20 Common Homophones in English with Meanings and Sentences
Homophones are an essential part of the English language, often making reading and writing more interesting and sometimes confusing. The primary keyword, homophones, refers to words that sound the same but have different meanings and spellings. Understanding homophones helps prevent common mistakes in communication, making it easier to grasp the nuances of English vocabulary and grammar.
What Are Homophones? Meaning & Definition
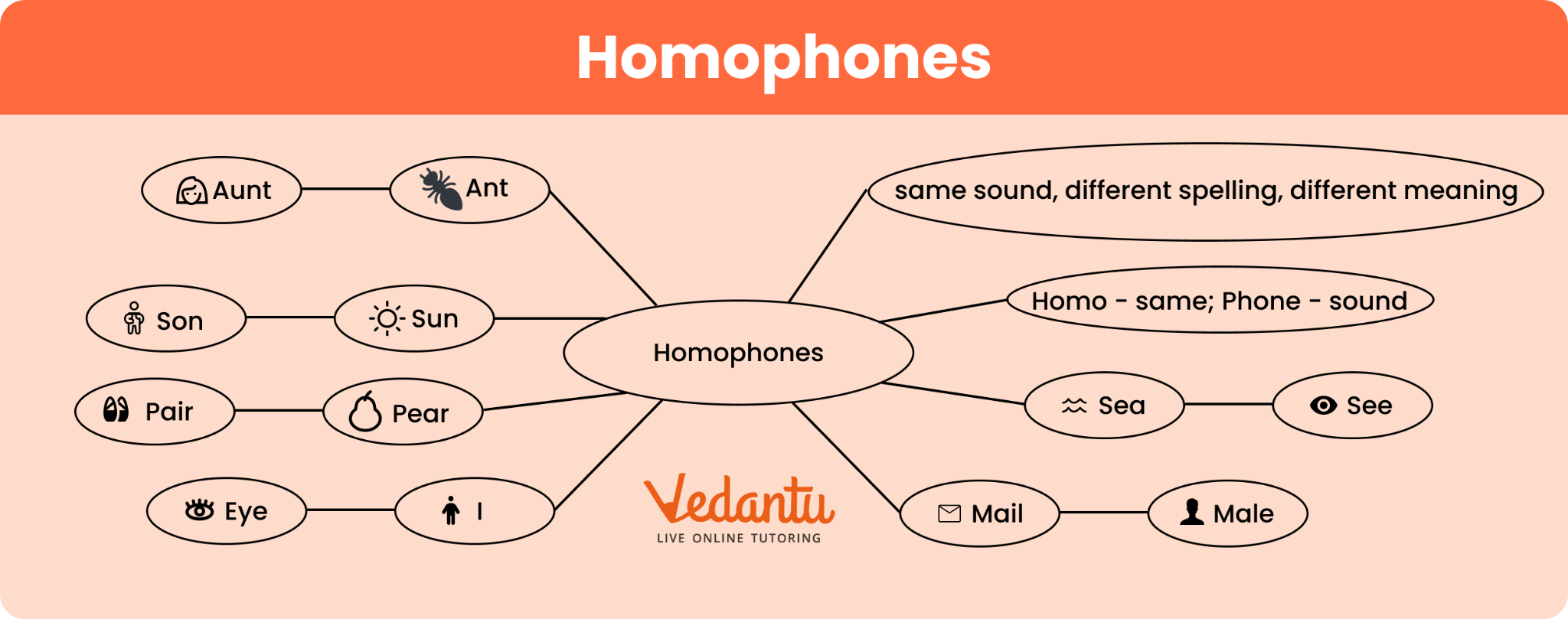
Homophones are words that have the same pronunciation but differ in their meanings, spellings, or origins. In simple terms, homophones sound alike but have distinct definitions and uses in sentences. The word homophone is derived from Greek, where "homo" means same, and "phone" means sound. For example, "two," "to," and "too" are homophones commonly used in daily English.
Knowing the meaning of homophones is especially useful for students and writers as it reduces confusion when reading or writing. Whether you are preparing homophones worksheets or looking for everyday usage, being familiar with homophones will make your English more precise and effective. For more grammar concepts, check out the English grammar page on Vedantu.
Homophones Examples With Sentences
| Homophone Pair | Meaning | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| bare / bear | bare: uncovered; bear: an animal | The bear walked with bare feet. |
| sun / son | sun: the star; son: male child | The son played under the sun. |
| flower / flour | flower: bloom; flour: powder for baking | She bought flour and a flower. |
| right / write | right: correct; write: to mark letters | Please write the right answer. |
| sea / see | sea: ocean; see: to look | I see the sea from my window. |
These examples of homophones show how words with the same pronunciation can have unique meanings and spellings. Using homophones correctly helps improve writing skills and reduces common spelling errors. You can also learn about similar word types such as homonyms and homographs for better clarity in English grammar.
List of Common Homophones Words
Here is a handy homophones list featuring some of the most frequently used homophones in English. These words often appear in class assignments, homophones worksheets, and daily communication:
Mail / Male - Mail means postal letter, while male refers to gender.
Blue / Blew - Blue is a color, blew is the past tense of blow.
Knight / Night - Knight is a warrior, night means the time after sunset.
Pain / Pane - Pain refers to discomfort, pane is a sheet of glass.
Weak / Week - Weak means lacking strength, week is a period of seven days.
Explore More About Homographs
Difference Between Homophones and Homonyms
Many learners confuse homophones and homonyms, but they are different. Homophones sound the same but have different meanings and spellings, while homonyms are words that sound and look the same but have different meanings, like "bat" (the animal) and "bat" (used in cricket).
Understanding the difference between homophones and homonyms will help you use words correctly and avoid miscommunication. For more about word types and their functions, visit the Parts of Speech page on Vedantu.
Homophones in English for Kids
Homophones for kids are a fun way to improve vocabulary and pronunciation. Simple pairs like "deer/ dear," "eye/ I," and "eight/ ate" are often included in young learners’ lessons and games, making language learning enjoyable. Practicing such topics for kids is beneficial for early English education.
Working with homophones examples and homophones worksheets prepares children for usage in sentences and comprehension tests. Interactive worksheets and activities are available on Vedantu to further aid practice.
Practicing Homophones with Sentences and Worksheets
One of the best ways to master homophones is with homophones worksheets and real-world sentences. Here are sample exercises for practice:
Fill in the blank: He read the whole/ hole story in one day.
Choose the correct word: She will meet / meat you at lunch.
True or False: "Buy/By/Bye" are examples of homophones.
Match homophones: hear/here, pair/pear, tail/tale.
Write sentences using: "peace/piece," "so/sew," "principal/principle."
Grammar Exercises for Kids
Homophones in Hindi and Other Languages
Sometimes, students look for homophones meaning in Hindi or other languages. In Hindi, homophones are called "समध्वन्य अर्थ." Learning homophones in English, with their meaning in Hindi, helps bilingual students reduce confusion. For example, "Right" (सही) and "Write" (लिखना) both sound the same in English but have different meanings and spellings.
20 Homophones With Meanings
Here is a quick list of 20 homophones, each with its meaning:
Allowed (permitted) / Aloud (spoken loudly)
Break (to shatter) / Brake (to stop)
Cite (to quote) / Site (location)
Great (excellent) / Grate (metal cover)
Here (in this place) / Hear (to listen)
Knew (past of know) / New (recent or fresh)
Knight (warrior) / Night (evening time)
No (negative) / Know (to be aware)
Peace (calm) / Piece (a part)
Plain (simple) / Plane (aircraft)
Read (to look at text) / Red (color)
Right (correct) / Write (to scribble)
Sail (move by boat) / Sale (discount)
Tale (story) / Tail (part of an animal)
Their (belonging) / There (place)
Toe (part of foot) / Tow (to pull)
Wait (to pause) / Weight (heaviness)
Weather (climate) / Whether (if)
Stare (look intently) / Stair (steps)
Weak (not strong) / Week (seven days)
Noun Questions and Answers
Homophones enrich English by adding depth and interest to communication. By learning definitions, examples, and practicing with sentences and worksheets, students can master homophones and avoid common spelling errors. Practicing homophones also builds vocabulary and makes writing clear and effective. For further learning, Vedantu offers interactive resources and worksheets for all levels.
FAQs on Homophones: Meaning, Examples, and Easy Guide
1. What is a homophone in English?
Homophones in English are words that sound the same but have different spellings and meanings. Understanding them helps improve spelling and writing.
Examples include:
- Flower (a plant) / Flour (used in baking)
- Two (number) / Too (also)
2. Can you give 20 examples of homophones?
Here are 20 homophone pairs with examples for students:
- Write / Right
- Two / Too
- Hair / Hare
- Flower / Flour
- Peace / Piece
- Buy / By
- Sun / Son
- Mail / Male
- Night / Knight
- Sea / See
- Wait / Weight
- Wood / Would
- Die / Dye
- Meet / Meat
- Pair / Pear
- Cell / Sell
- Blue / Blew
- Tale / Tail
- One / Won
- Stare / Stair
3. What is the difference between homonyms and homophones?
The main difference is:
- Homophones: Same sound, different spelling and meaning (e.g., to, two, too).
- Homonyms: Same spelling or pronunciation but different meanings (e.g., bat - an animal and bat - a cricket bat).
4. Why do we need to learn homophones?
Learning homophones helps students:
- Avoid spelling and grammar mistakes
- Understand exam questions accurately
- Improve reading and writing skills
- Build a stronger English vocabulary
5. How are homophones used in sentences?
Homophones are used in sentences to convey completely different meanings through similar sounds. Here are examples:
- He couldn’t bear (tolerate) the pain and walked bare (without shoes).
- The knight arrived at night.
- Can you see the sea from here?
6. What is a list of 100 homophone examples?
A homophone list includes numerous pairs and triplets like:
- Ate–Eight
- Flour–Flower
- Knight–Night
- Cell–Sell
- Road–Rode
- Bear–Bare
- To–Two–Too
- Mail–Male
- Sun–Son
- Buy–By
7. What are some common homophone mistakes and how can I avoid them?
Common mistakes with homophones happen due to their similar pronunciations. To avoid them:
- Always check word spelling in context.
- Practice using homophones in sentences.
- Use visual cues or stories to remember tough pairs.
8. Are there homophones with three or more words?
Yes, some homophone groups have three or more words with identical pronunciation but different meanings and spellings. For example:
- To (direction), Two (number), Too (also)
- Wear (to put on), Where (in which place), Ware (goods)
9. How can I remember homophones for exams?
To remember homophones for exams:
- Make flashcards with pairs and meanings
- Practice worksheets and quizzes regularly
- Learn homophones in context using sentences
- Associate words with images or stories
10. Do homophones exist in other languages?
Yes, homophones exist in many languages around the world, not just English. They occur when different words have identical pronunciation but diverse meanings and spellings, often influenced by the language’s phonetics and writing system.