some examples of non-SI units still in use today?
Various non-SI units are used globally in different fields. Examples include:
- Liter (L) for volume
- Minute and hour for time
- Degree Celsius (°C) for temperature
- Foot, inch, yard for length (especially in the US and UK)
- Tonne for mass
8. How do you convert between different units of measurement?
To convert between units of measurement, use appropriate conversion factors. For example, to convert from centimeters to meters, divide by 100, because $1\,\text{m} = 100\,\text{cm}$. General steps:
- Identify the source and target units.
- Find the conversion factor (e.g., $1\,\text{kg} = 1000\,\text{g}$).
- Multiply or divide the original value by this factor.
9. What is dimensional analysis in units of measurement?
Dimensional analysis is a mathematical process used to check the consistency of equations and to convert units. It involves:
- Comparing the dimensions (like length, mass, time) on both sides of an equation
- Ensuring all terms have compatible units

















