




Why Learning Shapes Is Important for Students
A pizza is the most ‘shape-filled’ object you’ll ever come across. Coming in a square box, the pizza is a circle itself. Hold up, the best part is yet to come, the slices are triangular!
Let’s just say you’ll realise the epitome of shapes that pizzas are hereafter. Let’s jump right in to understand the basic shapes and their properties.

Pizza
Plane Figures and Their Features
Any shape that lies flat on one plane can be called a plane figure. Our good old squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles all come under plane figures.
These shapes have sides, corners, and angles.
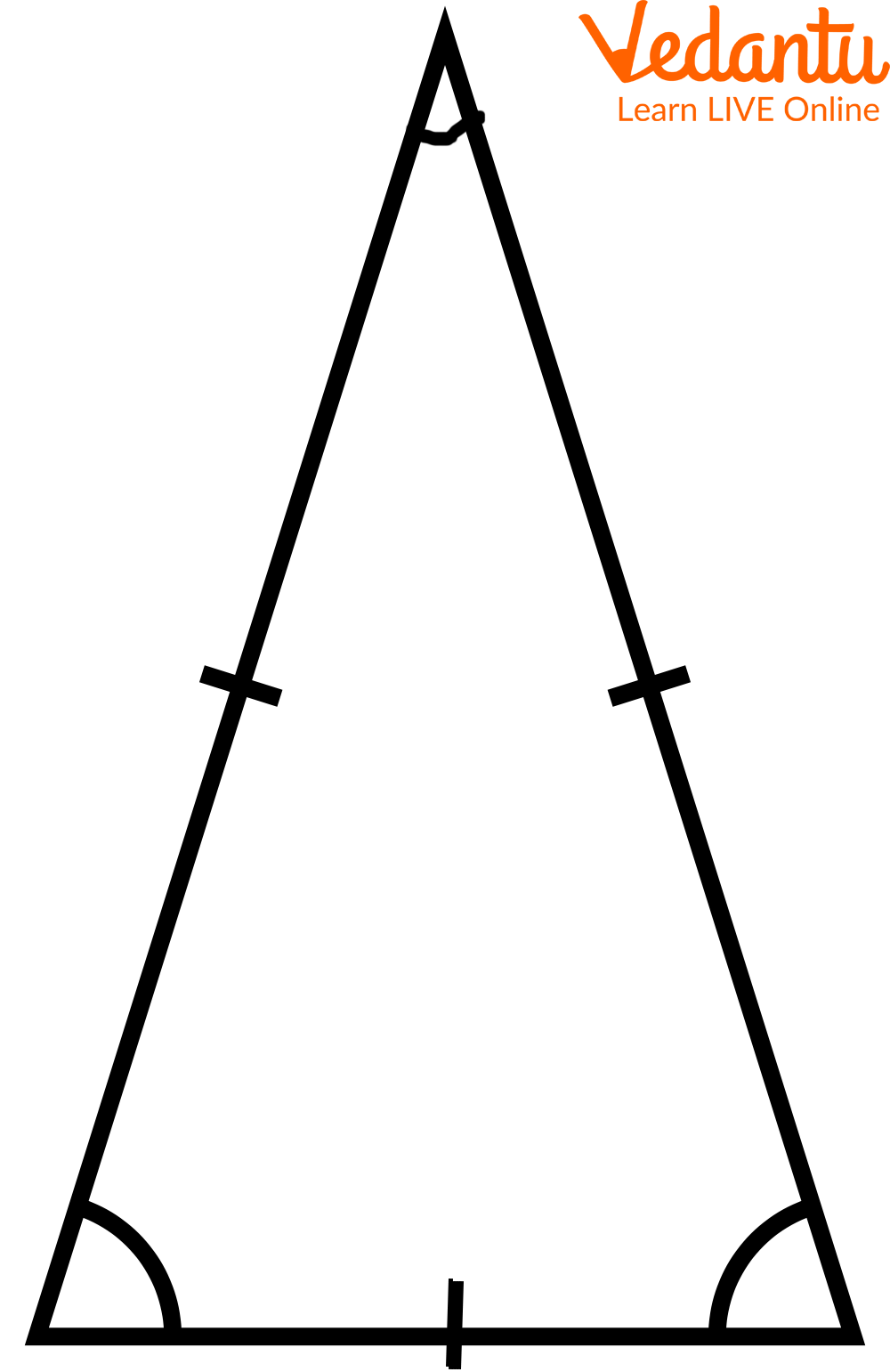
Sides and Corners of a Triangle
Square
The basic shape we’re starting with is that of a square.
A square has the following features:
4 equal sides
4 corners are placed perpendicularly
4 right angles between the sides (remember the L)

Sides, Angles, and Diagonals of a Square
Square-shaped Object Around Us
Rectangle
A rectangle has the following features:
4 sides
Opposite sides are equal to each other
4 corners are placed perpendicularly
4 right angles are placed between the sides

Sides and Angles of a Rectangle
Rectangle-shaped Objects Around us
Triangle
The name says it all for a triangle.
3 sides (base and opposite sides)
3 corners or vertices
Diagonals are not possible in a triangle.
Triangles can be further classified as illustrated below.
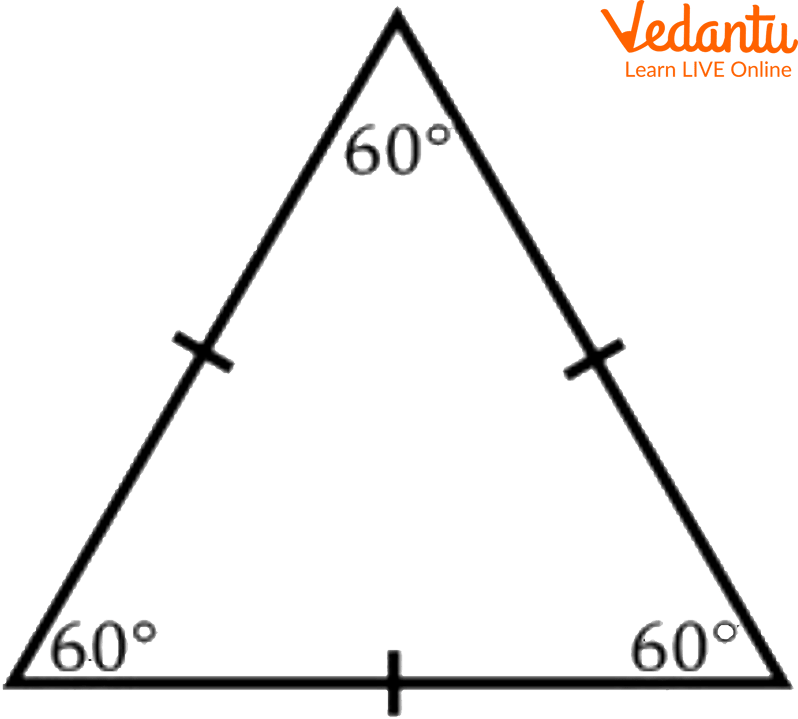
Triangle
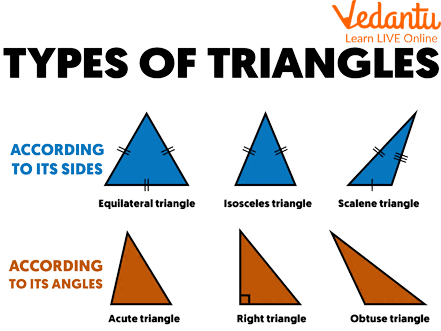
Types of Triangle
Circle
The circle is the hero of the show! No corners, no sides, no diagonals to deal with.
Features of the circle are as follows:
It is made up of curved lines with an origin
A diameter divides the circle into 2 equal halves ( it is the longest line that can be fit into it)
Half of a diameter is called the radius.
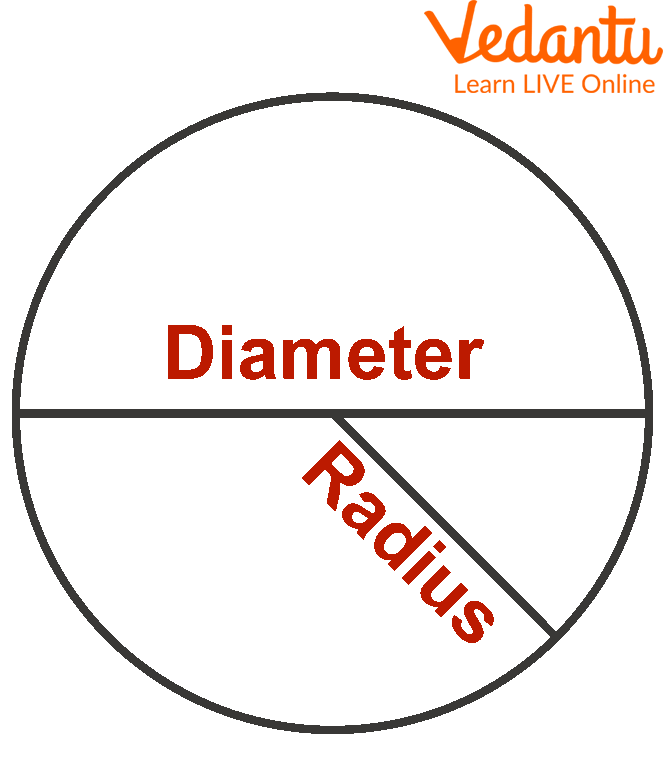
Parts of a Circle
Here O is the origin of the circle, line D is the diameter and R is the radius.

Circle-Shaped Objects Around us
Special Plane Figures
There are several other specialised plane figures that are one way or the other related to squares and rectangles. These are collectively known as quadrilaterals as they have 4 sides (quad meaning 4). Parallelogram, Trapezoid, Rhombus, and Kite fall under this category.
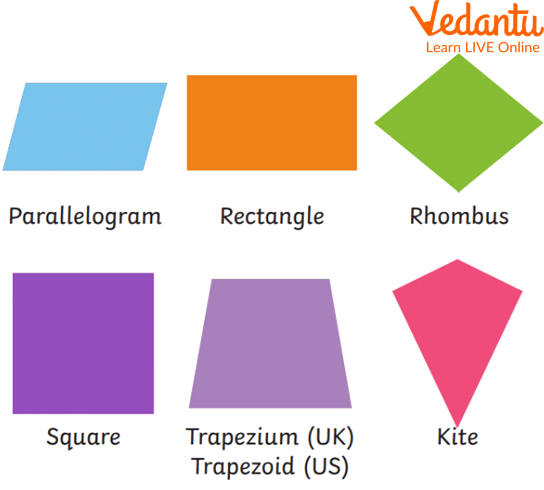
Special Plane Figures (Quadrilaterals)
Solid Figures and Their Features
Any shape that occupies space can be called a solid figure. Cubes, cuboids, prisms, cones, spheres, and cylinders fall under this category. These shapes have faces, edges, and vertices which give them their unique features. It is easier to remember solid figures as plane figures put together in all the possible dimensions. So, solid figures also have sides, corners, and angles.
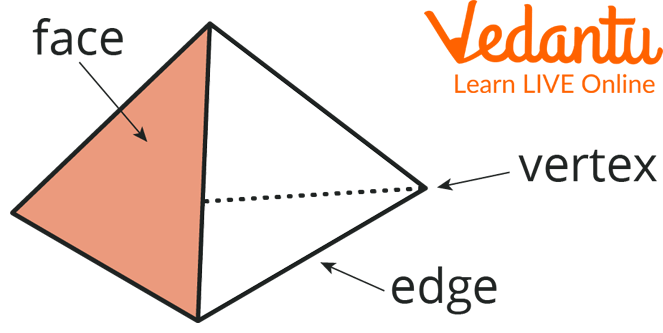
Parts of a Solid Shape

Types of Solid Shapes
Cube
Cubes are made up of squares but in 3 dimensions.
All faces and sides of a cube are equal.
The edges are equal.
There are 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices in a cube.
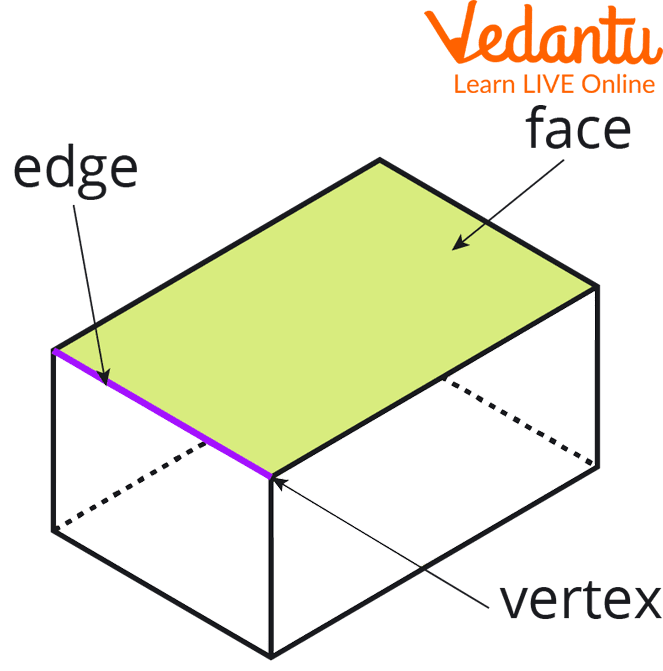
Faces, Edges, and Vertices of a Cube
Cube-Shaped Objects Around us
Cuboid
Slightly modified cubes give us cuboids.
The opposite faces of a cuboid are equal.
Opposite edges are equal.
There are 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices in a cuboid.
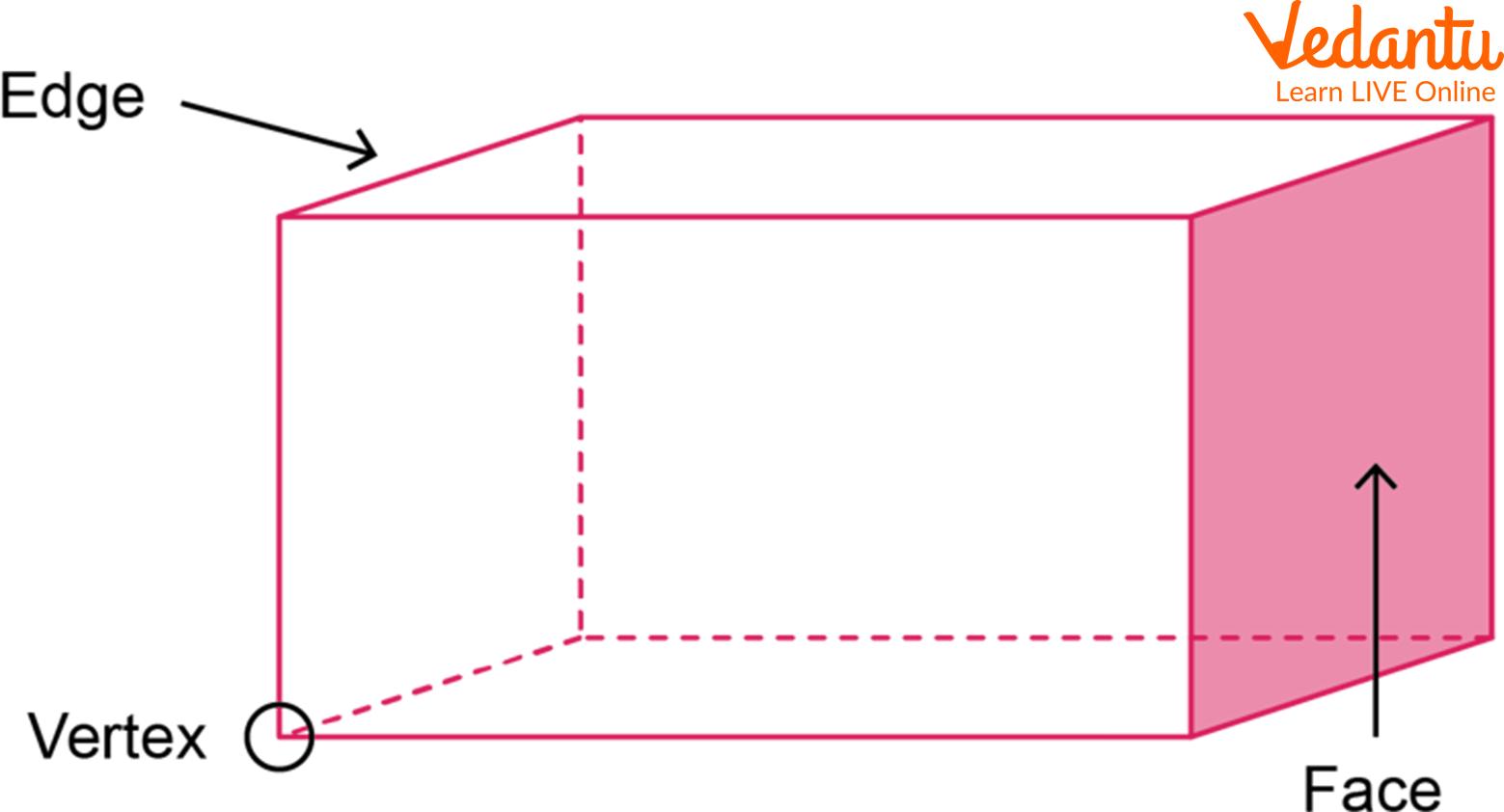
Faces, Edges, and Vertices of a Cuboid

Cuboid-shaped Objects
Cone
Birthday parties are all about cones! Ice cream cones, birthday caps, and whatnot. This peculiar solid shape has the following properties
It has one curved surface and one flat surface.
It has one vertex and one curved edge.
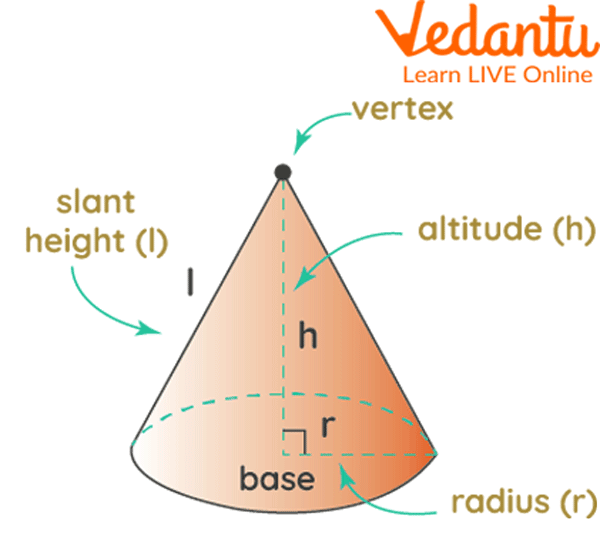
Parts of a Cone

Cone-Shaped Objects
Cylinder
The cylinder is a huge stack of circles placed on top of the other. The properties of a cylinder are as follows:
Three surfaces
It has no vertex
2 curved edges are present
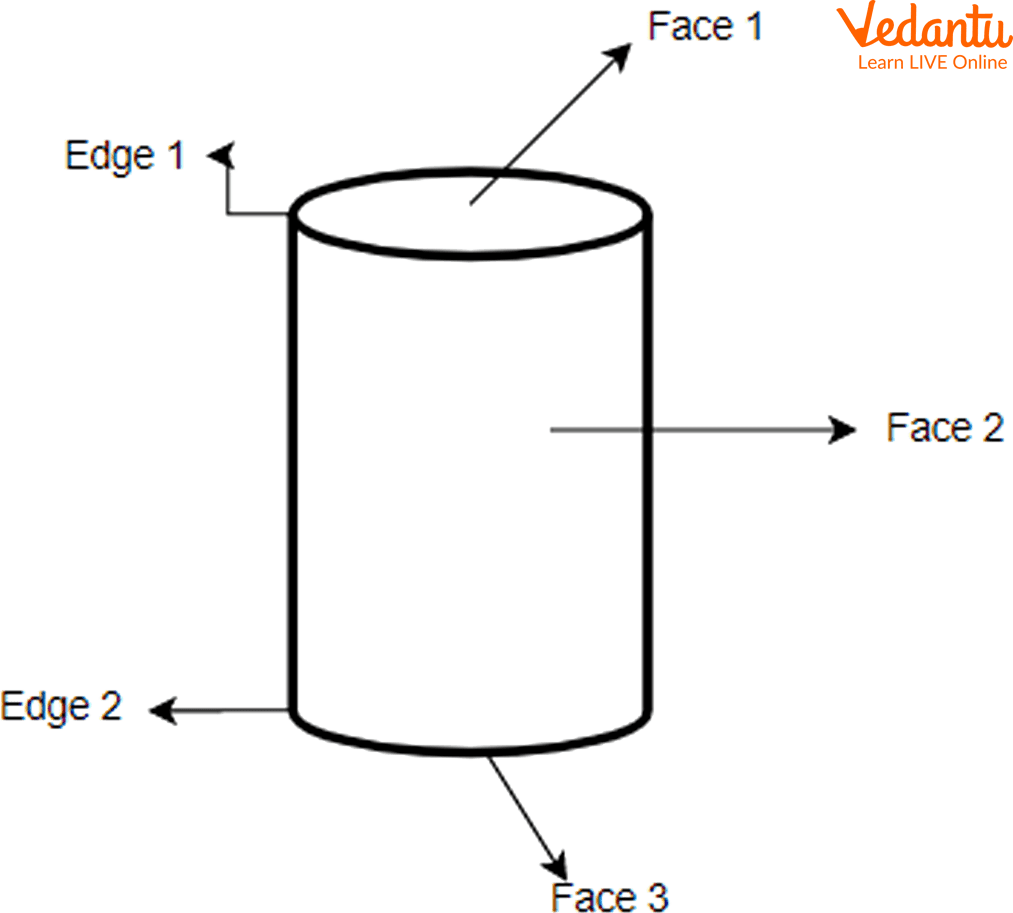
Parts of a Cylinder

Cylinder-shaped Objects
Sphere
A ball is the best example of a sphere. Properties of the sphere are as follows:
It has no edges or vertices.
It has one curved surface area.

Sphere

Spherical Objects Around Us
Practice Questions
Q1. ___________________ is a basic shape in which no diagonals are possible (Ans: Triangle)
Q2. _____________ sides are equal in a rectangle (Ans: opposite)
Q3. The longest line possible in a circle dividing the circle into 2 equal halves is called _______________ (Ans: diameter)
Summary
Basic shapes mainly are composed of plane figures and solid figures. Plane figures, also known as 2-dimensional shapes, lie on a single plane having length and breadth. Examples of plane figures include squares, rectangles, triangles, circles, and quadrilaterals.
Solid shapes include cubes, cuboids, cones, cylinders, and spheres having length, breadth, and height. These are also known as 3-dimensional objects as they occupy space. In common, all the basic shapes have faces, edges, vertices, corners, and angles and are of different types.
FAQs on Basic Shapes Names with Definitions and Examples
1. What are the basic 2D and 3D shapes we see around us?
The basic shapes we learn about are divided into two main types based on their dimensions.
- 2D (Flat) Shapes: These are shapes that can be drawn on a flat surface like paper. They only have length and width. Common examples you see around you include a circle (like a clock face), a square (like a single tile on a floor), a rectangle (like a door), and a triangle (like a slice of pizza).
- 3D (Solid) Shapes: These are solid objects that take up space. They have length, width, and height. Examples include a cube (like a dice), a sphere (like a ball), a cone (like a birthday hat), and a cylinder (like a tin can).
2. How are basic shapes important in our daily life?
Basic shapes are incredibly important because they form the building blocks of almost everything around us. For example, wheels on cars and buses are circles, which allows them to roll smoothly. Doors, windows, and books are typically rectangles, making them easy to manufacture and use. The use of shapes in design and construction helps make objects functional, strong, and recognisable.
3. Can you give some examples of shapes found at home or in a park?
Yes, you can be a shape detective anywhere you go!
- At Home: A television screen is a rectangle, a dinner plate is a circle, a sandwich can be cut into triangles or squares, and a dice is a cube.
- In a Park: A frisbee is a perfect circle, the frame of a swing set often uses triangles for strength, and a bench is made of long rectangles.
4. What are the different types of triangles based on their sides and angles?
A triangle is a shape with three sides, but not all triangles are the same. They can be classified in two main ways:
- Classification by Sides:
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are of equal length.
- Isosceles Triangle: Exactly two sides are of equal length.
- Scalene Triangle: All three sides have different lengths.
- Classification by Angles:
- Right-Angled Triangle: Has one angle that is exactly 90 degrees.
- Acute-Angled Triangle: All three angles are less than 90 degrees.
- Obtuse-Angled Triangle: Has one angle that is greater than 90 degrees.
5. Why is a square a special type of rectangle, but a rectangle is not always a square?
This is because of their properties. A rectangle is defined as a four-sided shape with four right angles and opposite sides of equal length. A square meets all these criteria, but it has one additional, stricter rule: all four of its sides are equal. Since a square fulfils all the conditions for being a rectangle, it is considered a special, more specific type of rectangle. However, a general rectangle is not a square because it only requires opposite sides to be equal, not all four.
6. What is the main difference between a circle and an oval?
The main difference lies in their curvature and radius. A circle is a perfectly round shape where every point on its edge is the exact same distance from its centre. Think of a coin. An oval, however, is like a stretched or squashed circle. It has a curved line, but the distance from the centre to the edge is not constant. Think of the shape of an egg or a running track.
7. How do sides and corners help us tell different shapes apart?
Sides (the straight lines) and corners (also called vertices, where the sides meet) are the fundamental properties that define many shapes, known as polygons. By simply counting them, you can identify a shape:
- A triangle is the only shape with exactly 3 sides and 3 corners.
- A quadrilateral (like a square or rectangle) always has 4 sides and 4 corners.
- A pentagon has 5 sides and 5 corners, a hexagon has 6, and so on.























