Parts of Speech
1. Nouns
2. Pronouns
3. Verbs
4. Adjectives
5. Adverbs
6. Conjunctions
7. Prepositions
8. Interjections
Sentence Structure
1. Types of Sentences
2. Clause and Sentence Structure
Tenses
1. Simple Present Tense
2. Present Continuous Tense
3. Present Perfect Tense
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
5. Simple Past Tense
6. Past Continuous Tense
7. Past Perfect Tense
8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
9. Simple Future Tense
10. Future Continuous Tense
11. Future Perfect Tense
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Voice
1. Active Voice and Passive Voice
Determiners and Articles
1. Function of Determiners
2. Types of Articles
Phrases
1. Noun Phrases
2. Adjectival Phrases
3. Adverbial Phrases
4. Prepositional Phrases
Word Order and Questions
1. Subject–Verb–Object Order
2. Question Formation through Subject-Verb Inversion
Conclusion
1. Encouragement to continue learning
2. Trust in self and the learning process
Your Complete Guide to English Grammar Mastery
Does English grammar feel like a maze of confusing rules? Worry not! Whether your child is just starting or preparing for school exams, this guide will make learning English grammar a breeze. By learning the basics, your child can write beautifully and communicate effectively.
Let’s dive into the fascinating world of English grammar and see how these basics can help your child excel!
Parts of Speech: Building Blocks of Grammar
Understanding the parts of speech is the first step in learning grammar. These are the foundational categories that every word belongs to. Let’s break them down:
1. Nouns
Nouns are the names of people, places, animals, things, or ideas. Examples include teachers, Mumbai, dogs, and happiness.
.png)
Why they matter: Nouns are essential to identify the subject and object in sentences. They help to form the core of communication.
2. Pronouns
Pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition.
Examples: he, she, they, and it.
Example in use: Instead of saying "Ravi loves Ravi’s bike," we say, "Ravi loves his bike."
3. Verbs
Verbs show action or a state of being.
Examples: run, eat, is, was.
Tip: Ensure the verb agrees with the subject. (e.g., He runs, not He run.)
4. Adjectives
Adjectives describe or modify nouns.
Examples: beautiful, tall, interesting.
Example in Use: The tall tree provides shade.
5. Adverbs
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They often answer “how,” “when,” “where,” or “to what extent.”
Examples: quickly, very, often.
Example in Use: She ran quickly to catch the bus.
6. Conjunctions
Conjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses.
Examples: and, but, because.
Example in Use: I wanted to go, but it was raining.
7. Prepositions
Prepositions show relationships between nouns and other words.
Examples: in, on, at, by.
Example in Use: The book is on the table.
8. Interjections
Interjections are words that express strong emotions.
Examples: Wow!, Oh no!, Hurrah!
Example in Use: Wow! That’s amazing!
Understanding these categories helps children create well-structured sentences.
Would you like your child to learn English grammar in a whole new way? Watch this engaging video from Vedantu to help your child grasp tricky grammar concepts with ease. Help them start building a strong language foundation today!
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s move on to sentence structures for clarity and communication.
Sentence Structure: Building Clear Communication
Strong sentences make strong communication. Understanding sentence types and clauses is crucial for effective expression. Here’s how to structure them right:
Types of Sentences
Sentences can serve different purposes, such as:
Declarative: Makes a statement.
Example: I love reading books.
Interrogative: Asks a question.
Example: Do you love reading books?
Imperative: Gives a command.
Example: Read this book now.
Exclamatory: Expresses strong emotion.
Example: What a great book!
Clauses and Sentence Structure
Sentences consist of clauses. They can be independent (complete thoughts) or dependent (incomplete thoughts).
Independent Clause Example: She is happy.
Dependent Clause Example: Because she won the competition.
Learning sentence structure allows for more dynamic writing.
Sentence structures set the stage, but tenses add the time element. Let’s dive into verb tenses!
Tenses: Expressing Time Perfectly
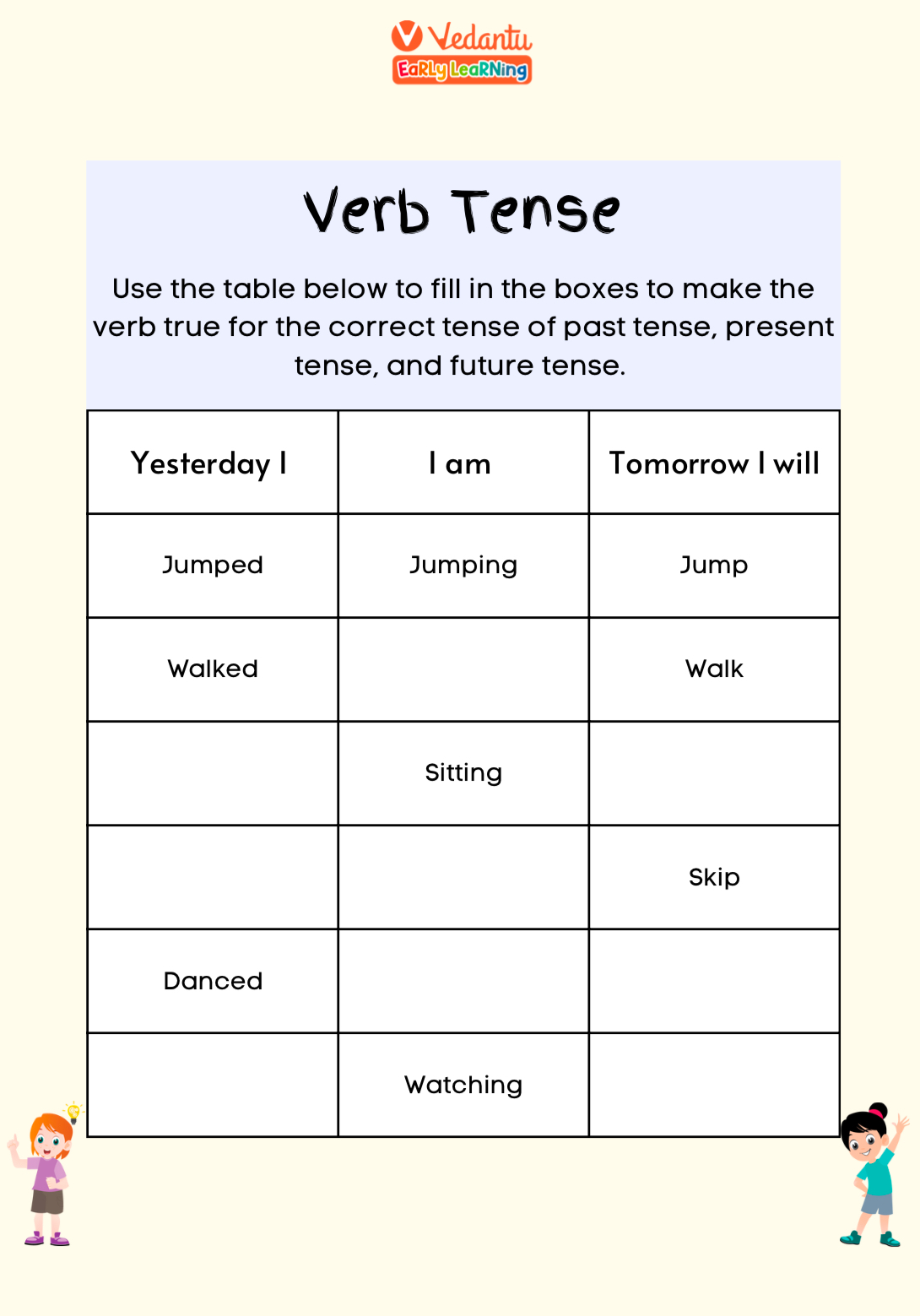
Tenses show when an action happens. Here’s a quick breakdown to understand the nuances:
Present Tenses
Simple Present: Facts or Habits.
Example: She writes daily.
Present Continuous: Ongoing actions.
Example: She is writing now.
Present Perfect: Actions completed recently.
Example: She has written a book.
Present Perfect Continuous: Actions ongoing over time.
Example: She has been writing for hours.
Past Tenses
Simple Past: Completed actions.
Example: She wrote a book.
Past Continuous: Actions ongoing in the past.
Example: She was writing a book.
Past Perfect: Actions completed before another past action.
Example: She had written it before dinner.
Past Perfect Continuous: Actions ongoing before another past action.
Example: She had been writing for hours before stopping.
Future Tenses
Simple Future: Actions to happen.
Example: She will write a book.
Future Continuous: Actions ongoing in the future.
Example: She will be writing tomorrow.
Future Perfect: Actions completed in the future.
Example: She will have written it by next week.
Future Perfect Continuous: Actions are ongoing and will be finished in the future.
Example: She will have been writing for hours by the time you arrive.
Tenses help children articulate time effectively, making their communication clear and precise.
Is your child confused about tenses? This fun and interactive video by Vedantu breaks down tenses step-by-step, making it simple for them to learn the rules of time in English.
Understanding tenses is key to accurate communication. Next, we’ll discuss active and passive voice.
Voice: Active vs. Passive
Active and passive voice affect how a sentence feels and functions. Let’s clarify the differences:
Active Voice
The subject acts.
Example: She wrote a letter.
Passive Voice
The subject receives the action.
Example: A letter was written by her.
Tip: Use active voice for clarity and passive voice when focusing on the action rather than the doer.
Teaching children to identify and use both voices enhances their writing versatility.
From voice, let’s move on to determiners and articles, which help specify and define nouns.
Determiners and Articles
Small words like determiners and articles help specify nouns and enhance sentence meaning.
Function of Determiners
Determiners specify nouns to clarify what’s being referred to.
Examples: this, some, every.
Types of Articles
Definite (the): Refers to something specific.
Example: The sun is shining.
Indefinite (a/an): Refers to something general.
Example: An apple a day keeps the doctor away.
Learning determiners helps children add precision to their language.
Transform your child into an English Superstar! With Vedantu’s English Superstar course, your child can learn grammar, reading, and writing in a fun and engaging way.
Now, let’s move to phrases that add depth to sentences.
Phrases: Adding Depth to Sentences
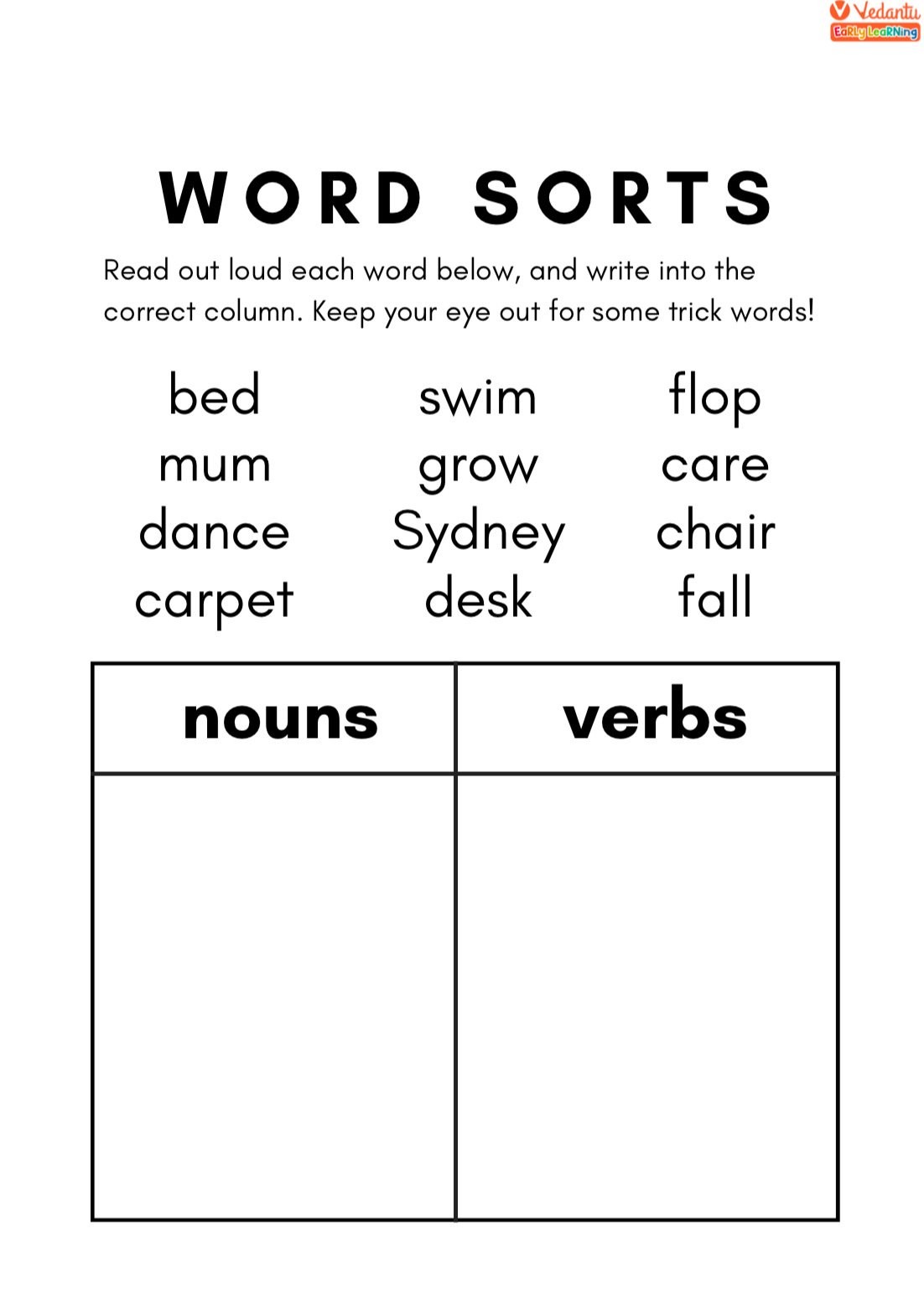
Phrases are groups of words without a subject-verb pair. They enrich sentence meaning. Here are the main types:
Noun Phrases
Focus on the noun.
Example: The tall boy won the race.
Adjectival Phrases
Describe nouns.
Example: The girl with curly hair is my sister.
Adverbial Phrases
Describe verbs.
Example: She ran with great speed.
Prepositional Phrases
Begin with prepositions.
Example: He sat under the tree.
Encouraging children to use phrases enhances their descriptive writing.
Want to boost your child’s confidence in speaking English? Vedantu’s Super Speakers program offers personalized training to enhance their grammar, vocabulary, and communication skills. Enroll them today and see the difference!
Next, it’s time to organize word order and questions effectively.
Word Order and Questions: Crafting the Perfect Sentence
Proper word order and question formation are key to effective grammar usage.
Subject–Verb–Object Order
Most English sentences follow this logical order:
Example: She (subject) eats (verb) apples (object).
Question Formation through Subject-Verb Inversion
In questions, the subject and verb switch places:
Example: She is coming. → Is she coming?
Teaching children these structures ensures they form grammatically correct sentences.
Conclusion
English grammar doesn’t have to be daunting. By breaking it down into smaller sections and practicing consistently, your child can gain confidence and excel in both speaking and writing. Remember, every expert was once a beginner. Encourage your child to keep learning and embrace the joy of language.
At Vedantu, we make learning fun and effective. With engaging lessons tailored to your child's needs, we ensure they confidently grasp concepts.
Book a free demo session today and let’s help your child master English grammar!


Parts of Speech
1. Nouns
2. Pronouns
3. Verbs
4. Adjectives
5. Adverbs
6. Conjunctions
7. Prepositions
8. Interjections
Sentence Structure
1. Types of Sentences
2. Clause and Sentence Structure
Tenses
1. Simple Present Tense
2. Present Continuous Tense
3. Present Perfect Tense
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
5. Simple Past Tense
6. Past Continuous Tense
7. Past Perfect Tense
8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
9. Simple Future Tense
10. Future Continuous Tense
11. Future Perfect Tense
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Voice
1. Active Voice and Passive Voice
Determiners and Articles
1. Function of Determiners
2. Types of Articles
Phrases
1. Noun Phrases
2. Adjectival Phrases
3. Adverbial Phrases
4. Prepositional Phrases
Word Order and Questions
1. Subject–Verb–Object Order
2. Question Formation through Subject-Verb Inversion
Conclusion
1. Encouragement to continue learning
2. Trust in self and the learning process



