




Small Shrimps and Baby Prawns
Both Shrimps and Prawns are small members of the crustacean family. They are usually eaten as food in mainly the United States and in some countries in Asia. Shrimps that act as food sources are usually brown or orange in colour but shrimps of various different colours exist. Shrimps also act as a popular food source even in their natural habitat as they are eaten by salmon and other large fishes. Shrimps and Prawns are very similar in their appearance and thus are oftentimes confused and the terms are used interchangeably.
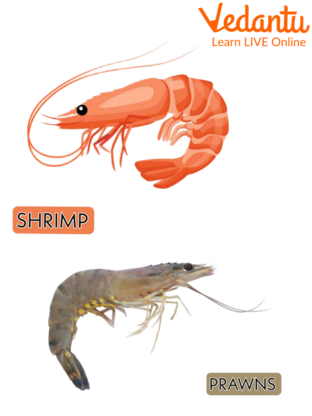
Shrimp and Prawn
What Do Shrimp Eat?
Shrimps are actually capable of eating anything and everything. Shrimps are scavengers and mainly help in decomposing. Scavengers or Decomposers are organisms that feed on dead organic matter and they play a very important role in maintaining the continuity of the food chain. In their natural habitat, they eat several things like algae, other dead shrimps, dead and living plants, worms and even decaying worms, fish, snails, and other dead organic matter. When kept in an aquarium, they can feed on anything which is available, for example, leftover fish food, some algae which may grow in the aquarium, etc.
Shrimp Facts
Some interesting and amusing facts about shrimps are mentioned below:
There are about 2000 species of shrimp recorded to date.
Some species of shrimps also have the ability to glow in the dark .
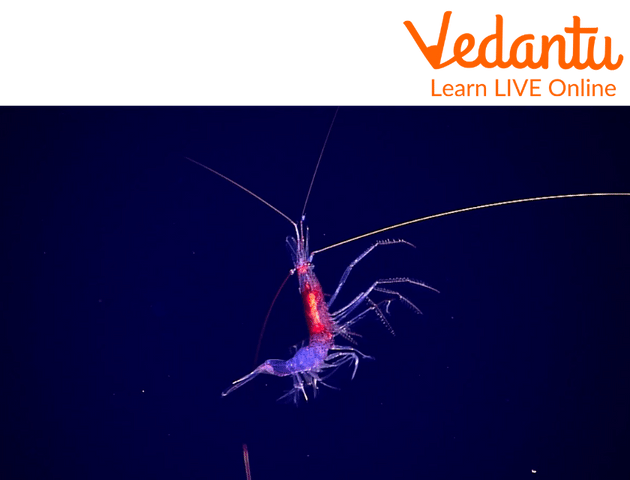

Shrimps Can Glow in the Dark
Shrimps usually swim backwards.
They have five pairs of legs.
Female shrimps can lay up to a thousand eggs at a time.
Baby shrimps are known as Larvae.
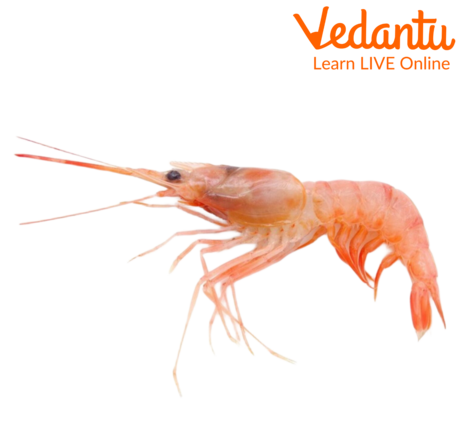

A Baby Shrimp
From a baby shrimp to an adult shrimp, there are 16 different stages of development.
Most of the shrimps can live for approximately one year but there are some shrimps which can live up to five or six years.
Every shrimp that is born is first born as a male organism and then it later develops into a female as it matures.
Where Do Prawns Live?
Prawns, like shrimps, can live in both salt and freshwater but unlike shrimps, most of their population is majorly found in freshwater. They also mainly reside in calm and still waters where they can easily lay their eggs.
Sample Questions
State whether the statements mentioned below are true or not:
1. Shrimps and Prawns are two names for the same organisms.
Ans: False, they are two different organisms.
2. Some shrimps can even glow in the dark.
Ans: True.
3. Shrimps are scavengers or decomposers.
Ans: True
4. Shrimps do not play any role in the ecosystem.
Ans: False, shrimps play an important role in the ecosystem.
Learn by Doing
Complete the statements mentioned below by filling in the blanks:
1. Shrimps are mainly found in __________.
Ans: seawater
2. Shrimps are ___________.
Ans: omnivore
3. They usually live for a ________.
Ans: year
4. Prawns are found in ________ water so they can lay their eggs.
Ans: Still
5. Shrimps have ___ development stages.
Ans: 16
Summary
Shrimps and prawns are very similar organisms which belong to the group of organisms known as crustaceans. Both shrimps and prawns serve as a source of food. Both the organisms can exist in freshwater and seawater but shrimps are mostly found in the seawater whereas prawns are mainly found in freshwater.
FAQs on What Do Shrimp Eat
1. What is the primary diet of shrimp in their natural habitat?
Shrimp are omnivores and scavengers with a highly varied diet. In their natural habitat, they primarily consume:
Algae and biofilm growing on rocks and plants.
Detritus, which is decaying organic matter from dead plants and animals.
Small organisms like worms, tiny crustaceans, and snails.
Plankton, especially in their larval stages.
2. Are shrimp herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Shrimp are classified as omnivores. This is because their diet consists of both plant-based material (like algae and decaying plant matter) and animal-based material (like small worms, other crustaceans, and plankton). Their ability to eat a wide range of organic material makes them highly adaptable survivors in their environment.
3. How does the diet of freshwater shrimp differ from that of saltwater shrimp?
While both types are omnivorous scavengers, their diets differ based on their environment. Freshwater shrimp primarily feed on biofilm, algae, and decaying plant matter found in rivers and streams. Saltwater (ocean) shrimp have access to a wider variety of food, including marine algae, plankton, tiny fish, and the remains of other sea creatures.
4. What is the ecological importance of a shrimp's feeding habits?
Shrimp play a crucial role as 'clean-up crews' in their ecosystems. By feeding on detritus (dead organic material) and waste, they act as decomposers and scavengers. This process is vital for recycling nutrients back into the food web, which helps maintain the health and balance of the aquatic environment.
5. What animals are the main predators of shrimp?
Shrimp are a key food source for many animals. Their main predators include a wide range of species such as crabs, starfish, various fish species (like flounder and cod), seabirds, whales, dolphins, and even other larger shrimp.
6. Do shrimp eat at the bottom of the ocean?
Yes, most shrimp are bottom-feeders. They spend much of their time, especially at night, searching the seafloor, riverbeds, or aquarium substrate for food. Their legs and antennae are adapted to sift through sand and mud to find algae, worms, and other bits of organic debris.
7. Do shrimp consume waste matter or faeces?
Shrimp are excellent at consuming detritus, which is a broad term for decaying organic matter. While this can include decaying waste products, they do not specifically seek out fresh faeces. Instead, they eat the biofilm and microorganisms that grow on waste as it breaks down, effectively helping to clean their environment.
8. Does a shrimp's diet change as it grows?
Yes, a shrimp's diet changes significantly throughout its life cycle. As larvae, they are very small and primarily feed on microscopic phytoplankton and zooplankton. As they grow into juveniles and adults, their diet diversifies to include larger items like algae, worms, and decaying matter found on the bottom.
9. Do shrimp have a brain to help them find food?
Yes, shrimp do have a brain, although it is very small and simple compared to that of a vertebrate. Their brain, located in the head region, processes information from their sensitive antennae and eyes to detect chemical signals and movements in the water, which helps them locate food sources effectively.





















