What Are the Main Types and Characteristics of Algae?
Algae are simple, plant-like organisms found in water, moist soils, and even on rocks. With varied sizes, shapes, and colors, they play a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems through photosynthesis. Whether in oceans, ponds, or freshwater lakes, the study of algae helps Class 11 students and biology enthusiasts understand their significance in food chains and environmental processes.
What is Algae?
Algae refers to a diverse group of generally autotrophic organisms that perform photosynthesis but are not true plants. Unlike higher plants, algae lack true roots, stems, or leaves. They can be microscopic, single-celled forms, like Chlorella, or large multicellular forms, such as giant kelps. Understanding what is algae helps us appreciate their importance in both aquatic and terrestrial environments.
Characteristics of Algae
Key algae characteristics include their simple body structure, called a thallus, and their ability to produce their own food using sunlight. Algae are often green, red, or brown depending on pigments present. They reproduce through diverse modes, such as binary fission, fragmentation, and spore formation, and can live in colonies or as single organisms.
- Mostly found in aquatic environments, both freshwater and marine.
- Contain chlorophyll and other pigments for photosynthesis.
- May be unicellular, colonial, or multicellular.
- Lack true tissues, roots, stems, or leaves.
- Cell walls often contain cellulose.
- Reproduce by vegetative, asexual, and sexual methods.
Classification and Types of Algae
Algae can be classified based on pigment, storage products, or structure. The three major types of algae are green algae, brown algae, and red algae. Each group displays unique features and plays specific roles in aquatic life.
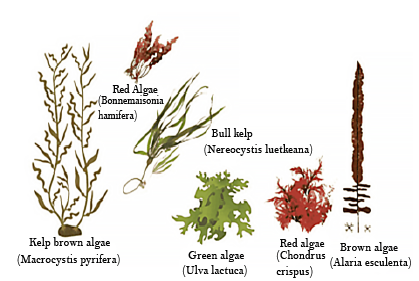
Green Algae (Chlorophyceae)
Green algae are rich in chlorophyll, giving them a bright green color. They are commonly found in ponds, lakes, and moist soils. Well-known examples of green algae include Chlamydomonas and Spirogyra.
Brown Algae (Phaeophyceae)
Brown algae contain the pigment fucoxanthin, making them brown to olive-green in color. These algae mostly occur in marine habitats, forming kelp forests. Examples are Laminaria and Sargassum.
Red Algae (Rhodophyceae)
Red algae get their color from phycoerythrin pigment. They are usually found in deeper parts of oceans due to their ability to absorb blue light. Porphyra and Batrachospermum are common red algae examples.
Other Types of Algae
Beyond green, red, and brown algae, there are additional categories based on their pigments and structures:
- Blue-Green Algae (Cyanobacteria): Actually prokaryotic, often called blue-greens or cyanobacteria.
- Golden Algae (Chrysophyceae): Mostly unicellular organisms like diatoms.
- Fire Algae (Dinoflagellates): Noted for bioluminescence and causing red tides.
Algae Examples
Algae are diverse, with many well-known species found in daily life, science labs, and nature.
- Chlorella: Used as a food supplement; rich in protein.
- Spirogyra: Common filamentous green algae seen in ponds.
- Ulva (Sea Lettuce): Edible green algae from marine habitats.
- Laminaria: Large brown algae, vital in kelp forests.
- Porphyra: Edible red algae, used for making sushi nori.
Importance and Uses of Algae
The importance of algae is extensive in nature, industry, and everyday life. They form the base of aquatic food chains and produce a significant portion of Earth's oxygen. Algae are also used in food, medicine, and environmental monitoring, making their study essential for life science enthusiasts and professionals alike.
- Primary Producers: Algae are vital for the aquatic food web.
- Oxygen Production: Algae generate large amounts of oxygen via photosynthesis.
- Food and Nutrition: Edible algae (like Spirogyra, Porphyra) provide nutrients and are used in diets worldwide.
- Industrial Uses: Used in cosmetics, biofuels, fertilizers, and natural dyes.
- Environmental Indicators: Algal blooms signal changes in ecosystem health and water quality.
- Medicinal Value: Some algae produce substances with antibacterial or antiviral properties.
Global concerns like climate change and environmental issues are intertwined with algal growth, as excessive nutrients can cause algal blooms. These events can threaten aquatic life but also highlight the need to understand the uses and importance of algae in maintaining ecological balance.
Algae in Class 11 and Exam Notes
For students preparing for exams, algae notes often cover: definition, types of algae, key algae characteristics, examples, and their roles in food chains. Class 11 syllabi may also discuss differences between algae and fungi or algae and bryophytes. Deepening your understanding of these differences and their ecological impacts benefits preparation for biology questions and projects.
Interesting Facts About Algae
Here are fascinating facts that illustrate why algae is such a unique biological group:
- Algae can be single-celled or grow over 50 meters long (kelp).
- Half of the world’s oxygen is produced by algae in oceans.
- Certain species glow in the dark — called bioluminescent algae.
- Spirulina, a blue-green algae, is a superfood rich in protein.
- Diatoms, a type of golden algae, form intricate glass-like shells.
Comparisons: Algae and Similar Organisms
Algae differ from fungi and plants in several key ways. Unlike fungi, algae are autotrophic, while fungi are heterotrophic. Compared to bryophytes, algae do not have true tissues or roots. These points are crucial in differentiating living organisms, a concept also explored in biological classification topics.
Algal Reproduction: Simple Life Cycles
Algae reproduce in several ways:
- Vegetative Reproduction: Fragments arise from the parent thallus, forming new organisms.
- Asexual Reproduction: Production of spores, such as zoospores.
- Sexual Reproduction: Fusion of male and female gametes occurs in some advanced species.
Each method helps algae adapt to changing conditions and ensures survival in diverse habitats.
Role of Algae in Nutrition and Ecosystems
In both freshwater and marine systems, algae contribute as the first trophic level in food chains. They are also a crucial topic in food science and in the context of nutrient cycles in biology.
- Source of single-cell protein in aquaculture and food supplements.
- Supply of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids in diets.
- Regulate carbon dioxide and oxygen balance in aquatic habitats.
Conclusion
Algae may seem simple, but their impact on ecosystems, human industries, and food security is immense. By understanding types of algae, their uses, and their ecological roles, students and researchers gain valuable insights. Exploring these topics with Vedantu supports your learning and helps you appreciate the fascinating world of biology.
To sum up, algae are vital for sustaining aquatic life, oxygen cycles, and even human nutrition and industries. With diverse forms like green, brown, and red algae, this group shows how microscopic organisms can shape entire ecosystems and supply resources for humanity.


FAQs on Understanding Algae for Students
1. What are algae?
Algae are simple, autotrophic organisms that perform photosynthesis and live mainly in aquatic environments. Common features of algae include:
- Singular or multicellular structure (unicellular, colonial, or multicellular)
- Presence of chlorophyll (chloroplasts for photosynthesis)
- Lack of true roots, stems, or leaves
- Wide distribution in freshwater and marine habitats
2. What are the main types of algae?
The three main types of algae based on their pigmentation and storage products are:
- Chlorophyceae (Green algae)
- Phaeophyceae (Brown algae)
- Rhodophyceae (Red algae)
3. What are the economic uses of algae?
Algae have many economic applications in industry, agriculture, and everyday life. Main uses include:
- Source of food (e.g., Spirulina, Chlorella)
- Production of agar, carrageenan, and alginate (used in food, pharmaceuticals)
- Fertilizers and soil conditioners
- Biofuel and biogas production
- Purification of wastewater (bioremediation)
4. How do algae reproduce?
Algae reproduce by both asexual and sexual methods. Common reproductive strategies include:
- Asexual reproduction: by fragmentation, binary fission, or spore formation (zoospores, aplanospores)
- Sexual reproduction: by fusion of gametes, which may be isogamous, anisogamous, or oogamous
5. What is the ecological importance of algae?
Algae play a fundamental role in aquatic ecosystems and the global environment by:
- Producing oxygen through photosynthesis
- Forming the primary base of aquatic food chains (primary producers)
- Regulating carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
- Providing habitat and food for a variety of aquatic organisms
6. What pigments are present in algae?
Algae contain several major pigments, which determine their classification and color.
- Chlorophylls (a, b, c, d, e)
- Carotenoids
- Phycobilins (phycocyanin, phycoerythrin)
7. What are the differences between green, brown, and red algae?
Green, brown, and red algae differ mainly in pigment content, storage products, and habitat. The key differences are:
- Green algae: Chlorophyll a and b, starch as reserve food, mainly freshwater
- Brown algae: Chlorophyll a, c, and fucoxanthin, laminarin and mannitol, mostly marine
- Red algae: Chlorophyll a, d, and phycoerythrin, floridean starch, mainly marine
8. How are algae classified?
Algae are classified mainly based on their pigmentation, storage materials, cell wall composition, and reproductive methods. Main classes include:
- Chlorophyceae (Green algae)
- Phaeophyceae (Brown algae)
- Rhodophyceae (Red algae)
9. Where are algae found?
Algae are widely distributed in aquatic habitats and moist terrestrial environments. Common habitats include:
- Freshwater (ponds, lakes, rivers)
- Marine environments (oceans, seas)
- Moist soils, rocks, tree trunks, and as endosymbionts
10. What is the role of algae in oxygen production?
Algae contribute significantly to global oxygen production through photosynthesis. Their roles include:
- Producing about half of the world's oxygen supply
- Balancing atmospheric gases by absorbing carbon dioxide
- Supporting aquatic life through oxygenation of water










