




What Are the Key Properties and Parts of a Circle for Kids?
You see different shapes in your daily life. Do you know what is the shape of a ring, or a coin, or that of the sun and the moon? Yes! It is a circle. A circle is a round shape. All points present on its boundary, a curved line, are placed at an equal distance from its centre. It is a two-dimensional shape. In your day-to-day life, you must have come across several objects that are in the shape of a circle.
For example, a ball, a dish, a clock, a doughnut, etc. Check the image below to know some objects that are in the shape of a circle.

Shape of a Circle
In the following sections, we will learn more about circles and their properties in detail.
Parts of Circle
The parts of a circle are shown in the below picture.
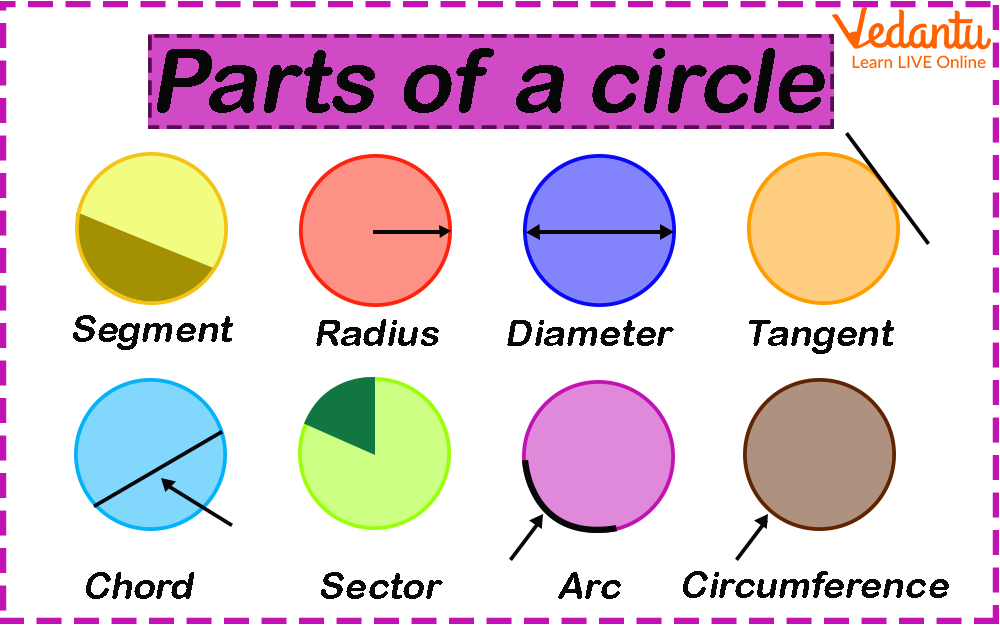
Parts of a Circle
Radius: A radius of a circle is a line drawn from the centre of the circle to any point on the circle edge. Letter ‘R’ is generally used to show the radius of the circle.
Circumference: Circumference of the circle is defined as the boundary of the circle. We can say that the measure of the boundary of the circle is called the circumference.
Chord: In a circle, a chord is a line segment that joins any two points on the circumference of the circle. It divides the circle into two parts. These parts are known as the segments of the circle.
Diameter: It is a line segment that passes through the centre of the circle. The endpoints of the diameter lie on the circumference of a circle. The diameter of a circle is double the length of the radius. It is generally represented by the letter ‘D’. Hence 2R=D.
Sector: A sector of a circle is the region formed by two of its radii and the arc in between. An angle is subtended at the centre of the circle by a sector.
Segment: A segment of a circle is the area that is bounded by an arc and a chord of the circle. There are two types of segments- minor and major. A segment that is made by a minor arc is called a minor segment and a segment that is made by a major arc is called a major segment.
Arc: The arc of a circle is a part of its circumference.
Tangent: In a circle, a tangent is a straight line that passes by touching the circumference of the circle only at one point. It is important to remember that it does not pass through the circle. The tangent meets the radius of the circle at an angle of 90o.
Conclusion
In the initial phase of introducing the concept of a circle to students, it is required to teach them the definitions of the parts of a circle. The definitions and concepts discussed above will be of great help for students learning about circles for the first time.
FAQs on Circles for Kids: Easy Guide to Definitions, Parts & Examples
1. How to explain circle to kids?
To explain a circle to kids, describe it as a round shape where every point on the edge is the same distance from the center. You can use simple examples like a clock face, a pizza, or a coin. Show how:
- The center is the middle point of the circle.
- The edge (or border) goes all the way around at the same distance from the center.
2. How to teach kids to make circles?
To teach kids to make circles, follow these simple steps:
- Encourage children to draw freehand circles on paper, like tracing round objects (cups, lids, or bangles).
- Demonstrate using a compass or a circular object for tracing.
- Practice drawing large circles with fingers in the air or sand to strengthen motor skills.
3. What is a fun fact about circles for kids?
A fun fact about circles for kids is that the wheel, one of the most important inventions in history, is a circle! Also, a circle has no corners or edges, and it looks the same from every direction. In mathematics, the special distance from the center to the edge is called the radius, and the distance all the way around the circle is the circumference. In Vedantu’s interactive sessions, children love learning about circles through games and stories involving these fun facts.
4. How long should circle time be for 3-4 year olds?
For 3-4 year olds, circle time should typically last between 10 to 15 minutes. Young children have short attention spans, so keeping circle time brief ensures they remain engaged and enjoy the activities. Vedantu’s live classes for young learners structure circle time with songs, stories, and simple math exercises, ensuring a fun and educational environment customized to children’s age and development stage.
5. What are the basic parts of a circle that kids should know?
The basic parts of a circle kids should know include:
- Center: The exact middle point of the circle.
- Radius: The straight line from the center to any point on the edge.
- Diameter: The line passing through the center connecting two points on the edge (it is twice the length of the radius, so $\text{Diameter} = 2 \times \text{Radius}$).
- Circumference: The distance all the way around the circle.
6. How can you use circles in everyday life examples for kids?
Circles are everywhere in everyday life! Examples for kids include:
- Clocks
- Plates and pizza
- Wheels on cars and bicycles
- Buttons and coins
7. Why is learning about circles important for kids?
Learning about circles is important because it helps kids:
- Develop spatial awareness
- Understand geometry basics
- Recognize shapes in daily life
- Build problem-solving and reasoning skills
8. What are some fun circle activities for preschoolers?
Some fun circle activities for preschoolers are:
- Sorting and counting circles in household items
- Playing “circle hunt” games, finding circles around the classroom or home
- Creating circle art with colored paper and crafts
- Using playdough to roll and shape circles
9. How can Vedantu help kids master the concept of circles?
Vedantu offers personalized live classes, interactive worksheets, and video lessons that teach the concept of circles for kids step-by-step. Our teachers use real-life examples, engaging visuals, and activities to ensure children grasp the idea of circles, their properties, and their usage in mathematics and daily life.
10. What is the difference between a circle and a sphere for kids?
A circle is a flat, round shape with just a single curved line (2D), while a sphere is a 3-dimensional shape like a ball.
- Circle: Only has length and width (e.g., drawn on paper).
- Sphere: Has length, width, and height—like a football or a marble.























