What Are the Main Levels and Examples in the Taxonomic Hierarchy?
In biology, the Taxonomic Hierarchy is an organized system used to classify and group living organisms. This method arranges species into categories based on shared characteristics and evolutionary history. Understanding the taxonomic hierarchy helps students and researchers study the immense diversity of life and ensures a scientific approach to naming and organizing organisms.
Taxonomic Hierarchy Definition
Taxonomic hierarchy refers to the system of arranging organisms into a series of ranked categories, ranging from the most general to the most specific. Each step, or rank, in this hierarchy represents a particular level of similarity, from large groups like kingdoms to individual species. This structure allows scientists to identify relationships among all forms of life.
Levels of Taxonomic Hierarchy
The taxonomic hierarchy consists of several levels or ranks that reflect an organism's similarities and differences. These ranks progress from the broadest classification down to the most specific. It is essential for students, especially in taxonomic hierarchy class 12, to remember the sequence and significance of each level.
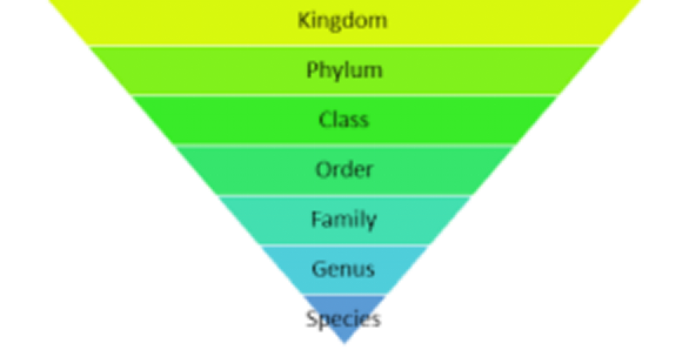
- Kingdom – Broadest category, grouping organisms with fundamental similarities.
- Phylum (for animals) / Division (for plants) – Divides kingdoms into groups based on major body plans or structures.
- Class – Further divides phylum/division based on more specific characteristics.
- Order – Groups organisms within a class with even more distinctive similarities.
- Family – Divides orders into groups with close relationships.
- Genus – Groups species that are very similar and likely evolved from a common ancestor.
- Species – The most specific rank, representing a single, unique organism population capable of interbreeding.
These ranks create an organized taxonomic hierarchy diagram, making it easier to identify and study living things.
Taxonomic Hierarchy Explanation
The taxonomic hierarchy helps scientists and students understand where an organism fits in the tree of life. As you move from kingdom to species, the similarities among organisms increase. This system provides a universal language for reporting discoveries and comparing organisms globally. It also supports research areas like environmental biology and life science by making organism relationships clear.
Taxonomic Hierarchy Examples
To clarify the taxonomic hierarchy definition, let’s consider a practical example. Take the domestic cat:
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Family: Felidae
- Genus: Felis
- Species: Felis catus
Other taxonomic hierarchy examples include a mango tree (Mangifera indica) and the house sparrow (Passer domesticus). This structure is vital for broader studies, including reproduction in plants and animal adaptations.
Major and Minor Categories in Taxonomic Hierarchy
In taxonomy, ranks can be grouped as major and minor categories:
- Major Categories: Kingdom, Phylum/Division, Class, Order, and Family represent broader groups.
- Minor Categories: Genus and Species are the most specific and closely related levels.
Understanding these categories helps with classification-related topics, and prepares students for questions in taxonomic hierarchy mcqs or competitive exams. You can find more examples in areas such as biological classification MCQs.
Significance and Applications of Taxonomic Hierarchy
The taxonomic hierarchy plays a critical role in biological sciences. It:
- Maintains consistency in naming organisms (binomial nomenclature).
- Aids in identifying newly discovered organisms.
- Helps track evolutionary history and relationships.
- Supports applied sciences like food science, agriculture, and medicine by organizing useful and harmful species.
- Makes it easier to communicate scientific information internationally.
An understanding of taxonomic hierarchy is valuable for research, biodiversity conservation, and practical tasks like distinguishing between acquired and inherited traits or studying the parts of the brain in different species.
Taxonomic Hierarchy Questions and Practice
Students often encounter taxonomic hierarchy questions in class tests, board exams, and entrance assessments. These can range from matching a species to its correct rank, analyzing a taxonomic hierarchy diagram, or identifying missing levels in a series. Practicing with biology MCQs and diagrams is an excellent way to master the topic.
Summary Table: Ranks and Examples
| Rank | Definition | Example (Human) |
|---|---|---|
| Kingdom | Largest group; main divisions of life | Animalia |
| Phylum | Based on basic body plan | Chordata |
| Class | Subdivision of phylum with more similarities | Mammalia |
| Order | Groups within a class | Primates |
| Family | Closely related genera | Hominidae |
| Genus | Very similar species | Homo |
| Species | Single unique population | Homo sapiens |
This table shows each major rank, its meaning, and where humans fit into the taxonomic hierarchy. Such tables also help visualize classifications for other organisms, plants, and animals.
The taxonomic hierarchy serves as the backbone of biological classification, supporting clear communication, research, and education. With practice, students will understand how this system helps organize nature’s diversity, making new discoveries and applied sciences easier to manage. Explore more Biology topics on Vedantu for deeper learning!


FAQs on Taxonomic Hierarchy Explained
1. What is taxonomic hierarchy?
Taxonomic hierarchy is the system by which living organisms are classified into a series of ranked levels, each smaller and more specific than the previous. Key ranks in this hierarchy include:
- Kingdom
- Phylum
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
2. What are the main levels of taxonomic hierarchy?
The main levels of taxonomic hierarchy are ordered from broadest to most specific:
- Kingdom
- Phylum/Division (for plants)
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
3. What is the purpose of taxonomic hierarchy in biology?
The chief purpose of taxonomic hierarchy is to systematically classify organisms, making their study and identification easier. Major objectives include:
- Organizing biodiversity logically
- Showing evolutionary relationships between organisms
- Enabling clear scientific communication across regions and languages
4. What do the terms genus and species mean in taxonomy?
In taxonomy, genus is a rank higher than species and groups together closely related species, while species is the most specific rank representing a group of similar individuals that can interbreed.
- Genus: e.g., Homo (humans)
- Species: e.g., sapiens (modern humans)
5. Why is classification important in biology?
Classification, organised through the taxonomic hierarchy, is important because it:
- Helps arrange organisms into groups for understanding relationships
- Makes study and identification efficient
- Enables scientists to give unique names and avoid confusion
6. Who introduced the concept of taxonomic hierarchy?
The concept of taxonomic hierarchy was introduced by Carolus Linnaeus, who is regarded as the Father of Taxonomy.
- Linnaeus developed the binomial system of naming and established standard taxonomic ranks
7. How does the taxonomic hierarchy reflect evolutionary relationships?
The taxonomic hierarchy reflects evolutionary relationships by grouping organisms based on shared characteristics and ancestry.
- Higher ranks include organisms with more general similarities
- Lower ranks (like genus and species) reflect close genetic relationships
8. What is the difference between a taxon and taxonomy?
Taxon is a term for any level or group in the taxonomic hierarchy (such as genus, family, species), while taxonomy is the science of classifying and naming organisms through this hierarchy.
9. Can you list the taxonomic hierarchy for human beings?
The taxonomic hierarchy for humans is as follows:
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Primates
- Family: Hominidae
- Genus: Homo
- Species: sapiens
10. What are the characteristics of different taxonomic categories?
Every taxonomic category has defining characteristics:
- Kingdom: Broadest, includes many diverse organisms
- Phylum: Groups organisms with major structural similarities
- Class: Breaks phyla into subgroups
- Order: Contains related families
- Family: Consists of related genera
- Genus: Groups similar species
- Species: Most specific, includes organisms that interbreed
11. What is binomial nomenclature and how is it related to taxonomic hierarchy?
Binomial nomenclature is the two-name scientific naming system for organisms and is closely linked to taxonomic hierarchy. The scientific name has:
- Genus name (First, with capital letter)
- Species name (Second, with small letter)
12. How are plants and animals classified differently in the taxonomic hierarchy?
In the taxonomic hierarchy, plants use the rank "Division" instead of "Phylum" used for animals. Rest of the categories remain similar, including class, order, family, genus, and species. This difference aligns with CBSE Biology curriculum.










