Ribose and Deoxyribose Roles in DNA and RNA Structure
Ribose and deoxyribose are both monosaccharides (simple sugars) with five carbon atoms, known as aldopentoses. These sugars play a vital role in the structure of nucleic acids, which are key to storing and transmitting genetic information. DNA Structure relies on deoxyribose, whereas RNA incorporates ribose.
Here, we will discuss the difference between ribose and deoxyribose, their structures, functions, discovery, and other intriguing facts. We will also explore how these sugars connect to genetics, covering topics like deoxyribose sugar in DNA, the deoxyribose formula, and more.
What is Deoxyribose?
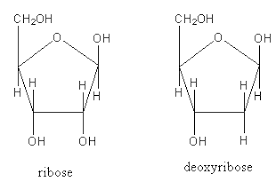
Deoxyribose is a pentose sugar that has one less oxygen atom than ribose. Its chemical formula is C₅H₁₀O₄, and it is also referred to as 2-deoxy-D-ribose. In deoxyribose, the second carbon atom is attached to a hydrogen (H) instead of a hydroxyl (OH) group.
Molecular Structure: 2-deoxy-D-ribose has a hydrogen at the second carbon instead of a hydroxyl group.
deoxyribose sugar in DNA: Deoxyribose is the sugar present in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Its presence gives DNA its name and helps form the DNA backbone along with phosphate groups.
Role in Genetics: Deoxyribose forms part of the nucleotides that link together to create the double-stranded DNA helix. The bases (adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) attach to the sugar, enabling the storage of genetic information.
Discovery: It was discovered by Phoebus Levene in 1929.
Additional Notes on Deoxyribose
deoxyribose sugar hair growth: Some studies explore the role of sugars and sugar analogues in biological processes, but there is no definitive evidence that deoxyribose alone promotes hair growth directly in humans.
deoxyribose sugar gel: In certain biochemical or laboratory techniques, sugar-based gels can be used. Deoxyribose itself is not typically used as a standalone gel, but sugar derivatives might be part of experimental media.
What is Ribose?
Ribose is a pentose sugar with the chemical formula C₅H₁₀O₅. It has a hydroxyl (OH) group at the second carbon. Ribose is primarily found in ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Molecular Structure: Ribose has an OH group at the second carbon, making it slightly heavier (higher molar mass) than deoxyribose.
Role in RNA: Ribose is crucial for forming ribonucleotides, which are the building blocks of RNA. RNA is responsible for coding, decoding, and regulating gene expression.
Discovery: Emil Fischer and Oskar Piloty first identified ribose in 1891.
Key Differences Between Ribose and Deoxyribose
Below is a concise comparison table highlighting the major distinctions:
This difference between ribose and deoxyribose is crucial in defining the difference between DNA and RNA molecules. The absence of an oxygen atom in deoxyribose makes DNA more chemically stable, which is beneficial for long-term genetic information storage. RNA, containing ribose, is more reactive and suitable for tasks like protein synthesis and gene regulation.
Biological Significance
Both sugars have an aldehyde group in their open-chain form and serve as essential components of nucleic acids:
Deoxyribose (DNA):
Stores genetic instructions.
Passes hereditary information to the next generation.
Ribose (RNA):
Translates DNA’s genetic code into proteins.
Acts in various regulatory and catalytic roles (e.g., messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomal RNA).
2-deoxy-D-ribose and Its Importance
2-deoxy-D-ribose is another name for deoxyribose.
It is crucial for making deoxyribonucleotides, which in turn form the structural units of DNA.
Its slight structural difference from ribose (missing an oxygen) significantly affects the function and stability of the nucleic acid.
Quick Quiz
Which sugar is found in DNA?
A. Ribose
B. Deoxyribose
Answer: B. Deoxyribose
Which sugar has the chemical formula C₅H₁₀O₅?
A. Ribose
B. Deoxyribose
Answer: A. Ribose
Who discovered ribose?
A. Phoebus Levene
B. Emil Fischer and Oskar Piloty
Answer: B. Emil Fischer and Oskar Piloty
Additional Fact
Just like we talk about the difference between DNA and RNA based on their sugar molecules, the subtle difference in sugar structures—hydroxyl (OH) in ribose versus hydrogen (H) in deoxyribose—makes a huge difference in their biological roles.
Related Topics to Explore


FAQs on Ribose vs Deoxyribose: Essential Differences Explained
1. What is the main difference between ribose and deoxyribose sugar?
The main difference lies in the chemical group attached to the second (2') carbon atom of the pentose sugar ring. In ribose (found in RNA), there is a hydroxyl (-OH) group at the 2' carbon position. In deoxyribose (found in DNA), this hydroxyl group is replaced by a hydrogen (-H) atom, meaning it has one less oxygen atom.
2. How does the presence of ribose versus deoxyribose affect the function and stability of RNA and DNA?
The difference in the sugar molecule directly impacts the molecule's stability and function:
- Deoxyribose in DNA: The absence of the 2' hydroxyl group makes DNA much more stable and less reactive. This is crucial for its role as a long-term storage medium for genetic information.
- Ribose in RNA: The presence of the 2' hydroxyl group makes RNA more reactive and susceptible to breakdown (hydrolysis). This instability is suitable for its role as a temporary messenger (mRNA) and in regulation, where it needs to be created and degraded as needed.
3. What are the chemical formulas for ribose and deoxyribose?
The difference in their structure is reflected in their chemical formulas. The chemical formula for ribose is C₅H₁₀O₅. Because deoxyribose is missing one oxygen atom, its chemical formula is C₅H₁₀O₄.
4. How is a pentose sugar related to ribose and deoxyribose?
A pentose sugar is a general classification for any monosaccharide (simple sugar) that has five carbon atoms. Both ribose and deoxyribose are specific examples of pentose sugars. Therefore, ribose is not different from a pentose sugar; it is a type of pentose sugar, just like deoxyribose is.
5. How are ribose and deoxyribose different from glucose?
Ribose and deoxyribose differ from glucose primarily in the number of carbon atoms they contain. Ribose and deoxyribose are pentose sugars, meaning they have five carbon atoms. In contrast, glucose is a hexose sugar, meaning it contains six carbon atoms. Their primary roles are also different, with glucose being a key molecule for energy production (cellular respiration).
6. Besides RNA, where else is ribose found in a cell?
While ribose is a fundamental component of RNA, it is also a crucial part of other vital biomolecules in the cell. The most important example is ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), the main energy currency of the cell. Ribose is also found in other essential molecules like the coenzymes NAD+ (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and FAD (Flavin adenine dinucleotide).
7. Are ribose and deoxyribose the only types of sugars found in nucleic acids?
In the standard DNA and RNA found in most living organisms, deoxyribose and ribose are indeed the exclusive pentose sugars that form the backbone. However, some synthetic nucleic acids or viral genomes can contain modified or different sugars, but for the scope of the CBSE/NCERT syllabus, ribose and deoxyribose are the only relevant sugars in nucleic acids.










