




What Happens on Heating a Solid?
By heating a matter you can change its state. So, upon heating a solid you can change it to a Liquid state. This process of conversion of solid to liquid through heating is called Melting. When we apply heat to the solid, the rise in temperature helps the molecules in the solid to break their intermolecular forces and become less closely packed, hence changing their state. For example, if you heat ice, it is converted to water.
Liquid Heating
Just as solids change their form to liquids upon heating, liquids also tend to change their form to a gaseous state. This process of conversion of liquid to a gaseous state while applying heat is called evaporation. For example, when you heat water it turns into water vapours. This conversion also occurs because the energy provided by heating helps the water molecules to break their intermolecular forces and move apart from each other, hence adopting the molecular structure of gases, thereby changing into water vapours.
Exception: However, there exists a liquid that defies this inherent characteristic of liquids and instead of transforming into the gaseous state, it turns into the solid state. This anomaly is exhibited by a solution composed of α-cyclodextrin (αCD), water and 4-methylpyridine (4MP). When you heat this mixture between 45 degrees celsius to 75 degrees celsius, instead of turning to gas, it turns into a solid and turns back to liquid when cooled down.
Effect of Pressure on States of Matter
Pressure can be used to change the states of matter. When we apply pressure to gases, they are converted to liquids and when we do the same to liquids they are converted to solids. When we apply pressure to a state of matter, the molecules in it come closer to each other and hence the state of that particular matter changes.
Learning by Doing
Q1) What is the process of conversion of liquids to gases called?
Condensation
Freezing
Melting
Evaporation
Ans: d) Evaporation
Q2) What is the process of conversion of solids to liquids called?
Condensation
Freezing
Melting
Evaporation
Ans: c) Melting
Solved Questions
Q1) Which liquid turns into a solid upon heating?
Ans: A solution composed of α-cyclodextrin (αCD), water and 4-methylpyridine (4MP) turns into a solid upon heating instead of turning into a gas.
Q2) Draw a diagram to show the interconversion of matter.
Ans:
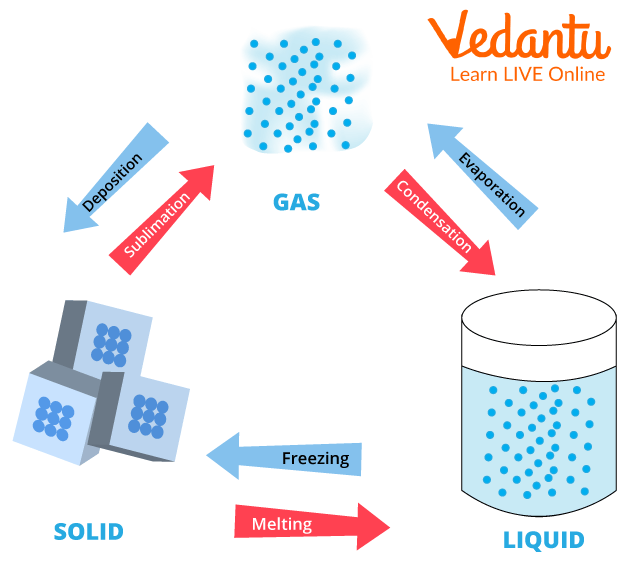
Interconversion of Matter
Summary
Solids, liquids and gases can be converted into one another with the help of external factors like temperature or pressure. When you apply pressure or change the temperature around a matter, its state changes. We can change solids to liquids and liquids to gases by increasing temperature. Further, we can change gases to liquids and liquids to solids either by decreasing the temperature or increasing the pressure. We hope you enjoyed reading this article and learnt something new today. Visit our website to read more about states of matter.
FAQs on Which Liquid Becomes Solid on Heating?
1. Which liquid becomes solid on heating?
An egg white is a common example of a liquid that becomes solid on heating. The main component of egg white is a protein called albumin, which is dissolved in water. When heated, this protein undergoes an irreversible chemical change called denaturation, causing it to coagulate and turn into a white, rubbery solid.
2. Why does an egg white solidify on heating, while ice melts?
This difference is due to the type of change occurring. Melting ice is a physical change; heating gives water molecules enough energy to break free from their fixed solid structure and move as a liquid. This is reversible. In contrast, heating an egg white causes a chemical change. The heat breaks the complex bonds of the protein molecules (denaturation), causing them to unravel and tangle together into a solid network. This process is not reversible by simple cooling.
3. What is the usual process when a solid is heated?
Typically, when a solid is heated, it undergoes a process called melting, where it changes from a solid state to a liquid state. As the solid absorbs heat energy, its particles vibrate more vigorously until they have enough energy to overcome the forces holding them in a fixed position. A common example is an ice cube melting into liquid water when heated.
4. What are some examples of liquids that turn into a solid upon cooling?
The process of a liquid turning into a solid upon cooling is called freezing or solidification. Common examples include:
- Water turning into ice.
- Melted chocolate hardening at room temperature.
- Liquid candle wax solidifying as it cools.
- Molten lava from a volcano cooling to form solid rock.
5. How does the particle arrangement change when a liquid freezes into a solid?
In a liquid, particles are close together but can move past one another. When a liquid is cooled, the particles lose energy and slow down. Eventually, they slow down enough that the attractive forces between them lock them into a fixed, orderly pattern, forming a solid. In this state, the particles can only vibrate in their fixed positions.
6. What is the difference between sublimation and condensation?
Sublimation is the process where a substance changes directly from a solid to a gas, bypassing the liquid state. An example is dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) turning into gas. Condensation is the opposite process, where a substance in a gaseous state changes to a liquid state upon cooling. An example is water vapour in the air forming liquid water droplets on a cold glass.
7. Is the solidification of an egg a reversible or irreversible change?
The solidification of an egg is an irreversible change. It is a chemical process where the protein structure is permanently altered by heat. Once cooked, an egg cannot be turned back into its liquid state by cooling. This is different from a physical change like freezing water, which is reversible because melting the ice returns it to liquid water without changing its chemical composition.





















