What are the main organs and organ systems in the human body?
The human body anatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the body’s organs, tissues, and systems. From the smallest cells to complex organs like the heart and brain, understanding anatomy of human body helps us learn how our body works, grows, and heals. This knowledge is essential for medicine, health, fitness, and many disciplines in life science.
What is Anatomy of Human Body?
Anatomy of human body refers to the scientific study of the structure of the human organism. It covers all internal and external parts, detailing how organs, tissues, and cells are arranged. Human body anatomy reveals not only the location of every part but also their roles in keeping us alive, healthy, and able to adapt.
Chemical Composition of the Human Body
When we look inside of human body, we find it made mostly of water and various organic compounds. Nearly 60% of our body weight is water, which acts as a solvent enabling chemical reactions essential for life.
- Proteins: Build structures (like skin and collagen) and perform important functions as enzymes.
- Lipids: Include fats, phospholipids, and cholesterol—vital for energy storage, insulation, and cell membrane structure.
- Carbohydrates: Mainly act as fuels, circulating as sugars or stored as glycogen in liver and muscles.
- Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA store and transmit genetic instructions.
- Minerals: Calcium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, magnesium, and iron play structural and metabolic roles.
To learn more about biomolecules and their importance, visit this Vedantu resource on biomolecules.
Levels of Organization in Human Anatomy
The human body is organized in layers, each building upon the next. Let’s break down these organizational levels to understand the inside of human body from the most basic unit to the highest level.
- Cells: The basic living unit. The body has trillions of cells, which perform specific functions. (Find more at Vedantu Cell Theory)
- Tissues:
- Epithelial tissue: Covers and protects surfaces.
- Connective tissue: Supports and connects (includes bone and blood).
- Muscle tissue: Enables movement.
- Nervous tissue: Transmits signals.
- Organs: Groups of tissues working together, such as the heart or liver.
- Organ Systems: Groups of organs joining to perform complex functions. Example: digestive, skeletal, or circulatory systems.
- The Whole Organism: All systems functioning together make up the human body.
Main Organ Systems in Human Body Anatomy
The structure of human body is defined by several major organ systems. Each system is made of organs and tissues with specialized functions, which together ensure survival, growth, and adaptation.
- Skeletal System: Provides support and protection; includes bones, cartilage, and joints. Explore human skeletal system.
- Muscular System: Enables movement and posture. Visit muscular tissue overview.
- Nervous System: Controls and coordinates body functions.
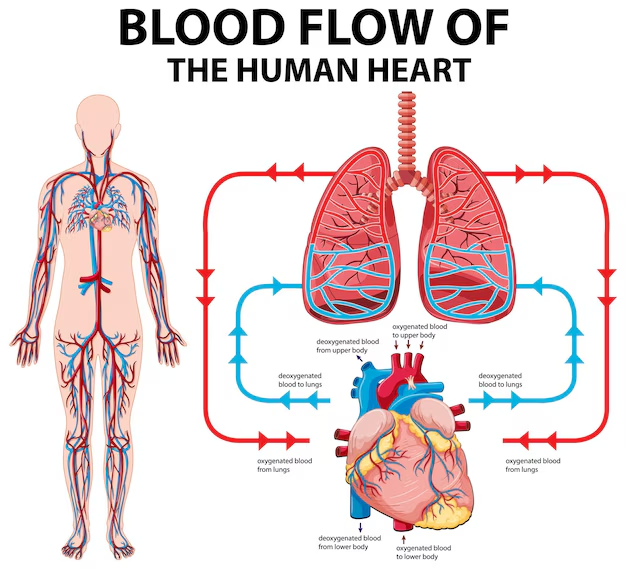
- Circulatory System: Transports nutrients, gases, and wastes. Learn about the human cardiovascular system.
- Respiratory System: Enables gas exchange, like breathing.
- Digestive System: Breaks down and absorbs food.
- Excretory System: Removes waste. Read more at excretion in humans.
- Endocrine System: Releases hormones to regulate processes. More at Vedantu's endocrinology guide.
- Reproductive System: Ensures continuation of species. Details on male and female anatomy.
Each system is essential for balance (homeostasis) and adapts to changes in environment, as discussed in climate change effects.
Differences in Human Body Female Anatomy
While the fundamental anatomy human body is similar across all humans, males and females have important structural differences, especially in the reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics such as fat distribution, bone structure, and hormone levels. Female anatomy includes specialized organs like ovaries and uterus, supporting pregnancy and childbirth. Males and females also have differences in bone shape and muscle distribution, which can be explored in detail at Vedantu’s dedicated topics.
Medical and Everyday Relevance of Human Body Anatomy
Knowledge of human body anatomy is not limited to doctors and scientists. It helps in diagnosing illnesses, treating injuries, understanding nutrition, and improving fitness. For example, understanding how nutrients affect body organs is explained in nutrient functions. Applications also extend to environmental health and the impact of pollution on human body systems, as described in environmental issues.
Quick Reference Table: Main Human Body Systems & Functions
| System | Main Organs | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Skeletal | Bones, Joints, Cartilage | Support, Protection, Movement |
| Muscular | Muscles | Movement, Heat Production |
| Digestive | Stomach, Intestines, Liver | Digestion, Absorption |
| Nervous | Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves | Control, Coordination |
| Circulatory | Heart, Blood Vessels | Transport of Substances |
| Respiratory | Lungs, Trachea | Gas Exchange |
| Reproductive | Ovaries, Testes, Uterus | Reproduction |
This table summarizes the key systems in human body anatomy and how they contribute to everyday life, health, and growth.
Summary
An understanding of human body anatomy connects every aspect of health, medicine, and daily wellbeing. From cells and tissues to entire organs and systems, learning about the inside of human body deepens our appreciation for its complexity. For more in-depth biology topics and interactive learning, explore Vedantu’s comprehensive resources.


FAQs on Human body anatomy explained simply
1. What is human body anatomy?
Human body anatomy is the scientific study of the structure and organization of the human body. It includes:
- Understanding the organs, tissues, and systems
- Examining how structural features relate to function
- Providing the foundation for medical and biological studies
2. What are the main systems of the human body?
The human body comprises several essential systems that work together to maintain health and function. The major systems are:
- Circulatory system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Nervous system
- Musculoskeletal system
- Excretory system
- Endocrine system
- Reproductive system
- Lymphatic system
3. Why is it important to study human anatomy?
Studying human anatomy is crucial because it helps us:
- Understand the structure and function of the human body
- Identify how different organs and systems interact
- Support medical diagnosis and treatment
- Prepare for biology exams and practical applications
4. What is the difference between anatomy and physiology?
The main difference between anatomy and physiology is their focus:
- Anatomy studies the structure, location, and relationships of body parts
- Physiology examines how body parts function and interact
5. Name the levels of structural organization in the human body.
The human body is organized in a hierarchy from simplest to most complex:
- Chemical level (atoms, molecules)
- Cellular level (cells)
- Tissue level (groups of cells)
- Organ level (different tissues forming organs)
- Organ system level (groups of organs performing shared functions)
- Organism level (the complete human body)
6. What are the major organs in the human body and their functions?
Major organs in the human body include:
- Heart: Pumps blood throughout the body
- Lungs: Facilitate gas exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out)
- Brain: Controls thoughts, actions, and sensations
- Liver: Processes nutrients and detoxifies chemicals
- Kidneys: Filter waste from blood and regulate fluids
- Stomach: Aids in digestion of food
7. What is the structural and functional unit of the human body?
The cell is considered the structural and functional unit of the human body. Key points include:
- All body systems are made up of cells
- Cells carry out essential processes for life
- Different types of cells form tissues and organs
8. What are the types of tissues found in the human body?
The human body contains four main types of tissues:
- Epithelial tissue: Covers body surfaces and lines cavities
- Connective tissue: Supports, binds, and protects organs
- Muscle tissue: Enables movement
- Nervous tissue: Transmits impulses for coordination
9. Which organ system controls body activities and responds to stimuli?
The nervous system controls most body activities and responses to environmental stimuli. It includes:
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Nerves
10. Explain the structure of the human heart.
The human heart is a muscular organ with four chambers:
- Two atria (upper chambers)
- Two ventricles (lower chambers)










