Structure, Types and Key Functions of Hormones (with Diagram and Examples)
Hormones are vital chemical messengers that regulate growth, metabolism, development, and homeostasis in living organisms. The study of hormones is foundational for understanding health, disease, and life processes. In this topic page, you will discover the definition, types, examples, and major functions of hormones, illustrated with diagrams and real-life applications. This guide supports both board exam preparation and deeper exploration of biology.
Hormones Definition
Hormones are organic substances secreted by endocrine glands directly into the bloodstream. These messengers travel to target tissues or organs, triggering specific physiological responses. The hormones definition highlights their role in controlling vital activities such as metabolism, growth, reproduction, and stress response.
What are Hormones? Understanding Their Role
Hormones act as the body’s signaling molecules, ensuring proper coordination and regulation among different organ systems. By maintaining balance (homeostasis), hormones help adapt to internal and external changes. This is particularly important in contexts like environmental adaptation, as explained in topics related to animal adaptations and climate changes.
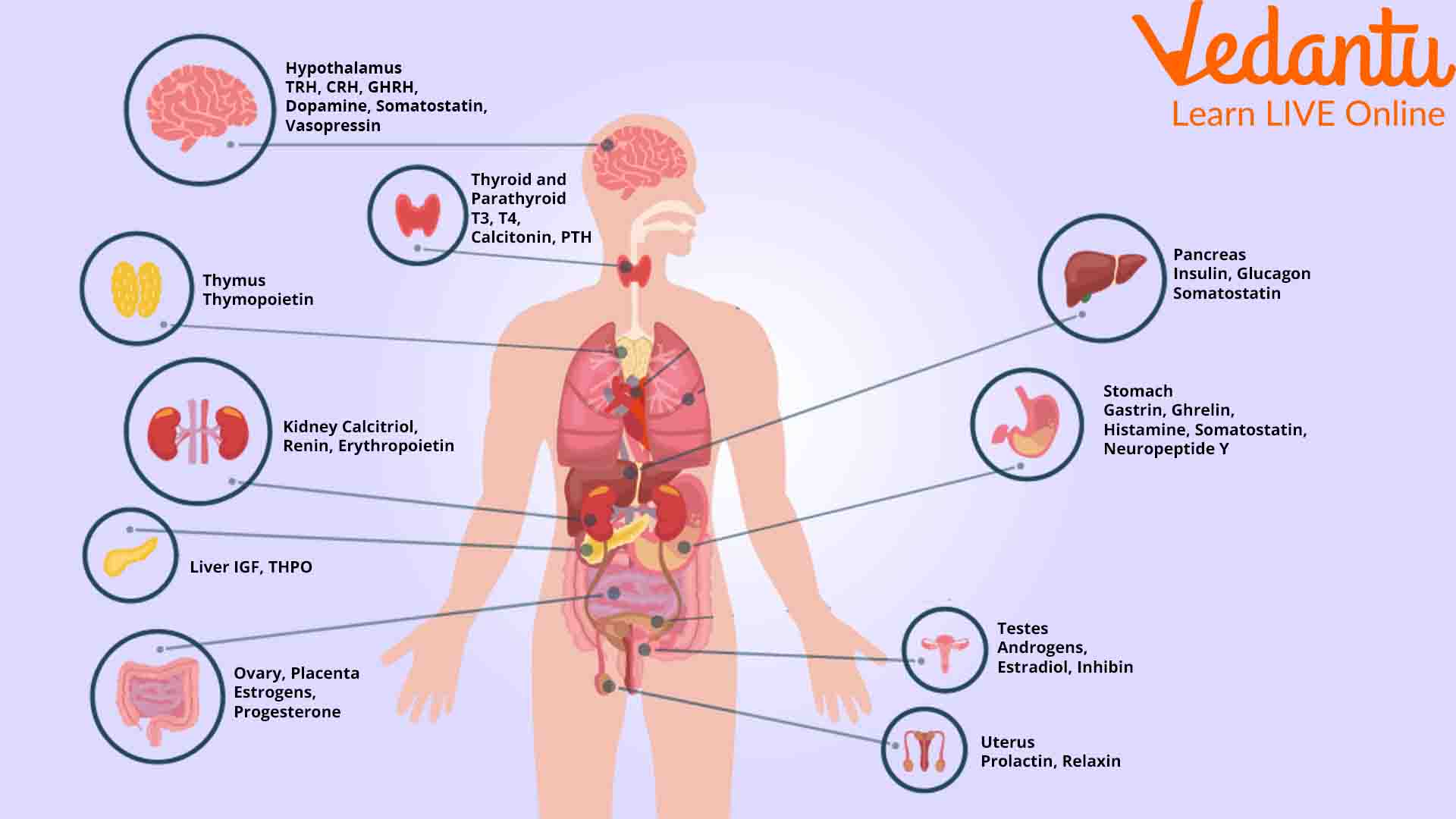
Types of Hormones & Main Endocrine Glands
Hormones are produced by various glands throughout the endocrine system. Each gland secretes distinct hormones with unique functions. Below are the major endocrine glands and their key hormones.
- Hypothalamus: Releases regulatory hormones such as TRH, GnRH, GHRH, CRH, and dopamine.
- Pituitary gland: Known as the “master gland,” it produces ACTH, TSH, GH, FSH, LH, PRL, oxytocin, and ADH.
- Pineal gland: Secretes melatonin to regulate sleep patterns.
- Thyroid gland: Produces thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) for metabolism regulation.
- Parathyroid gland: Releases parathyroid hormone (PTH) for calcium and phosphate balance.
- Pancreas: Produces insulin and glucagon, controlling blood sugar levels (learn more).
- Adrenal glands: Secrete cortisol, aldosterone, adrenaline, noradrenaline, and DHEA, important for stress and metabolism.
- Gonads (Ovaries & Testes): Release estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone for sexual development and reproduction.
Other body tissues, including the heart, kidneys, and digestive tract, can also produce hormones. See our page on endocrinology for more on glands and their coordination.
Hormones Diagram & How They Work
A typical hormones diagram shows the main endocrine glands and the pathways connecting them. The hormone travels from the secretion site, through blood, to the target cell, where it binds specific receptors and triggers changes. Feedback mechanisms ensure that hormone levels remain balanced.
- Hormone release often involves negative feedback loops (e.g., thyroid hormones and TSH).
- Some hormones are peptides/proteins (e.g., insulin), others are steroids (e.g., cortisol), or amines (e.g., adrenaline).
- Cell response may be rapid (adrenaline), or slow (growth hormone).
Detailed diagrams are covered in CBSE Class 12 and board exams. Practice drawing and labeling endocrine glands for better understanding of this biology topic.
Hormones Examples in Humans
Here are some common hormones examples found in the human body:
- Insulin – Controls blood glucose levels (pancreas).
- Adrenaline (epinephrine) – Prepares the body for stress (adrenal gland).
- Thyroxine – Regulates metabolism (thyroid gland).
- Estrogen – Supports female reproductive system (ovaries).
- Testosterone – Aids male secondary sexual traits (testes).
- Growth hormone – Stimulates growth (pituitary gland).
- Melatonin – Manages sleep-wake cycles (pineal gland).
To compare hormones and enzymes, see Difference Between Hormone and Enzyme.
Major Functions and Importance of Hormones
Hormones play diverse and essential roles across many biological functions.
- Regulate metabolism, energy balance, and glucose management.
- Drive growth, cell division, and tissue repair.
- Control puberty, reproduction, pregnancy, and lactation.
- Help the body respond to stress or emergencies.
- Maintain water, salt, and mineral balance.
Many diseases, such as diabetes or thyroid disorders, arise from hormone imbalance. Understanding hormones is crucial in medicine, agriculture, and environmental science. Topics like food and health and nutrition are closely linked with hormonal regulation.
Hormones Class 12: Exam Key Points
For Class 12 and entrance exams, focus on:
- Hormones definition and their chemical nature.
- Main endocrine glands and secreted hormones.
- Hormonal diseases—examples like diabetes, hypothyroidism, Addison’s disease.
- Mechanism of hormone action and feedback regulation.
- Drawing and labeling hormones diagrams for structure and pathways.
Download hormones ppt or practice hormones mcqs for revision. For more, check Vedantu’s MCQ resources and important diagrams.
Table: Major Endocrine Glands and Their Hormones
| Endocrine Gland | Main Hormones Secreted | Main Function |
|---|---|---|
| Pituitary | GH, TSH, FSH, LH, ACTH, PRL, ADH, Oxytocin | Growth, metabolism, reproduction |
| Thyroid | Thyroxine (T4), Triiodothyronine (T3) | Metabolism regulation |
| Adrenal | Adrenaline, Cortisol, Aldosterone | Stress response, water balance |
| Pancreas | Insulin, Glucagon | Blood sugar regulation |
| Ovaries/Testes | Estrogen, Progesterone, Testosterone | Sexual development, reproduction |
| Pineal | Melatonin | Sleep-wake cycle |
This table summarizes the main glands, the hormones they release, and their principal functions. Understanding these relationships is key for exams and real-life health awareness.
Applications and Real-world Significance
Hormones have wide applications, including:
- Medical treatments, e.g., insulin therapy for diabetes, hormone replacement in deficiencies.
- Understanding plant hormones for better crops (plant hormones and agriculture).
- Studying disorders like hypothyroidism, Cushing’s syndrome, dwarfism, and infertility.
- Linking nutrition, health, and environment for holistic well-being (life science guides).
Sample Hormones MCQs (Practice Questions)
Test your knowledge with these sample hormones questions:
- Which hormone regulates the sleep-wake cycle?
- What is the main function of insulin?
- Name a disorder caused by deficiency of thyroxine.
- Which gland is known as the "master gland"?
- Which hormone prepares the body for ‘fight or flight’ response?
For more practice, explore endocrine glands and difference between hormones and enzymes for revision.
Page Summary
Hormones are essential for coordinating life’s processes, from metabolism to reproduction. By mastering hormones definition, examples, mechanisms, and real-world importance, students gain valuable insight for exams and daily health. Referencing credible resources and Vedantu’s MCQs or diagrams, you can deepen your understanding of this core biology topic.


FAQs on What are Hormones and How Do They Work?
1. What are hormones?
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands that regulate various functions in the body.
- Hormones travel through the bloodstream to target organs.
- They control processes such as growth, metabolism, reproduction, and mood.
- Examples include insulin, adrenaline, thyroxine, and estrogen.
2. What is the function of hormones in the human body?
The main function of hormones is to coordinate and control activities of different organs in the body.
- Regulate growth and development.
- Maintain metabolism and energy balance.
- Control reproductive functions and puberty.
- Help the body respond to stress (e.g., adrenaline).
3. What are the types of hormones based on their chemical nature?
Hormones can be classified based on their chemical nature as follows:
- Peptide hormones (e.g., insulin, glucagon)
- Steroid hormones (e.g., estrogen, testosterone)
- Amino acid-derived hormones (e.g., thyroxine, adrenaline)
4. How are hormones different from enzymes?
The key difference between hormones and enzymes is that hormones are signaling molecules, while enzymes are biological catalysts.
- Hormones are secreted by glands and affect distant organs.
- Enzymes speed up chemical reactions inside cells.
- Hormones act in very low concentrations; enzymes are usually present in higher amounts.
5. Name the major endocrine glands and the hormones they produce.
Major endocrine glands and their hormones include:
- Pituitary gland: growth hormone, ADH
- Thyroid gland: thyroxine
- Pancreas: insulin, glucagon
- Adrenal gland: adrenaline, cortisol
- Ovaries/testes: estrogen, testosterone
6. What happens if there is an imbalance of hormones in the body?
A hormonal imbalance can disturb normal body function and lead to disorders.
- Excessive or deficient hormones can cause diseases (e.g., diabetes, hypothyroidism, gigantism).
- Symptoms can include mood changes, abnormal growth, metabolic problems, and reproductive issues.
- Treatment depends on restoring hormonal balance.
7. How does the endocrine system differ from the nervous system?
The endocrine system uses chemical messages (hormones), while the nervous system relies on electrical signals.
- Endocrine responses are slower but last longer.
- Nervous system responses are rapid and short-lived.
- The two systems often work together to maintain homeostasis.
8. What is the role of insulin and how does it affect blood sugar levels?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps control blood glucose levels.
- It allows cells to absorb glucose from the blood for energy.
- Lack of insulin causes high blood sugar, leading to diabetes.
- Proper insulin function maintains normal metabolism.
9. Why are hormones called chemical messengers?
Hormones are called chemical messengers because they transmit signals from one part of the body to another.
- Produced by glands, released into the bloodstream.
- Act on specific target organs to regulate body processes.
- Ensure proper coordination and control of body functions.
10. How do hormones affect growth and development in humans?
Hormones such as growth hormone, thyroxine, and sex hormones are essential for normal growth and development.
- Stimulate cell division and protein synthesis.
- Regulate bone growth and development during childhood and adolescence.
- Control sexual maturation and secondary sex characteristics.










